Deploying Salesforce Using Bamboo
As we reach article number four in the series I've written about Continuous Integration with Salesforce, we will finally focus on the deployment to Salesforce using Atlassian Bamboo.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
As we reach article number four in the series I've written about Continuous Integration with Salesforce, we will finally focus on the deployment to Salesforce using Atlassian Bamboo. If you need to catch up, below are links to the prior three articles:
The Development Lifecycle
At this point, the development lifecycle appears as listed below:
Developer uses a Salesforce sandbox Org to make updates.
Once finished, the developer uses the Force IDE within Eclipse to Refresh from Server in order to download the metadata/code from the Salesforce Org to the git-based repository - like Atlassian Stash.
The developer checks-in the code (using either git commands or Atlassian SourceTree) and submits a Pull Request (PR) ... or a code review.
When the PR request is approved and merged into the working branch, which I called develop, Bamboo will sense this update and automatically kick off the build process.
The build process in Bamboo will use the Force Migration Tool and Apache Ant to call the Salesforce Metadata API to push the code into a Salesforce org dedicated to the build process. As a part of this process, the unit tests within Salesforce will be fired - just as they are during a Production deployment.
What's Next?
The goal of this article will be to accomplish the following items:
Create a Release Candidate in Stash, which will be used to deploy code to other Salesforce Orgs.
Build a Release in Bamboo, which will be used as a container to track releases across all the Orgs in our environment.
Deploy the actual code to the Salesforce orgs.
Merge the release code into the master branch in Stash.
Creating the Release Candidate in Stash
Within Bamboo, a stage called Create Release has been created:
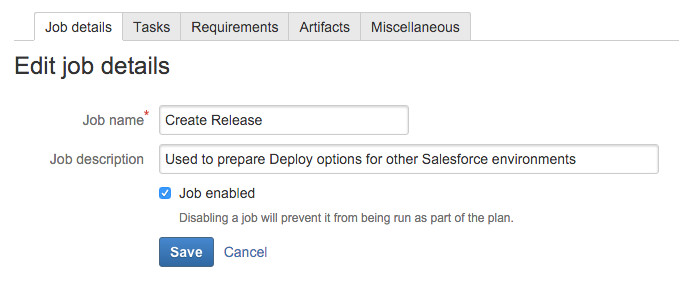
The job will include the following tasks:
Prompt the user for a Release Candidate Id, which is typically the date of our current sprint, plus a unique ID. The value will be stored in a variable, like bamboo.release.name. An example might be 2015.12.16_006.
Source Code Checkout - pulls a copy of the current develop branch, which has been reviewed and approved as a part of the PR process.
An Artifact called Salesforce Build is created in Bamboo, which is a current snapshot of the code at this point.
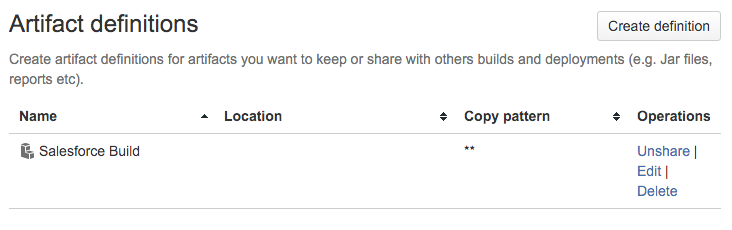
Executes a series of git commands:
git remote set-url origin ssh://git@stash.yourdomaingoeshere.com/crm/sfdc.git
git pull origin
git checkout -b release/${bamboo.release.name}
git push origin release/${bamboo.release.name}
git statusBuilding the Release in Bamboo
Within the Deployment side of Bamboo, a new Deployment is created, which includes targets for each Salesforce org. An example appears as listed below:
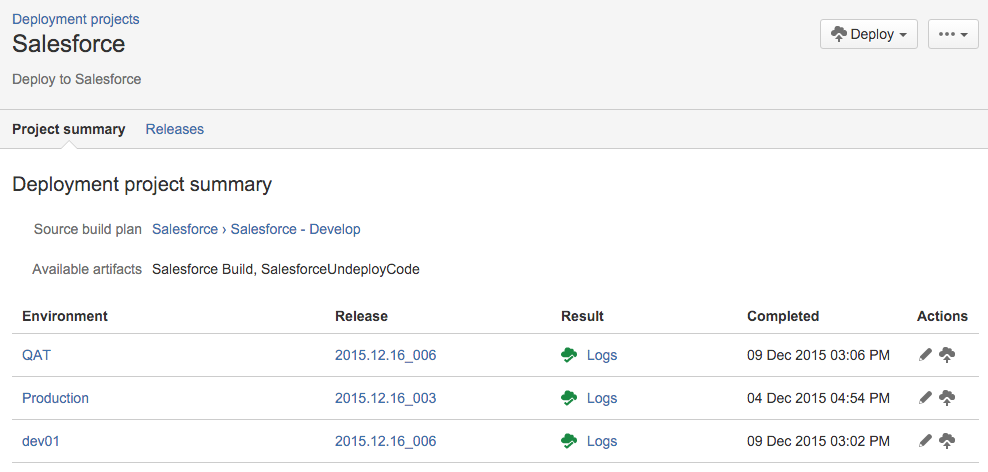
Using the dev01 environment as example, the following tasks exist:
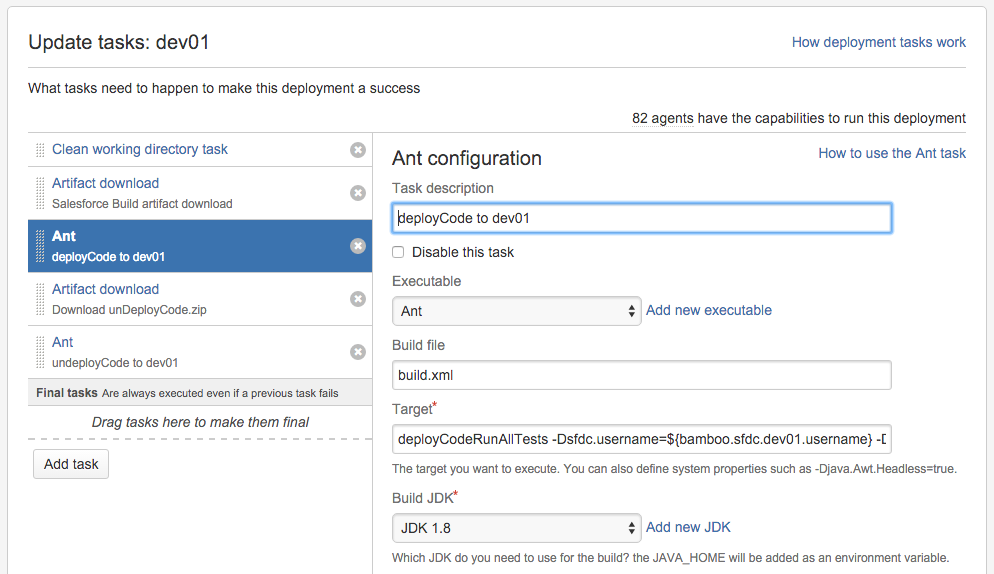
At a high-level:
Clean working directory - makes sure the target directory is empty.
Artifact download - pulls down a copy of the Salesforce Build artifact created above.
Ant - calls the deployCodeRunAllTests target in the build.xml, using Bamboo variables for user name, password, security token and target server URL.
(second) Artifact download - pulls down a copy of the unDeployCode artifact used for destructive changes.
(second) Ant - executes the unDeployCode target to perform destructive changes, similar to Ant task above.
Bamboo allows environments to be cloned. A good rule of thumb is to work on one environment (i.e. Dev01) until everything is functional, then simply clone the tasks for other environments, like Dev02, Dev03, etc.
Merging into Master
With everything in place, the Build Manager merely needs to use the ... | Create Release function within Bamboo once the Create Release stage has been completed. The release will appear using the name provided by the build manager.
At this point, clicking the cloud-looking deploy icon next to each environment will deploy the code into the appropriate Salesforce org. Bamboo allows for notifications to be pushed via Email and even Atlassian HipChat, so that your team has visibility into your build status.
The Production deployment should be configured to execute once last series of git-commands:
git remote set-url origin ssh://git@stash.yourdomaingoeshere.com/crm/sfdc.git
git pull origin
git checkout -b release/${bamboo.release.name}
git config --local user.name "bamboo"
git config --local user.email "devops@yourdomaingoeshere.com"
git config --list --local
git checkout -f master
git merge --no-ff release/${bamboo.release.name}
git push origin master
These commands will merge the release candidate code into the master branch. As a rule of thumb, I typically refresh all my sandboxes after Production has been refreshed, so that everyone is on the same code level before we start the next sprint.
Conclusion
While Salesforce may be a market leader in the CRM space, it is far from a market leader from a Continuous Integration perspective. These articles have attempted to provide a starting point for DevOps teams to put some organization around Salesforce deployments. They are far from being complete, because each organization has different goals and needs within their Continuous Integration process.
As I've noted all along, it took some time to get our environment working and I certainly realize it will only keep working until it breaks again. Most of the time, the issues are related to unexpected changes from Salesforce and not our design and implementation.
Have a really great day!
Published at DZone with permission of John Vester, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments