Understand Java Callable and Future
A tutorial to help you understand how to use Callable and Future in Java.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn Java multithreading programs, we extensively use Java Callable and Future. I believe all of you have the basic understanding of threads. In brief, The thread is a separate path of execution, so if you have to do a repetitive task, you can break the work into multiple chunks (tasks) and assign them to threads. Multiple Threads will execute tasks in parallel to get the result quickly.
In Java 5, java.util.concurrent was introduced. The callable interface was introduced in concurrency package, which is similar to the Runnable interface, but it can return any object, and is able to throw an Exception.
The Java Callable interface uses Generics, so it can return any type of Object. The Executor Framework offers a submit() method to execute Callable implementations in a thread pool. Actually, the Java Executor Framework follows WorkerThread patterns, wherein a thread pool you can initiate threads by using the Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); method. Then you can submit a task to it. As you may remember in Java, a runnable acts as the target of a thread, and in the runnable interface, a public void run() method has to be implemented where you define the task, which will be executed by threads in the thread pool. The Executor Framework assigns work (runnable target) to threads only if there is an available thread in the pool. If all threads are in use, the work has to wait. Once a task is completed by the thread, that thread returns to the pool as an available thread. Callable is same as Runnable but it can return any type of Object if we want to get a result or status from work (callable).
Java Future
Java Callable tasks return java.util.concurrent.Future objects. Java Future provides a cancel() method to cancel the associated Callable task. This is an overloaded version of the get() method, where we can specify the time to wait for the result. It’s useful to avoid a current thread getting blocked for a longer time. Please note that the get method is a synchronous method. Until the callable finishes its task and returns a value, it will wait for a callable. There are also isDone() and isCancelled() methods to find out the current status of an associated Callable task.
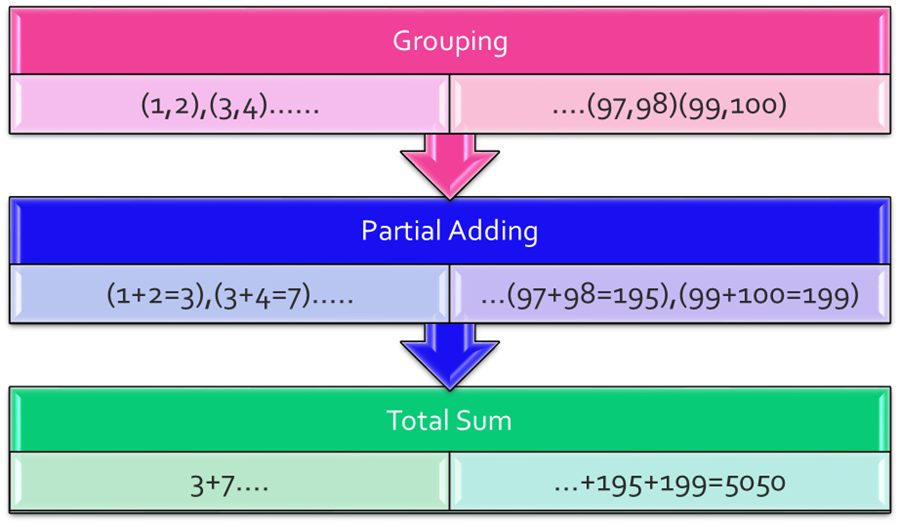
Example: Suppose the problem is to find a sum of all numbers from 1 to 100. We can do it by looping 1 to 100 sequentially and adding them.
Another way we can do it by the divide and Conquer rule. Group the numbers in a way so each group has exactly two elements. Then Assign that group to a pool of threads
So each thread returns a partial sum in parallel. Then collect those partial sums and add them to get the whole sum.
Code
Step 1: Create an Adder class and implement a callable to do the Partial sum on the group:
package com.example.thread.callable;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
publicclass CallableAdder implements Callable<Integer> {
Integer operand1;
Integer operand2;
CallableAdder(Integer operand1,Integer operand2)
{
this.operand1=operand1;
this.operand2=operand2;
}
public Integer call() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" says : partial Sum for " + operand1 + " and "+ operand2+ " is " +(operand1+operand2));
return operand1+operand2;
}
}Step 2: Create a manager class, which is responsible for grouping integers, and submit the group to the Executor Framework for partial add. Collect the partial sum, wait until all partial sums return, and add them:
package com.example.thread.callable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class ParallelAdder {
public Integer parallelSum()
{
//long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
List <Future<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<Future<Integer>>();
int count=1;
int prev=0;
for(int ;i<;i++)
{
if(count%2=)//grouping
{
System.out.println("Prev :" + prev + " current: " + i);
Future<Integer> future = executor.submit(new CallableAdder(prev,i));
list.add(future);
count=1;
continue;
}
prev=i ;
count++;
}
int totsum=0;
for(Future<Integer> fut : list)
{
try {
totsum = totsum+ fut.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("Total Sum is " + totsum);
//long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
//System.out.println("Time taken by parallelSum " + (t2-t1));
return totsum;
}
public int sequentialSum()
{
//long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
Integer totsum=0;
for(int ;i<;i++)
{
totsum=totsum+i;
}
//long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("sequentialSum Total Sum is " + totsum);
//System.out.println("Time taken by sequentialSum " + (t2-t1));
return totsum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ParallelAdder adder = new ParallelAdder();
int pSum= adder.parallelSum();
int sSum= adder.sequentialSum();
System.out.println("parallel Sum equals to Sequential Sum ? " );
System.out.println("Answer is :: " + (pSum==sSum));
}
}This is just a test example. The performance-wise Sequential sum is faster than the parallel sum.
Published at DZone with permission of Shamik Mitra, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments