Distributed and Guaranteed Executor Service
An overview.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
You may also like: Using Java's Future and ExecutorService
If you have ever implemented an async API/Event listener then the following would have been the typical implementation
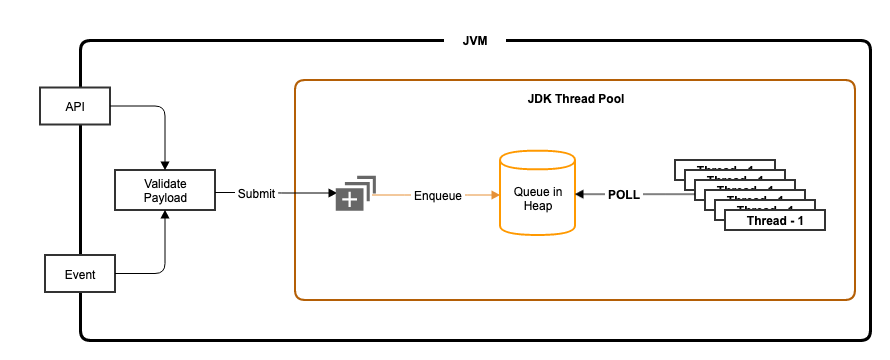
- Validate the payload.
- Extract the needed parameters from the payload into a runnable and submit it to JDK Executor service.
- Respond with a correlation ID in case of an API and acknowledge the event broker in case of async event listener respectively.
- JDK Executor threads poll from the queue and execute them asynchronously.
When you have implemented as above and raised a code review, have you ever been stumbled over the following questions from reviewers?
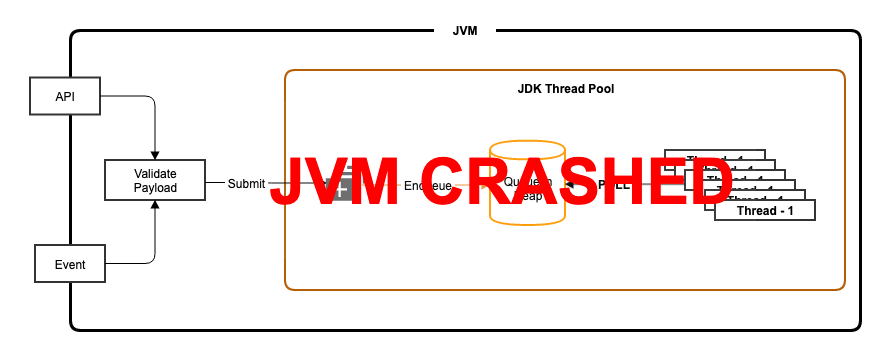
- How the submitted runnable execution is guaranteed in the below cases?
- JVM crashes when the executor service queue is piled up with 100s of runnable.
- JVM crashes while executing a runnable.
- If runnable execution fails due to unavailability of a downstream service
- How to retry the failed execution?
Well, we also have faced the same questions for our async implementations.
Following is the typical answer to the above as most of us could imagine.
- Validate the payload.
- Extract the needed parameters from the payload and store it in the DB table.
- Implement a scheduled job that picks each record from the DB table, executes it and maintains the state.
We have stopped here.
We would welcome a new set of challenges with scheduler and state management etc. and need to rewrite the whole implementation.
So, I decided to delve deeper into JDK Executor service implementation to figure out a solution and following are the questions that we discussed while doing so.
Q1: How does the Executor service store a runnable?
A1: It stores in in-memory(heap) Linked Blocking Queue.
The root cause for the first challenge: Runnables are stored in heap. Hence, they are potentially at risk as the heap is cleared when JVM crashes.
Q2: It is possible to change the implementation of Executor service?
What Does it Mean?
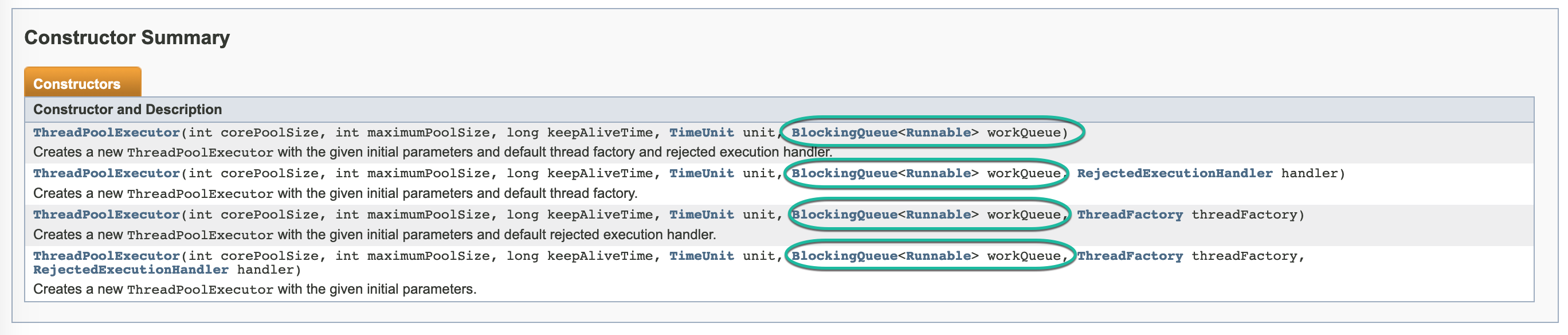
Instantiate the Executor service thread pool with appropriate BlockingQueue that stores the runnable out of JVM heap memory.
Q3: Now, how to implement such a BlockingQueue?
A3: Let's try to find out of the box solutions.
Q4: Did we find it?
A4: Yes, indeed. A beautiful open source library Redisson that has BlockingQueue implementation based on Redis and more.
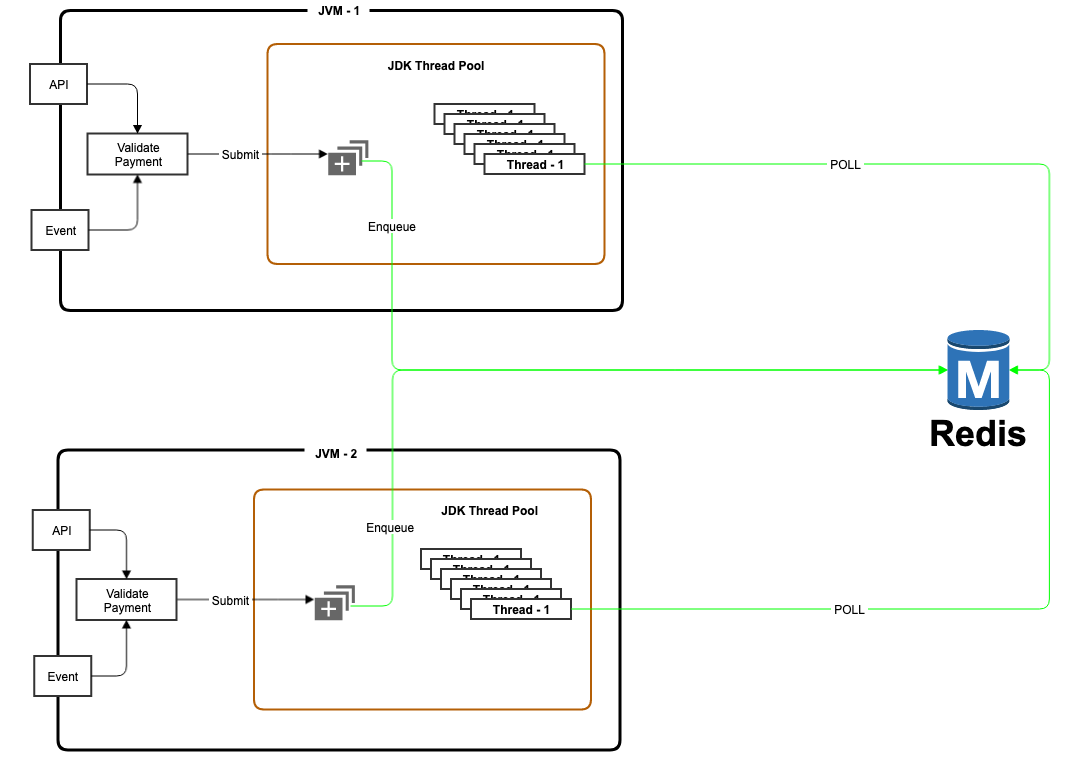
Q5: How does the solution be the savior from JVM crashes?
A5: Indeed, it is for the following reasons.
If JVM is crashed when it has submitted several runnable but not executed them
- If the service cluster has more than one JVM then another JVM can pick them from the queue and execute as Executor service threads across service cluster poll the same runnable queue i.e. based on Redis.
- If the service cluster has only one JVM then the re-spawned JVM will pick them from the queue and execute.
WOW, we solved the first challenge i.e. guaranteed execution.
We could NOT get out of the box solution for the second challenge i.e. retrying failed runnable execution.
Q6: How did we solve the second challenge?
A6: We have enhanced the Redisson BlockingQueue implementation as following:
- Keep a copy of runnable in Redisson RMap.
- If runnable execution fails due to any re-triable errors such as downstream unavailability then keep the copy otherwise remove it.
- Implemented a scheduler that periodically scans the RMap and puts its elements into the Redisson BlockingQueue so that the Executor service threads could pick them and execute.
Thus, we have solved the challenges posed to us with very minimal extra code and zero modification to the already implemented code.
Further Reading
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments