How to Choose the Right Database Among Cassandra, MongoDB, and MySQL for Your Applications
See how to choose the right database for your applications.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
In this article, I compared ACID properties, CAP attributes, and other features among Cassandra, MongoDB, and MySQL databases to help you choose the right database for your applications. Choosing the right database primarily depends on application needs. There are many factors that need to be considered while choosing the database, In this article, I mainly focused on the transactional aspect.
Cassandra: A key-value-store that stores data in a schema-less way.
MongoDB: A document database that expands on the basic idea of key-value-store.
Mysql: A relational database management system.
First, let’s looks at ACID supportability.
What Is ACID?
ACID: A set of properties that guarantees a database transaction is reliable. ACID stands for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. ACID Properties are an essential part of the database.
Generally, most relational databases support all ACID properties. However, NoSQL databases have various levels of support for ACID. Cassandra and MongoDB are NoSQL databases whereas MySQL is a SQL database.
| Database | DB Type | Atomicity | Consistency | Isolation | Durability |
| Cassandra | NoSQL | Write operations are atomic at the partition level | Eventual /Tunable | Row Level | Writes are durable |
| MongoDB | NoSQL | Supports single document atomicity | Support | Adjustable | Supports multiple durability options |
| MySQL | SQL | InnoDB Storage Engine support transaction atomicity | InnoDB uses a file flush technique called doublewrite | Offers different levels of isolation | Can be tuned using configurable parameters |
What Is the CAP Theorem?
A theorem that describes how the laws of physics dictate that a distributed system MUST make a tradeoff among desirable characteristics.CAP stands for Consistency, Availability, and Partition tolerance.
Generally, most databases support two CAP attributes.
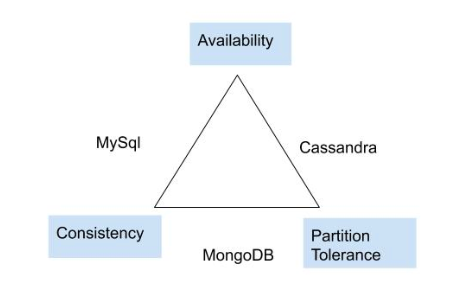
Some databases make an effort to support all three, but they still prioritize them in a certain way. For example, Cassandra provides high availability and partition tolerance, and it also supports consistency using eventual consistency. If you are looking for high availability and consistency, then MySQL could be the right choice. MongoDB supports Partition Tolerance and Consistency. MongoDB also supports availability to some extent.
Finally, Let’s compare other attributes
| Properties | Cassandra | MongoDB | MySQL |
| Transaction Rollback | No | Yes | Yes |
| Faster Writes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Locking Mechanism | No | Yes | Yes |
| Table Joins | No | No | Yes |
| Master Less Architecture | Yes | No | No |
Conclusion
The important thing is to understand the needs of your application. Then, check which database is closely matching to your requirements. Sometimes, you may not be able to find a comprehensive database that can support all your requirements. In that case, you may have to trade off something to fulfill your top priorities.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments