How to Create Tables in Java
Learn how to use the JTable method to create a table in your Java applications.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn Java, tables are used to arrange data into columns and rows. A column is space that runs horizontally on a table, while a row is a space that runs horizontally in your table. The intersection between a column and a row is called a cell and is used to hold a singular piece of data. In Java, developers can use the JTable method to create a table in their applications. JTable is a Swing component that inherits from the JComponent class.
Master Java Programming | Enroll in Free Online Course Today*
*Affiliate link. See Terms of Use.
How to Create a Table in Java
To create a table, you need to make an instance of the JTable class. You need to provide two arguments (row and column) in its constructor for the table to be constructed, as shown in this example code snippet:
JTable table = new JTable (row, column);The row and column values can consist of two integer values, like below:
JTable table = new JTable (5,3);The above statement creates a table with 5 rows and 3 columns. Instead of providing the JTable constructor with integers, programmers can also supply a two dimensional array for the data in each row, and a one dimensional array for the column names. Here is how you can use arrays to create a table in Java:
JTable(Object[][] rowData, Object[] columnNames)Here is some example code showing how to create a table in Java and fill it with data:
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.table.*;
import java.awt.*;
class Table{
public static void main(String args[]){
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
String[] columnNames = {"Name", "Age", "Student"};
Object[][] data = {
{"Ken", new Integer(5), new Boolean(false)},
{"Tom", new Integer(3), new Boolean(true)},
{"Susan", new Integer(2), new Boolean(false)},
{"Mark",new Integer(20), new Boolean(true)},
{"Joe", new Integer(10), new Boolean(false)}
};
JTable table = new JTable(data, columnNames);
frame.add(table);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(400,400);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}If you run this code in your integrated development environment (IDE) or code editor, it will produce the following output:

When you click on any one of the above cells, you will notice that the data in it is editable. This is not a particularly desirable feature if you are just presenting data to your user. Also, all the data is treated as a string when in its presentation to a user. Another point of concern is that, in case you were querying a database object for particular values, you would have to copy all values to an array or vector. To avoid these problems, you can instead create your Java table using a model.
How to Create a Table Using a Model in Java
First, it is important to understand how table data is handled. All tables (including a table created using JTable()) use a table model to manage their data. When developers do not provide a table model to the constructor of JTable, an instance of DefaultTableModel will be automatically created for it. Therefore, if you need to use a custom model, you need to provide it to the JTable constructor, as shown in this example code:
JTable table = new JTable(new MyTableModel());To define a table model, programmers need to create a class that extends the AbstractTableModel class:
class MyTableModel extends AbstractTableModel{
}In your table model, you can include the data for your rows and column names, just as shown in the earlier JTable example. To ensure that your table model class is a concrete class, you need to implement the following three methods of AbstractTableModel:
public int getRowCount();
public int getColumnCount();
public Object getValueAt(int row, int column);You can implement more methods, but you must ensure that the above methods are among those you implement. You can find the description of other methods from the official Oracle API docs. The code example below shows how you can use a table model in Java:
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.table.*;
import java.awt.*;
class TableUsingModel{
public static void main(String args[]){
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
JTable table = new JTable(new MyTableModel());
frame.add(table);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(400,400);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
class MyTableModel extends AbstractTableModel {
String[] columnNames = {"Name", "Age", "Location"};
Object[][] data = {
{"Ken", new Integer(25), "Nairobi"},
{"Tom", new Integer(31), "Geneva"},
{"Sheila", new Integer(29), "Paris"},
{"Mark",new Integer(20), "Cairo"},
{"Jessie", new Integer(18), "Miami"}
};
public int getRowCount() {
return data.length;
}
public int getColumnCount() {
return columnNames.length;
}
public Object getValueAt(int row, int col) {
return data[row][col];
}
}This results in the following output (Display):
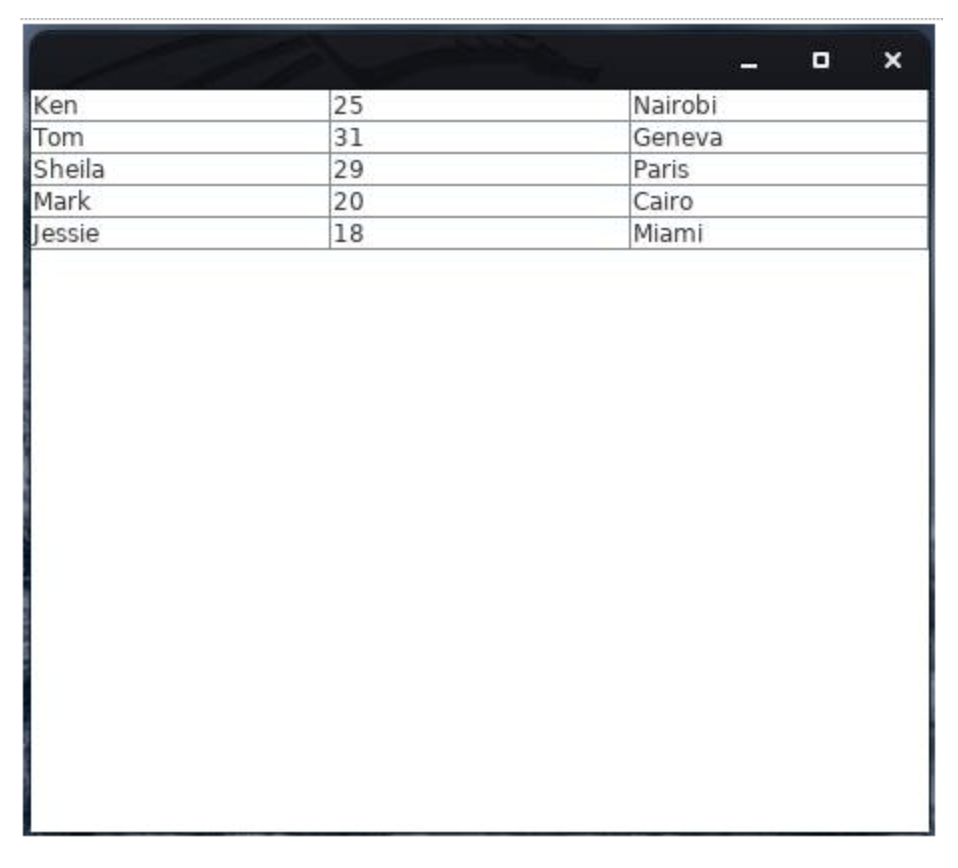
This time, if you try double-clicking on any cell, you will notice that it is not editable.
How to Manage Column Width and Height in Java
If you want to set the height of rows, you can use the setRowHeight() method.
JTable table = new JTable(data, columnNames);
table.setRowHeight(80);The above example sets the height of each row 80 pixels. To set the width of columns, you can use the setPreferredWidth() method. First, you need to create a column model of type TableColumnModel. Then you can get the particular column you want and then set its preferred width. Here is some example code showing how to set the column width of a table in Java:
TableColumnModel columnModel = table.getColumnModel();
columnModel.getColumn(2).setPreferredWidth(200);Final Thoughts on Java Tables
In this programming tutorial, programmers learned how to use JTable, or a table model, to create a table in Java. The code examples shown above add the tables directly to the JFrame container. However, you can instead add your table to a scroll pane so that your user can easily navigate through the data when it does not fit its container.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments