A Bayesian view of Amazon Resellers
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Freei was buying a used book through amazon this evening. three resellers offered the book at essentially the same price. here were their ratings:
- 94% positive out of 85,193 reviews
- 98% positive out of 20,785 reviews
- 99% positive out of 840 reviews
which reseller is likely to give the best service? before you assume it’s the seller with the highest percentage of positive reviews, consider the following simpler scenario.
suppose one reseller has 90 positive reviews out of 100. the other reseller has two reviews, both positive. you could say one has 90% approval and the other has 100% approval, so the one with 100% approval is better. but this doesn’t take into consideration that there’s much more data on one than the other. you can have some confidence that 90% of the first reseller’s customers are satisfied. you don’t really know about the other because you have only two data points.
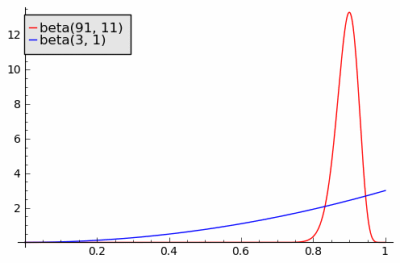
a bayesian view of the problem naturally incorporates the amount of data as well as its average. let θ a be the probability of a customer being satisfied with company a’s service. let θ b be the corresponding probability for company b. suppose before we see any reviews we think all ratings are equally likely. that is, we start with a uniform prior distribution θ a and θ b . a uniform distribution is the same as a beta(1, 1) distribution.
after observing 90 positive reviews and 10 negative reviews, our posterior estimate on θ a has a beta(91, 11) distribution. after observing 2 positive reviews, our posterior estimate on θ b has a beta(3, 1) distribution. the probability that a sample from θ a is bigger than a sample from θ b is 0.713. that is, there’s a good chance you’d get better service from the reseller with the lower average approval rating.
now back to our original question. which of the three resellers is most likely to satisfy a customer?
assume a uniform prior on θ x , θ y , and θ z , the probabilities of good service for each reseller. the posterior distributions on these variables have distributions beta(80082, 5113), beta(20370, 417), and beta(833, 9).
these beta distributions have such large parameters that we can approximate them by normal distributions with the same mean and variance. (a beta( a , b ) random variable has mean a /( a + b ) and variance ab /(( a + b ) 2 ( a + b +1)).) the variable with the most variance, θ z , has standard deviation 0.003. the other variables have even smaller standard deviation. so the three distributions are highly concentrated at their mean values with practically non-overlapping support. and so a sample from θ x or θ y is unlikely to be higher than a sample from θ z .
in general, going by averages alone works when you have a lot of customer reviews. but when you have a small number of reviews, going by averages alone could be misleading.
thanks to charles mccreary for suggesting the xkcd comic.
source:
http://www.johndcook.com/blog/2011/09/27/bayesian-amazon/
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments