Building a Static Website on Amazon S3 With Microservices
Learn how to build a static website made up of microservices developed with the help of an API gateway and AWS Lambda.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeBackground
The trend of hosting static websites on Amazon S3 is a becoming very popular. This approach has been adopted by many organizations due to its advantages over traditional server-based hosting. Static websites are websites that do not require any runtime environment like JRE, .NET, etc. and are mostly based on HTML, CSS, JS, and other static resources (audio/video files, documents, etc.). AWS provides all the necessary services and tools that enable you to build and manage static websites on the AWS cloud very easily.
Like other cloud-based hostings, there is no CAPEX investment. However, there is a negligible operational cost for hosting the static website. You can find more benefits here.
First, we will discuss some of the main architectural components of the system. This discussion will help you understand all the building blocks and workings of the system. The architecture you choose to build for your website will depend entirely on your requirements. At the end of the blog, we will also provide a step-by-step guide on building a static website on AWS.
Architecture
S3
The first mandatory service required is S3. It is a secure and durable object storage service that enables you to store your files in cloud-based storage units called buckets. Every file inside a bucket has a unique URL associated with it that can be used to access it if the user has the privileges. As a first step, you would need to upload the complete contents of a static website into an S3 bucket. Enabling web hosting and making the bucket public will enable it to serve the content of your website. More details can be found here.
Route53
When you have hosted your website on S3, you will have an AWS region-based default website endpoint which you can directly use to access the website. You also have the option to map your custom domain to point to your static website default endpoint, and this is where Route53 comes into play. Details on how to use Route53 for this purpose can be found here.
Cognito (Optional)
To provide an authentication mechanism for your website, you can use AWS Cognito. You can create a pool of users and provide a login to the users in that pool. Cognito user pools offer functionality for federated identity providers (for example, login via Facebook and Google), password recovery, and user authorization security in the cloud.
Microservices Development (Using Lambda, API Gateway, and RDS)
You can develop microservices using a combination of API Gateway and AWS Lambda. These microservices can be used directly by your website to GET and POST data from a data source. Hence, your static website can also have the functionality of a dynamic webpage. For example, on an event (e.g. click of a button, form submission, etc) you can use Jquery Ajax to call the microservice to load data and display on the web page.
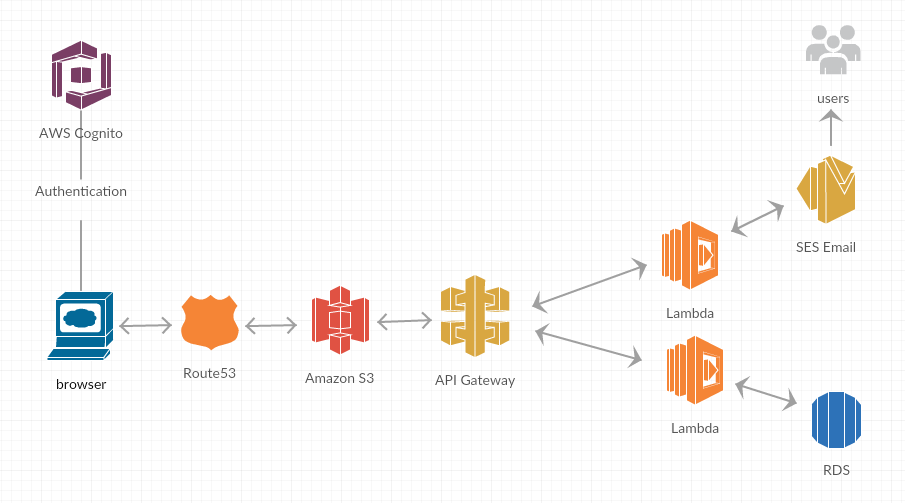
You can create microservices for complete CRUD operations and more with the help of these services within your website to make your site act fully dynamic. Similarly, you can create microservices which interact with other AWS services like SES in case you want to send email notifications through the website.
Basically, you use the AWS SDK to write Lambda functions that provide functionality for your microservice. Through Lambda, you can communicate with any AWS service. API Gateway integrates with Lambda to provide you with an API endpoint.
Step-by-Step Guide
Basic Configurations
Go to the S3 console and create a new bucket with default settings
Go the propertiesof your bucket and choose the option "Static website hosting."
Enable the option "Use this bucket to host a website."
Provide the names of the HTML to be displayed as the homepage and the HTML file that will be displayed in case an error occurs on your site.
Optionally, provide redirection rules if you want to route requests conditionally according to specific object key names, prefixes in the request, or response codes to some other object in the same bucket or external URL.

Now, go the Permissionssection of your bucket and add the following into your Bucket Policy section:
{
"Version":"2018-07-15",
"Statement":[{
"Sid":"PublicReadForGetBucketObjects",
"Effect":"Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action":["s3:GetObject"],
"Resource":["arn:aws:s3:::your-bucket-name/*"
]
}
]
}
Replace your-bucket-name with the name of your bucket.
To enable your S3 static website to respond to requests like GET and POST coming from an external application hosted on a certain domain, you would need to configure CORS in your bucket settings. To do this, add the following into the CORS configuration section of Permissions:
<!-- Sample policy -->
<CORSConfiguration>
<CORSRule>
<AllowedOrigin>*</AllowedOrigin>
<AllowedMethod>GET</AllowedMethod>
<MaxAgeSeconds>3000</MaxAgeSeconds>
<AllowedHeader>Authorization</AllowedHeader>
</CORSRule>
<CORSRule>
<AllowedOrigin>*</AllowedOrigin>
<AllowedMethod>POST</AllowedMethod>
<MaxAgeSeconds>3000</MaxAgeSeconds>
<AllowedHeader>Authorization</AllowedHeader>
</CORSRule>
</CORSConfiguration>
Upload your code. For this tutorial, create two simple HTML files by the name of index.html and error.html and upload them to the bucket.

To launch and test the site, the endpoint can be retrieved from Properties > Static website hosting.
Enrich Your Website by Adding Dynamic Behavior
You can use a combination of HTML5 and CSS3 to graphically enrich your website. You can also use Jquery Ajax to call an API (microservice) and dynamically fetch data from a data source and display it on your website. Similarly, by invoking API endpoints using Ajax, you can store any kind of user’s data back to your data source, like any other web application. If your requirement is to use AWS only for all your development needs, you can use a combination of API Gateway and Lambda to build APIs, a tutorial for which can be found here.
CORS Settings in API Gateway Endpoints
It is important to note that when developing APIs (microservices) using an API Gateway and Lambda, make sure to do the following:
Enable CORS in the API gateway at the time of creating a new resource.
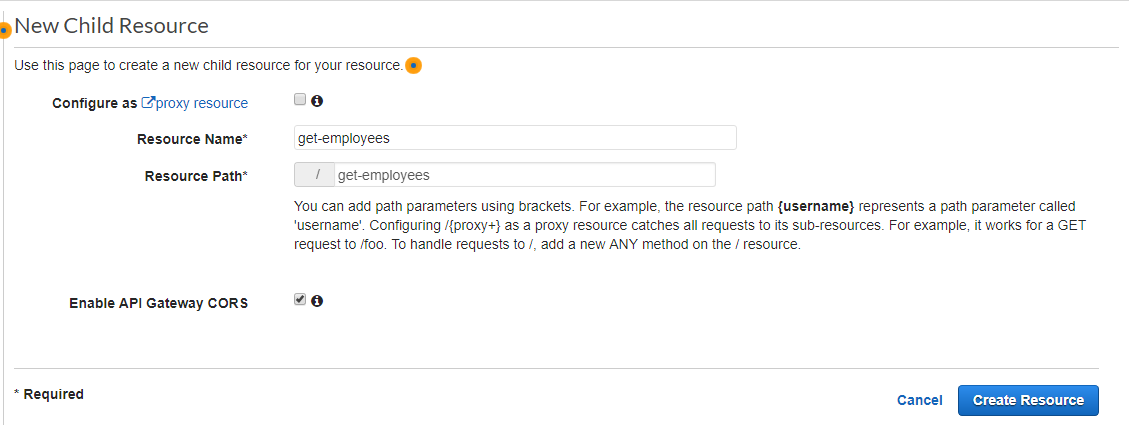
When writing the lambda function (which you will integrate with the API Gateway endpoint to provide functionality to your microservice), make sure to add an additional parameter into the response header by the name of Access-Control-Allow-Origin with the value “*”
If you are the following the tutorial I mentioned before for developing microservices, for this purpose, you can observe the following line of code in the example function handler given in that tutorial:
headerJson.put("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");Conclusion
If your website is mainly informational, does not expect too many changes, and the goal is to achieve easy management and low cost, then S3 should be your first choice. Also, using a service-oriented architecture, as shown above, can dynamically display data and post data back to any data source, which gives you the power to make your website achieve many functionalities.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.


Comments