Cloud Security in Hybrid and Multi-Cloud
Cloud Security Challenges in a Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environment. Complexities involved with it and strategies for mitigation.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIncreasing adoption of SaaS Applications and Web Based solutions created a demand for data and resource sharing. Cloud computing provides a combination of infrastructure, platforms, data storage, and software as services. It has replaced grid computing over the years and changed the way people share access, and store information. As more companies use cloud computing, maintaining cloud security in hybrid and multi-cloud systems becomes more challenging. These methods provide flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, but they also present special difficulties for data protection and upholding a strong security posture. The difficulties with cloud security that exist in hybrid and multi-cloud setups will be examined in this article, along with methods for successfully reducing the risks involved.
Understanding Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
Organizations can take advantage of both private and public Clouds by combining them in hybrid cloud setups. To disperse workloads and prevent vendor lock-in, multi-cloud setups use several cloud service providers (CSPs). These configurations have advantages, including better geographic distribution, redundancy, and resource allocation. This setup allows a multi-server on-demand system. The combined bandwidth provides increased availability and fast access to resources. The resources are provided on demand allowing maximum utilization. The sharing of hardware resources provides great data storage, i.e., Amazon S3 provides affordable data storage to various platforms and applications. The combination of multiple clouds as one huge visualized system has brought a paradigm shift in the digital world. However, there are many difficulties in maintaining security across various platforms, networks, and providers.
Workload Management in Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
In a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud environment, the strengths of both public and private clouds can be used. While public clouds provide greater access to audience and reach, private cloud offers safety and data isolation. The workload that requires greater care and confidentiality can be kept in a private cloud while the rest is loaded in a public cloud. Most hybrid cloud users keep their top sensitive data in a private cloud, while the non-confidential data, such as Products and services, is in a public cloud. In this, the security, scalability, and confidentiality of data are ensured in a visualized environment.
Complexity and Lack of Standardization
Problem: Environments with many clouds and hybrid configurations make maintaining security more difficult. A cloud platform's and service provider's individual security settings, setups, and Management interfaces may vary. This lack of standardization makes it difficult to identify vulnerabilities, detect attacks, and respond appropriately. Also makes it difficult to achieve a unified view of security throughout the environment.
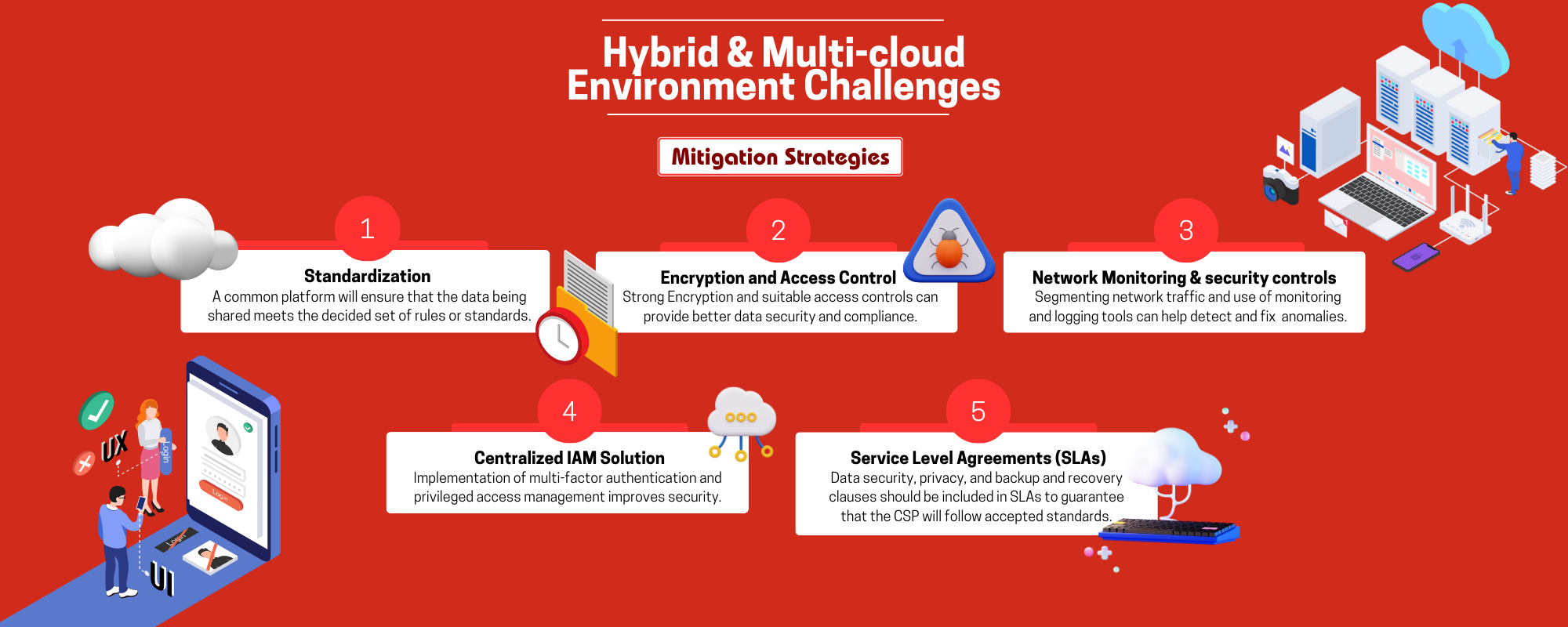
Mitigation Strategy: Setting up a common platform for managing cloud security that connects with many cloud service providers can provide you with a consolidated picture of security controls, make it easier to implement policies consistently, and speed up security monitoring and incident response. A common platform will ensure that the data being shared meet the decided set of rules or standards and goes through the decided protocols.
Data Security and Compliance
Problem: In every cloud context, data security is a top priority, but in hybrid and multi-cloud environments, it gets even more complicated. Data must move effortlessly across many cloud platforms and CSPs, sometimes spanning numerous geographical and judicial boundaries. While maintaining data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, organizations must navigate data residency, privacy regulations, and compliance obligations.
Mitigation Strategy: Protecting data while it travels through hybrid and multi-cloud systems can be done by utilizing strong encryption techniques, both in transit and at rest. Compliance is ensured while upholding the principle of least privilege by implementing data classification and access controls based on regulatory requirements.
Network Security and Segmentation
Problem: Networks cover on-premises infrastructure and several cloud platforms in hybrid and multi-cloud scenarios. Complex jobs include establishing secure network connectivity, maintaining appropriate segmentation, and managing network traffic. Unauthorized access or lateral movement inside the environment is more likely when there are configuration errors, lax access rules, or low network visibility.
Mitigation Strategy: Segmenting network traffic can be enforced, and network traffic can be protected by putting in place network security controls such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs). Tools for network monitoring and logging enable prompt detection of any suspicious activity or anomaly and enable appropriate responses.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) Challenges
Problem: IAM is essential for safeguarding access to cloud services and data, which presents a problem. However, it can be difficult to manage identities and access privileges uniformly across many cloud platforms and providers. It may be challenging to retain centralized control, enforce stringent authentication standards, and manage user privileges efficiently because each platform may have its own IAM procedures.
Mitigation Strategy: Consistent identity management and access controls are made possible across many cloud platforms by implementing a centralized IAM solution or identity federation technique. By assuring correct user authentication and limiting privileged access, the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) and privileged access management (PAM) improves security.
Vendor Lock-In and Dependency Risks
Problem: Many times, hybrid and multi-cloud environments depend on numerous CSPs. This reduces the risk of dependence on a single vendor but also creates problems with vendor lock-in and dependency issues. Contracts, service-level agreements (SLAs), and exit plans must all be carefully considered by organizations to prevent interruptions or data loss in the event that cloud providers are switched. Vendor lock-in can reduce flexibility, raise expenses, and stifle innovation since businesses may find it difficult to adapt to or migrate their data and apps to different cloud platforms.
Mitigation Strategy: In order to guarantee that organizations maintain complete control and ownership of their data throughout the engagement with the CSP, contracts should expressly state data ownership. This avoids any controversies or issues with data access and retrieval while switching to a new supplier. Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are essential for controlling expectations and guaranteeing the effectiveness and accessibility of cloud services. SLAs should be carefully reviewed by organizations to understand the caliber of service they can anticipate from the CSP. Data security, privacy, backup, and recovery clauses should be included in SLAs to guarantee that the CSP will follow accepted standards.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has changed the way people communicate and share resources. Multiple clouds can be combined to enhance their efficiency and performance. Multi-clouds are the combination of multiple clouds into one centralized form. In contrast, hybrid clouds combine public and private clouds to gain the strength to ensure good workload management. The use of such groupings can lead to cloud complexity, lack of common standards, security challenges, IAM challenges, dependency risks, etc.
By following the mitigation strategies explained in the article, IT Admins and SREs can reduce the risks associated with multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud environments.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments