Node.js Event Loop Explained
This article covers the main components of Node.js with practical examples so that people can actually run the snippet and play with it.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeI read many articles on how Node.js works internally, but I didn’t find any satisfactory answer, and hence I decided to write an article myself with practical examples so that people can actually run the snippet and play with it.
Primarily I’ll be covering the main components of this architecture like ‘Event Loop,’ ‘Event Queue,’ and a few concepts like ‘blocking’ and ‘non-blocking’ codes.
I’ll take an example of an HTTP API endpoint written in express (the most popular framework of Node.js). Towards the end, I’ll also try to explain why it is said not to use Node.js for CPU-intensive applications (because it is completely related to what we’re going to discuss).
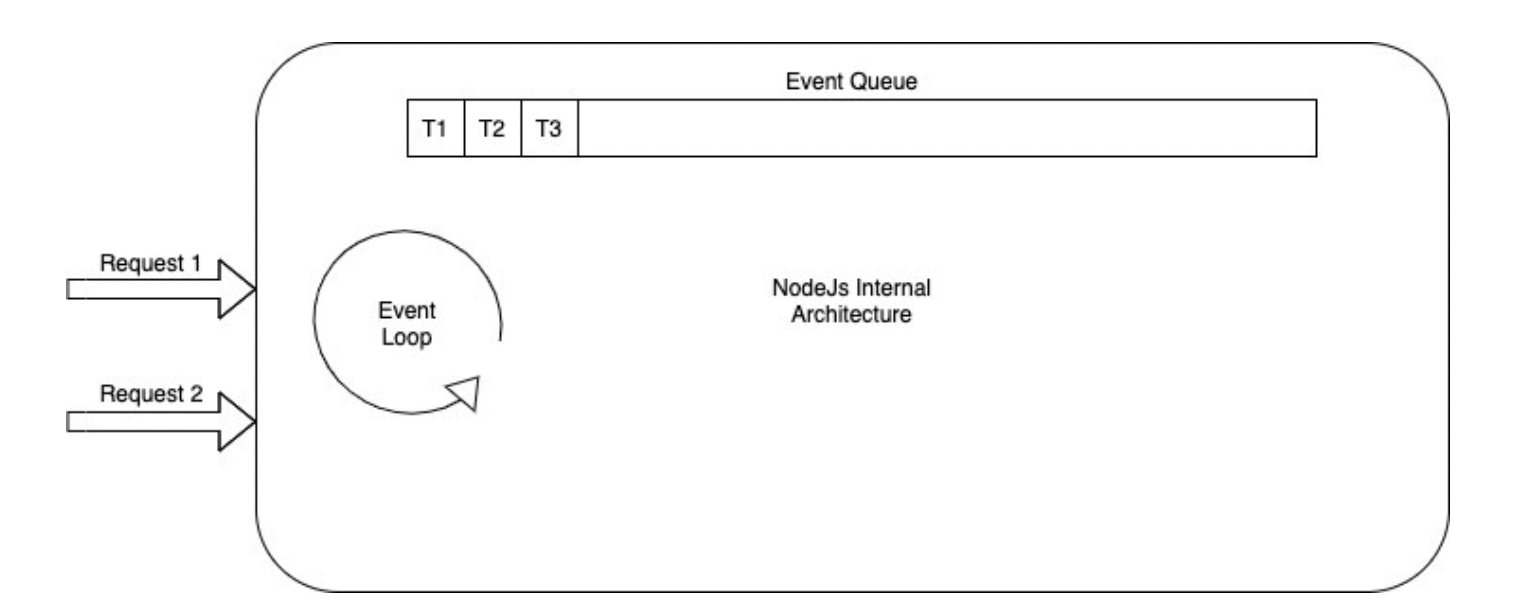
Event Loop: An event loop is an endless loop, which waits for tasks, executes them, and then waits until it receives more tasks. The event loop executes tasks from the event queue only when the call stack is empty, i.e., there is no ongoing task.
Event Queue: The event Queue is the list of pending callback functions to be executed. Once an operation is completed, a callback assigned to that operation is added to the event queue, which will eventually be picked by the event loop.
Nodejs single-threaded event loop architecture: As there is only a single thread, only one task can be executed at a time, and a task could be anything; it could be listening for new requests via event loop, or it could be the execution of statements, let's dive deep into the example.
A function that can keep looping for given milliseconds (can keep the event loop busy).
const sleep = (milliseconds) => {
const date = Date.now();
let currentDate = null;
do {
currentDate = Date.now();
} while (currentDate - date < milliseconds);
}API 1: It can keep the event loop busy for ‘timeout’ milliseconds given with API request.
router.get('/api1', (req, res, next) => {
const start_time = new Date().valueOf()
sleep(req.query.timeout)
const end_time = new Date().valueOf()
return res.jsonp({ name: 'api1', start_time, end_time, execution_time: end_time - start_time, start_time_readable: new Date(start_time).toISOString(), end_time_readable: new Date(end_time).toISOString(), timeout: req.query.timeout });
});API 2: Basic API will respond after ‘timeout’ milliseconds given with API request.
router.get('/api2', (req, res, next) => {
const start_time = new Date().valueOf();
setTimeout(() => {
const end_time = new Date().valueOf();
return res.jsonp({ name: 'api2', start_time, end_time, execution_time: end_time - start_time, start_time_readable: new Date(start_time).toISOString(), end_time_readable: new Date(end_time).toISOString(), timeout: req.query.timeout });
}, req.query.timeout);
});Script to call these APIs programmatically.
const request = require('request');
const async = require('async')
const request_p = (options) => {
return new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => {
try {
request(options, (error, response) => {
if (error) throw new Error(error);
if (typeof response.body == 'string') {
response.body = JSON.parse(response.body)
}
return resolve(response.body)
});
} catch (e) {
return reject(e)
}
})
}
const combination = async (options) => {
async.parallel([(cb) => {
console.log(new Date(), 'section 1 start')
const options1 = {
'method': 'GET',
'url': options.req1
};
request_p(options1).then((__res1) => {
console.log(new Date(), 'section 1 end with response:', __res1)
return cb()
})
}, (cb) => {
console.log(new Date(), 'section 2 start')
const options1 = {
'method': 'GET',
'url': options.req2
};
request_p(options1).then((__res1) => {
console.log(new Date(), 'section 2 end with response:', __res1)
return cb()
})
}], (err, res) => {
process.exit(0)
})
}
//experiment 1
combination({ 'req1': 'http://localhost:3000/api1?timeout=5000', 'req2': 'http://localhost:3000/api2?timeout=2000' })
//experiment 2
//combination({'req1':'http://localhost:3000/api2?timeout=2000','req2':'http://localhost:3000/api1?timeout=5000'})Note: These many parameters are returned to support the explanation.
Experiment 1:
combination({ 'req1': 'http://localhost:3000/api1?timeout=5000', 'req2': 'http://localhost:3000/api2?timeout=2000' })This will call API1 first with a timeout of 5000ms, and immediately it’ll call API2 with a timeout of 2000ms.
The output of Experiment 1:
2022-09-10T05:28:22.828Z section 1 start
2022-09-10T05:28:22.835Z section 2 start
2022-09-10T05:28:27.854Z section 1 end with response: {
name: 'api1',
start_time: 1662787702846,
end_time: 1662787707846,
execution_time: 5000,
start_time_readable: '2022-09-10T05:28:22.846Z',
end_time_readable: '2022-09-10T05:28:27.846Z',
timeout: '5000'
}
2022-09-10T05:28:29.866Z section 2 end with response: {
name: 'api2',
start_time: 1662787707854,
end_time: 1662787709859,
execution_time: 2005,
start_time_readable: '2022-09-10T05:28:27.854Z',
end_time_readable: '2022-09-10T05:28:29.859Z',
timeout: '2000'
}
How come section 2's start_time_readable is after section'1 start_time_readabled?
Why Is Node.js's Async Nature Not Helping Here?
While API1 was invoked with 5s and API2 was invoked with 2s, so ideally, API2 should respond first. But no, and that’s where the secret is “how Node.js internally works” on a single thread. Let’s understand this in detail.
- Invocation started for API1 first, so obviously, it reached to event loop first, and the event loop was available and immediately started its execution.
- As the nature of the API is blocking, it's a for loop running for given seconds, so the event loop will be busy executing this, and it’ll not be available for taking new requests for a given timeout value (for this example, 5s).
- After completion of this 5s, the next statement is to return the response; an event loop will follow that, and the response will be returned.
- Now event loop is available to take new requests, and you can see that the start time of API2 (2022-09-10T05:28:27.854Z) is after the end time of API1 (2022-09-10T05:28:29.859Z).
- And API2 will start execution, and as this is a waiting call, after a given timeout (2s in this case) callback function will be given to the event queue and event loop (who will be free to take items from the event queue) will dequeue this function and will execute it and will return the response (as written in the code).
- From the timeline perspective, if API1 and API2 are invoked at the 0th second in this sequence (first API1 and then API2 in parallel), then API1 will respond at the 5th second, and API2 will respond at the 7th second.
Now let’s do another experiment and reverse the order of APIs.
Experiment 2:
combination({'req1':'http://localhost:3000/api2?timeout=2000','req2':'http://localhost:3000/api1?timeout=5000'})This will call API2 first with a timeout of 2000ms, and in parallel, it’ll call API1 with a timeout of 5000ms.
The output of Experiment 2:
2022-09-10T05:33:45.317Z section 1 start
2022-09-10T05:33:45.323Z section 2 start
2022-09-10T05:33:50.347Z section 2 end with response: {
name: 'api1',
start_time: 1662788025342,
end_time: 1662788030342,
execution_time: 5000,
start_time_readable: '2022-09-10T05:33:45.342Z',
end_time_readable: '2022-09-10T05:33:50.342Z',
timeout: '5000'
}
2022-09-10T05:33:50.350Z section 1 end with response: {
name: 'api2',
start_time: 1662788025341,
end_time: 1662788030344,
execution_time: 5003,
start_time_readable: '2022-09-10T05:33:45.341Z',
end_time_readable: '2022-09-10T05:33:50.344Z',
timeout: '2000'
}
How Exactly Both the APIs Responded at the Same Time
While section 1 was invoked with 2s, and section 2 was invoked with 5s, so ideally, section 1 should respond first. Let’s understand this in detail.
- Invocation started for API2 first, so obviously, it reached to event loop first, and the event loop was available and immediately started its execution.
- As the nature of this API (API2) is non-blocking, so the event loop will start its execution and will be free from this, and it’ll be ready to take the next requests.
- At this time, API1 will be reached the event loop and start its execution.
- As the nature of the API (API1) is blocking, it is a for loop running for given seconds, so the event loop will be busy executing this, and it’ll not be available for taking requests for the event queue for a given timeout value (for this example 5s).
- After completion of this 5s, the next statement is to return the response; an event loop will follow that, and the response will be returned for API1.
- Now event loop will be free to take requests from the event queue where the timeout function of API2 will be waiting from the last 3s; it will dequeue this function, execute it, and return the response (as written in the code).
- From the timeline perspective, if API2 and API1 are invoked at the 0th second in this sequence (first API2 and then API1 in parallel), then API1 will respond at the 5th second, and API2 will respond at the 5th second (API2 will respond immediately after API1).
I hope now the internal working of Node.js is clear, and it is also clear why not to use Node.js for CPU-intensive applications.
I’m attaching a code snippet from GitHub.
That’s all for today. Thank you so much for reading!
Published at DZone with permission of Dinesh Agrawal. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments