How to Accelerate Hyper-Automation With Industrial IoT
This article will walk you through specific areas where industrial IoT integration can help accelerate your pace of hyper-automation.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeMany enterprises have already adopted business process automation (BPA) to improve efficiency and reduce human error. However, by and large, industrial automation is fragmented – it applies to specific business aspects but is not used across the entire organization yet. The key to expanding automation across the company is hyper-automation.
In 2020, Gartner named hyper-automation the # 1 technology trend of the year. So what is it, and how can large and small businesses benefit from it? This article will walk you through specific areas where industrial IoT integration can help accelerate your pace of hyper-automation.
What is Hyper-Automation?
Hyperautomation is the extension of legacy business process automation beyond individual processes. By combining AI tools with RPA, hyper-automation can automate almost any repetitive task performed by business users. It even takes it to the next level and automates automation by dynamically detecting business processes and creating bots to automate them.
With a range of tools such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Machine Learning (ML), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) that work in harmony to automate complex business processes, hyper-automation is a driver of real digital transformation.
"Hyperautomation is an unavoidable market state in which organizations must rapidly identify and automate all possible business processes." Gartner
In order to successfully achieve hyper-automation, organizations need transparency across their entire operations. With industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) solutions, you can capture and analyze data from plants, processes, and products, enabling this level of visibility. Furthermore, on top of your industrial IoT solution, you can deploy applications and advanced capabilities that allow you to continuously automate aspects of your business.
Automation vs. Hyper-Automation
Traditional approaches to enterprise automation focus on how best to implement automation in a specific context. These automation tools are very software-specific. For example, workload automation uses scripting to automate many repetitive processes. BPM tools can automate tasks in the context of a specific workflow.
AI extends traditional automation to take on more tasks, such as using optical character recognition (OCR) technology to read documents, natural language processing (NLP) to understand them, or natural language generation (NLG) to provide a summary to humans. Hyperautomation makes it easy to integrate AI and machine learning (ML) into automation with pre-built modules delivered through an app store or corporate repository.
Low-code development tools reduce the experience required to build automation. Hyperautomation can further simplify automation design by using intelligent process analysis to identify and automatically generate new automation prototypes. Today, these auto-generated templates need to be further refined by humans to improve quality. However, improvements in hyper-automation will reduce this manual effort.
How Does Hyper-Automation Work?
RPA, enriched with AI and machine learning, is becoming the core enabling hyper-automation technology. The combination of RPA and AI technologies offers the power and flexibility to automate where automation was impossible before: undocumented processes that rely on unstructured input.
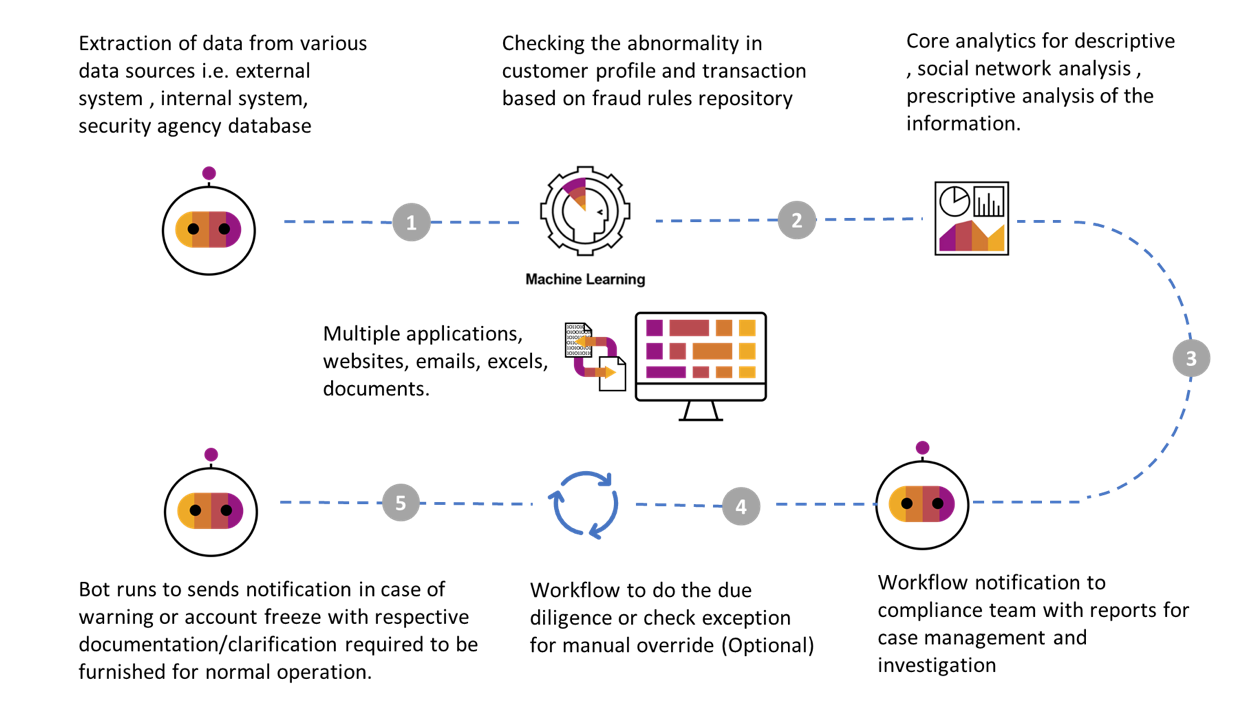
The advanced technologies used in hyper-automation include the following:
- Intelligent analysis tools for processes and tasks to identify and prioritize automation opportunities.
- Automation design tools to reduce the effort and cost of automation. These include RPA, no-code / low-code development tools, integration platform-as-service (iPaaS), and workload automation tools.
- Business logic tools to make automation easier to adapt and reuse, including intelligent business process management, decision management, and business rule management.
- AI and ML tools to empower automation. The toolbox in this area includes NLP, OCR, computer vision, virtual agents, and chatbots.
Hyper-Automation Ecosystem
- Automation Opportunities Discovery
- Process mining
- Task mining
- Process analytics
- Automation Implementation
- RPA
- No-code/low-code
- PaaS/iPaas
Workload automation
Business logic tools:
Intelligent business process management suites
Decision management
Business rules management
Automation Extension with AI
Machine learning
Deep learning
Natural language processing (NLP)
Computer vision (CV)
Optical character recognition (OCR)
Virtual agents
Voice technology
AI chatbots
Hyper-automation refers to a learned approach to automation. The practice of hyper-automation includes:
- Determining what types of work to automate.
- Choosing the right automation tools.
- Increasing flexibility by reusing automated processes.
- Empowering them with different varieties of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Hyperautomation initiatives are often coordinated through R and D that helps drive automation efforts.
The goal of hyper-automation is not only to save costs, increase productivity and increase efficiency through automation but also to benefit from the data collected and created through digitized processes. Organizations can use this data to make more informed and timely business decisions.
Rather than referring to a single off-the-shelf technology or tool, hyper-automation focuses on adding more intelligence and taking a broader systems approach to scaling automation efforts. This approach emphasizes the importance of striking the right balance between replacing manual effort with automation and optimizing complex processes to eliminate steps.
The key question is to determine who should be responsible for automation and how it should be done. Frontline employees can better identify boring tasks that can be automated. Business process experts can better identify the automation capabilities.
Process Intelligence analyzes enterprise software logs from business management software such as CRM and ERP systems to build a view of process flows.
Task Mining uses computer vision software running on each user's desktop to build a view of processes spanning multiple applications.
Digital Twins allow organizations to visualize how functions, processes, and KPIs interact to create value. They can help organizations assess how new automation tools create value, open up new opportunities, or create new bottlenecks that need to be addressed.
AI and ML components enable you to automate your interactions with the world in a variety of ways. For example, OCR allows you to automate text processing from PDF documents. NLP can extract and organize information from documents, such as determining which company is billed and what it is for, and automatically entering this data into the accounting system.
The hyper-automation platform may sit right at the top of the technology that companies already have. One of the paths to hyper-automation is RPA, and all leading RPA vendors are adding support for AI integration, process mining, digital worker analytics, etc.
In addition, other types of low-code automation platforms, including business process management packages (BPMS / intelligent BPMS), also add support for additional components of the hyper-automation technology.
Why is Hyper-Automation Important for Business Growth and Resilience?
As businesses embrace hyper-automation, there are many ways to use this discipline to improve business operations. In terms of social media and customer retention, a company can use RPA and machine learning to generate reports and pull data from social platforms to determine customer sentiment. You could design a process to make this information available to the marketing team, which could then create targeted campaigns for customers in real-time.
If an enterprise launches a product quickly and digital automation metrics show strong customer demand, the product can scale quickly to help the company increase its revenues. Conversely, if extended analysis shows that the product is not in demand from customers, the company can minimize losses by quickly abandoning it.
The main benefits of hyper-automation include the following:
- Reduces the cost of automation.
- Improves consistency between IT and business.
- Reduces the need for shadow IT, which improves security and governance.
- Promotes the introduction of AI and ML into business processes.
- Improves the ability to measure digital transformation impact.
- Helps prioritize future automation efforts.
Hyper-Automation Use Cases
Condition Monitoring
Condition monitoring is an analysis of the key parameters of an asset, eliminating the possibility of human judgment when faults are detected. In practice, your condition monitoring application can identify an overly vibrating part or asset operating at high temperatures.
In many cases, these anomalies are early signs of a malfunction that can lead to failure. With a condition monitoring app, you can implement automatic alarms that will notify your teams when an anomaly occurs. Condition monitoring can be applied to assets, installations and systems.
Industrial IoT health monitoring can be performed remotely or locally to reduce equipment downtime and improve plant reliability.
Implementation of condition monitoring through the IIoT implementation proves to be more efficient than other methods because the IIoT provides an accurate and continuous stream of parameter data in near real-time.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is an industrial IoT solution that continuously collects and analyzes asset health and performance data in real-time to understand the root cause of quality and manufacturing issues.
Prior to the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) implementation, the maintenance of manufacturing assets typically took a calendar or operational maintenance approach. Both approaches can lead to overhead and disruption. Conversely, predictive maintenance analysis determines the optimal time and frequency to service assets, thereby preventing downtime. By automating decisions about when and how often to maintain assets, your team can spend more time highlighting areas that differ from each other.
Digital Twins
Using a digital twin creates a closed feedback loop to better understand how products and processes work in real-life situations. A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical product or process.
Digital twins can be seen as an extension of hyper-automation as they uncover previously unavailable data and take action on performance data for IoT products. These capabilities provide clear insights to help industrial organizations optimize decision-making. By leveraging IoT data to understand how products and processes perform in the real world, you can take action to improve asset utilization, efficiency, and availability, and test new processes – all without compromising production.
Hyper-Automation Challenges
Before embarking on the full path to hyperautomation, there are several issues you should consider:
- Finding ways to measure success (does your tool of choice provide advanced analytics?).
- Return on investment calculation.
- Choosing the right Hyper-Automatic Infrastructure.
- Getting support from your stakeholders and employees (robust onboarding can help here).
- Lack of previous information about business processes, which complicates and slows down hyper-automation implementation, etc.
Despite these challenges, however, hyperautomation provides significant and measurable benefits. These include the higher-level productivity, functionality, and workflow optimization that hyper-automation offers your organization. It allows employees to work smarter and avoid repetitive tasks, and it also offers your business a range of tools to ensure its presence in the future!
Conclusion
We are on the path to hyperautomation and can already see its examples in our daily lives. For enterprises, hyperautomation offers the opportunity for even greater efficiency, faster time-to-market, lower costs, and higher profits. While standard automation may already have freed employees from many time-consuming (and tedious) tasks, hyper-automation will undoubtedly take it further.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments