Cloud-Native Middleware Microservices
With cloud-native microservices, you can develop, test, deploy, and maintain independent lightweight services while combining various other technologies.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeCloud-native microservices offer many benefits. You can develop, test, deploy, and maintain independent lightweight services. You can easily combine various technologies, including programming languages such as Java or Go, and tools like integration middleware.
However, as you do not build monoliths anymore, "that complexity has moved and [...] increased [to] the outer architecture," as Gartner states. For this reason, new design patterns (have to) emerge to solve the challenges of independent, distributed microservices.
Middleware is used to interconnect everything. This is even more important in microservice architectures, where you have even more independent, distributed, and scaled business logic. Thus, as I discussed already around two years ago: microservices might be the death of the Enterprise Service Bus, but integration and middleware (and other things like API Management or cloud-native concepts) will be needed more than ever before for microservice architectures.
Circuit Breaker Design Pattern for Resilient Microservice Architectures
The Circuit Breaker is one of these cloud-native design patterns. It allows for:
Fast failing and rapid recovery
Preventing cascading failures
Latency tolerance logic
Fault tolerance logic
Fallback Options
This is realized by rejecting service requests if a service is not available for whatever reason; in a microservice architecture, there can be many reasons or issues. The rejection is configured by various parameters such as request volume threshold or error threshold percentage. Martin Fowler has a great explanation of the Circuit Breaker design pattern. Therefore, I will just explain it shortly using one of his graphics:

The circuit is closed in the beginning. All service request get a successful response from the service. If a threshold of 5 failures is reached, the circuit is opened. New service requests are rejected. After a timeout of 1 minute, a new service request tries if the service is available again; therefore the circuit is half open in this state. Depending on the success or failure, the circuit is opened or closed after this service request.
This relatively simple pattern can get very powerful (depending on the configuration options) and allows you to build resilient microservice architectures with reduced latency and lowered resource consumption.
Netflix's Open-Source Implementation: Hystrix
Hystrix was open sourced by Netflix a few years ago and is by far the most widely used framework for using the circuit breaker pattern in a microservices architecture.
Microservice architectures and cloud-native platforms such as CloudFoundry or Kubernetes can leverage Hystrix to build resilient microservice deployments. In addition, you can use the Hystrix Dashboard to get some near real-time visualization. The video “Hystrix Dashboard — Tech Talk and Demo” shows a great introduction. Here is just a screenshot explaining the key aspects of the dashboard:
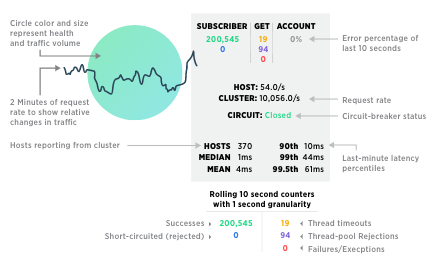
The dashboard does its job. But in a more sophisticated microservices architecture, you might leverage the benefits of a real-time streaming analytics visualization tool such as Zoomdata, Striim, or TIBCO Live Datamart. This allows not just monitoring live streaming data, but also applies continuous aggregations, rules, consolidation, and predictive analytics for automated or human- driven decision-making instead of just showing a monitoring dashboard for every microservice.
Read the rest of this article and a lot more in:
DZone's Guide to the Cloud: Native Development and Deployment
Including:
- Industry Research Data
- Articles Written by Industry Experts
- Cloud Architecture Infographic
- Directory of the Best Tools & Solutions
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments