Strategic Deployments in AWS: Leveraging IaC for Cross-Account Efficiency
This article provides a step-by-step strategy to streamline Docker deployments on AWS ECS with secure, multi-account CloudFormation.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, deploying Docker images across multiple Amazon Web Services (AWS) accounts presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities for organizations aiming for scalability and security. According to the State of DevOps Report 2022, 50% of DevOps adopters are recognized as elite or high-performing organizations.
This guide offers a comprehensive blueprint for leveraging AWS services—such as ECS, CodePipeline, and CodeDeploy — combined with the robust Blue/Green deployment strategy, to facilitate seamless Docker deployments. It also emphasizes employing best security practices within a framework designed to streamline and secure deployments across AWS accounts. By integrating CloudFormation with a cross-account deployment strategy, organizations can achieve an unparalleled level of control and efficiency, ensuring that their infrastructure remains both robust and flexible.
Proposed Architecture
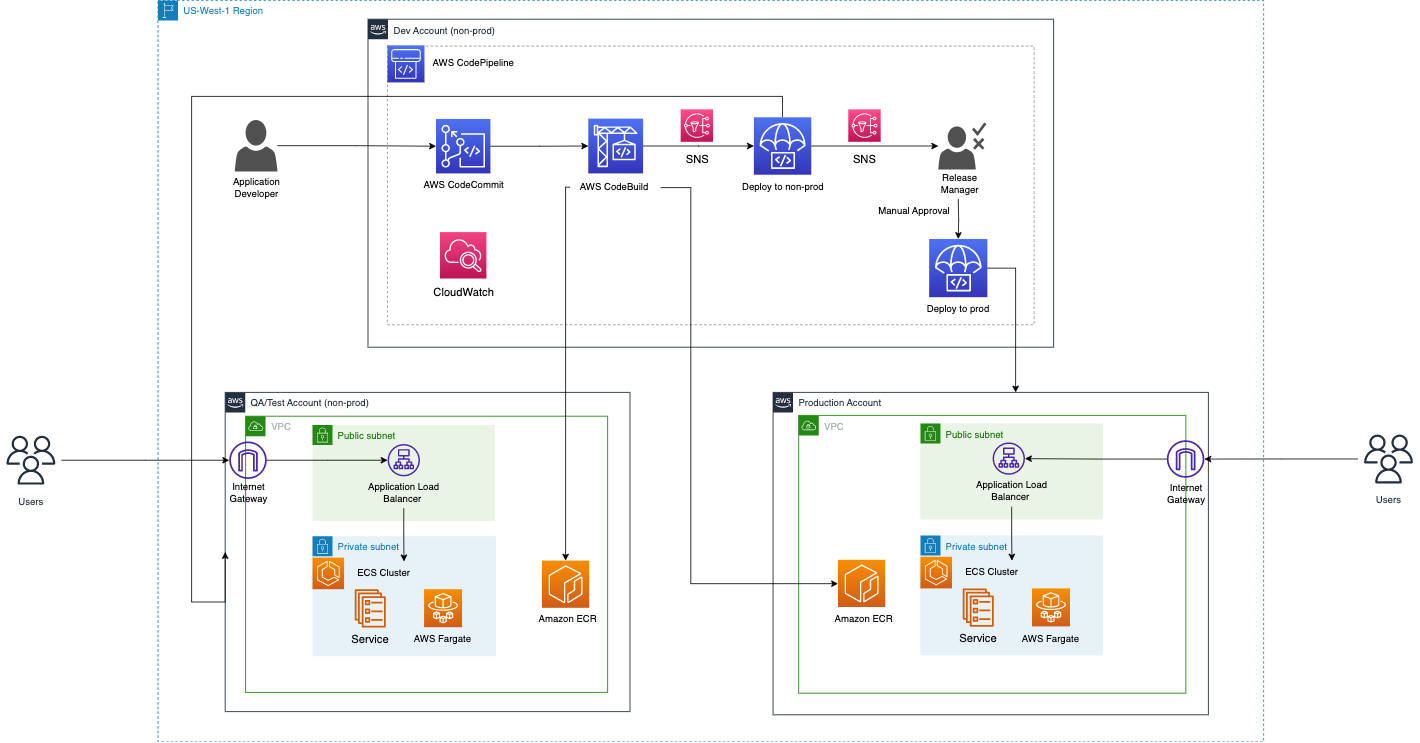
The architecture diagram showcases a robust AWS deployment model that bridges the gap between development and production environments through a series of orchestrated services. It outlines how application code transitions from the development stage, facilitated by AWS CodeCommit, through a testing phase, and ultimately to production. This system uses AWS CodePipeline for continuous integration and delivery, leverages Amazon ECR for container image storage, and employs ECS with Fargate for container orchestration. It provides a clear, high-level view of the path an application takes from code commit to user delivery.
Prerequisites
To successfully implement the described infrastructure for deploying Docker images on Amazon ECS with a multi-account CodePipeline and Blue/Green deployment strategy, several prerequisites are necessary. Here are the key prerequisites:
- Create three separate AWS accounts: Development, Test, and Production.
- Install and configure the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) and relevant AWS SDKs for scripting and automation.
- Fork the aws-cicd-cross-account-deployment GitHub repo and add all the files to your CodeCommit.
Environment Setup
This guide leverages a comprehensive suite of AWS services and tools, meticulously orchestrated to facilitate the seamless deployment of Docker images on Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) across multiple AWS accounts.
Before we start setting up the environment, use this code repo for the relevant files mentioned in the steps below.
1. IAM Roles and Permissions
- IAM roles:
- Create IAM roles required for the deployment process.
- Use cross-account.yaml template in CloudFormation to create cross-account IAM roles in Test and Production accounts, allowing necessary permissions for cross-account interactions.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09"
Parameters:
CodeDeployRoleInThisAccount:
Type: CommaDelimitedList
Description: Names of existing Roles you want to add to the newly created Managed Policy
DevelopmentAccCodePipelinKMSKeyARN:
Type: String
Description: ARN of the KMS key from the Development/Global Resource Account
DevelopmentAccCodePipelineS3BucketARN:
Type: String
Description: ARN of the S3 Bucket used by CodePipeline in the Development/Global Resource Account
DevelopmentAccNumber:
Type: String
Description: Account Number of the Development Resources Account
Resources:
CrossAccountAccessRole:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::Role'
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS:
- !Join [ ":", [ "arn","aws","iam:",!Ref DevelopmentAccNumber,"root" ] ]
Service:
- codedeploy.amazonaws.com
- codebuild.amazonaws.com
Action:
- 'sts:AssumeRole'
Policies:
- PolicyName: CrossAccountServiceAccess
PolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- 's3:List*'
- 's3:Get*'
- 's3:Describe*'
Resource: '*'
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- 's3:*'
Resource: !Ref DevelopmentAccCodePipelineS3BucketARN
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- 'codedeploy:*'
- 'codebuild:*'
- 'sns:*'
- 'cloudwatch:*'
- 'codestar-notifications:*'
- 'chatbot:*'
- 'ecs:*'
- 'ecr:*'
- 'codedeploy:Batch*'
- 'codedeploy:Get*'
- 'codedeploy:List*'
Resource: '*'
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- 'codedeploy:Batch*'
- 'codedeploy:Get*'
- 'codedeploy:List*'
- 'kms:*'
- 'codedeploy:CreateDeployment'
- 'codedeploy:GetDeployment'
- 'codedeploy:GetDeploymentConfig'
- 'codedeploy:GetApplicationRevision'
- 'codedeploy:RegisterApplicationRevision'
Resource: '*'
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- 'iam:PassRole'
Resource: '*'
Condition:
StringLike:
'iam:PassedToService': ecs-tasks.amazonaws.com
KMSAccessPolicy:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::ManagedPolicy'
Properties:
PolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Sid: AllowThisRoleToAccessKMSKeyFromOtherAccount
Effect: Allow
Action:
- 'kms:DescribeKey'
- 'kms:GenerateDataKey*'
- 'kms:Encrypt'
- 'kms:ReEncrypt*'
- 'kms:Decrypt'
Resource: !Ref DevelopmentAccCodePipelinKMSKeyARN
Roles: !Ref CodeDeployRoleInThisAccount
S3BucketAccessPolicy:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::ManagedPolicy'
Properties:
PolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Sid: AllowThisRoleToAccessS3inOtherAccount
Effect: Allow
Action:
- 's3:Get*'
Resource: !Ref DevelopmentAccCodePipelineS3BucketARN
Effect: Allow
Action:
- 's3:ListBucket'
Resource: !Ref DevelopmentAccCodePipelineS3BucketARN
Roles: !Ref CodeDeployRoleInThisAccount2. CodePipeline Configuration
- Stages and actions: Configure CodePipeline actions for source, build, and deploy stages by running the pipeline.yaml in CloudFormation.
- Source repository: Use CodeCommit as the source repository for all the files. Add all the files from the demo-app GitHub folder to the repository.
3. Networking Setup
- VPC Configuration: Utilize the vpc.yaml CloudFormation template to set up the VPC. Define subnets for different purposes, such as public and private.
Description: This template deploys a VPC, with a pair of public and private subnets spread
across two Availability Zones. It deploys an internet gateway, with a default
route on the public subnets. It deploys a pair of NAT gateways (one in each AZ),
and default routes for them in the private subnets.
Parameters:
EnvVar:
Description: An environment name that is prefixed to resource names
Type: String
VpcCIDR:
#Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for this VPC
Type: String
PublicSubnet1CIDR:
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the public subnet in the first Availability Zone
Type: String
PublicSubnet2CIDR:
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the public subnet in the second Availability Zone
Type: String
PrivateSubnet1CIDR:
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the private subnet in the first Availability Zone
Type: String
PrivateSubnet2CIDR:
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the private subnet in the second Availability Zone
Type: String
DBSubnet1CIDR:
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the private subnet in the first Availability Zone
Type: String
DBSubnet2CIDR:
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the private subnet in the second Availability Zone
Type: String
vpcname:
#Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the private subnet in the second Availability Zone
Type: String
Resources:
VPC:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPC
Properties:
CidrBlock: !Ref VpcCIDR
EnableDnsSupport: true
EnableDnsHostnames: true
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Ref vpcname
InternetGateway:
Type: AWS::EC2::InternetGateway
Properties:
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Ref EnvVar
InternetGatewayAttachment:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPCGatewayAttachment
Properties:
InternetGatewayId: !Ref InternetGateway
VpcId: !Ref VPC
PublicSubnet1:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
AvailabilityZone: !Select [ 0, !GetAZs '' ]
CidrBlock: !Ref PublicSubnet1CIDR
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvVar} Public Subnet (AZ1)
PublicSubnet2:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
AvailabilityZone: !Select [ 1, !GetAZs '' ]
CidrBlock: !Ref PublicSubnet2CIDR
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvVar} Public Subnet (AZ2)
PrivateSubnet1:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
AvailabilityZone: !Select [ 0, !GetAZs '' ]
CidrBlock: !Ref PrivateSubnet1CIDR
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvVar} Private Subnet (AZ1)
PrivateSubnet2:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
AvailabilityZone: !Select [ 1, !GetAZs '' ]
CidrBlock: !Ref PrivateSubnet2CIDR
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvVar} Private Subnet (AZ2)
DBSubnet1:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
AvailabilityZone: !Select [ 0, !GetAZs '' ]
CidrBlock: !Ref DBSubnet1CIDR
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvVar} DB Subnet (AZ1)
DBSubnet2:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
AvailabilityZone: !Select [ 1, !GetAZs '' ]
CidrBlock: !Ref DBSubnet2CIDR
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvVar} DB Subnet (AZ2)
NatGateway1EIP:
Type: AWS::EC2::EIP
DependsOn: InternetGatewayAttachment
Properties:
Domain: vpc
NatGateway2EIP:
Type: AWS::EC2::EIP
DependsOn: InternetGatewayAttachment
Properties:
Domain: vpc
NatGateway1:
Type: AWS::EC2::NatGateway
Properties:
AllocationId: !GetAtt NatGateway1EIP.AllocationId
SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnet1
NatGateway2:
Type: AWS::EC2::NatGateway
Properties:
AllocationId: !GetAtt NatGateway2EIP.AllocationId
SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnet2
PublicRouteTable:
Type: AWS::EC2::RouteTable
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvVar} Public Routes
DefaultPublicRoute:
Type: AWS::EC2::Route
DependsOn: InternetGatewayAttachment
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PublicRouteTable
DestinationCidrBlock: 0.0.0.0/0
GatewayId: !Ref InternetGateway
PublicSubnet1RouteTableAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PublicRouteTable
SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnet1
PublicSubnet2RouteTableAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PublicRouteTable
SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnet2
PrivateRouteTable1:
Type: AWS::EC2::RouteTable
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvVar} Private Routes (AZ1)
DefaultPrivateRoute1:
Type: AWS::EC2::Route
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PrivateRouteTable1
DestinationCidrBlock: 0.0.0.0/0
NatGatewayId: !Ref NatGateway1
PrivateSubnet1RouteTableAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PrivateRouteTable1
SubnetId: !Ref PrivateSubnet1
PrivateRouteTable2:
Type: AWS::EC2::RouteTable
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvVar} Private Routes (AZ2)
DefaultPrivateRoute2:
Type: AWS::EC2::Route
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PrivateRouteTable2
DestinationCidrBlock: 0.0.0.0/0
NatGatewayId: !Ref NatGateway2
PrivateSubnet2RouteTableAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PrivateRouteTable2
SubnetId: !Ref PrivateSubnet2
NoIngressSecurityGroup:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupName: "no-ingress-sg"
GroupDescription: "Security group with no ingress rule"
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Outputs:
VPC:
Description: A reference to the created VPC
Value: !Ref VPC
PublicSubnets:
Description: A list of the public subnets
Value: !Join [ ",", [ !Ref PublicSubnet1, !Ref PublicSubnet2 ]]
PrivateSubnets:
Description: A list of the private subnets
Value: !Join [ ",", [ !Ref PrivateSubnet1, !Ref PrivateSubnet2 ]]
PublicSubnet1:
Description: A reference to the public subnet in the 1st Availability Zone
Value: !Ref PublicSubnet1
PublicSubnet2:
Description: A reference to the public subnet in the 2nd Availability Zone
Value: !Ref PublicSubnet2
PrivateSubnet1:
Description: A reference to the private subnet in the 1st Availability Zone
Value: !Ref PrivateSubnet1
PrivateSubnet2:
Description: A reference to the private subnet in the 2nd Availability Zone
Value: !Ref PrivateSubnet2
NoIngressSecurityGroup:
Description: Security group with no ingress rule
Value: !Ref NoIngressSecurityGroup4. ECS Cluster and Service Configuration
- ECS clusters: Create two ECS clusters: one in the Test account and one in the Production account.
- Service and task definitions: Create ECS services and task definitions in the Test Account using new-ecs-test-infra.yaml CloudFormation templates.
Parameters:
privatesubnet1:
Type: String
privatesubnet2:
Type: String
Resources:
ECSService:
Type: AWS::ECS::Service
# DependsOn: HTTPListener
# DependsOn: HTTPSListener
Properties:
LaunchType: FARGATE
Cluster: new-cluster
DesiredCount: 0
TaskDefinition: new-taskdef-anycompany
DeploymentController:
Type: CODE_DEPLOY
HealthCheckGracePeriodSeconds: 300
SchedulingStrategy: REPLICA
NetworkConfiguration:
AwsvpcConfiguration:
AssignPublicIp: DISABLED
Subnets: [!Ref privatesubnet1 , !Ref privatesubnet2]
LoadBalancers:
- TargetGroupArn: arn:aws:elasticloadbalancing:us-east-1:487269258483:targetgroup/TargetGroup1/6b75e9eb3289df56
ContainerPort: 80
ContainerName: anycompany-test- Create ECS services and task definitions in the Test account using new-ecs-prod-infra.yaml CloudFormation templates.
Parameters:
privatesubnet1:
Type: String
privatesubnet2:
Type: String
Resources:
ECSService:
Type: AWS::ECS::Service
# DependsOn: HTTPListener
# DependsOn: HTTPSListener
Properties:
LaunchType: FARGATE
Cluster: new-cluster
DesiredCount: 0
TaskDefinition: new-anycompany-prod
DeploymentController:
Type: CODE_DEPLOY
HealthCheckGracePeriodSeconds: 300
SchedulingStrategy: REPLICA
NetworkConfiguration:
AwsvpcConfiguration:
AssignPublicIp: DISABLED
Subnets: [!Ref privatesubnet1 , !Ref privatesubnet2]
LoadBalancers:
- TargetGroupArn: arn:aws:elasticloadbalancing:us-east-1:608377680862:targetgroup/TargetGroup1/d18c87e013000697
ContainerPort: 80
ContainerName: anycompany-test
5. CodeDeploy Blue/Green Deployment
- CodeDeploy configuration: Configure CodeDeploy for Blue/Green deployments.
- Deployment groups: Create specific deployment groups for each environment.
- Deployment configurations: Configure deployment configurations based on your requirements.
6. Notification Setup (SNS)
- SNS configuration: Manually create an SNS topic for notifications during the deployment process.
- Notification content: Configure SNS to send notifications for manual approval steps in the deployment pipeline.
Pipeline and Deployment
1. Source Stage
CodePipeline starts with the source stage, pulling Docker images from the CodeCommit repository.
2. Build Stage
The build stage involves building and packaging the Docker images and preparing them for deployment.
3. Deployment to Development
Upon approval, the pipeline deploys the Docker images to the ECS cluster in the Development account using a Blue/Green deployment strategy.
4. Testing in Development
The deployed application in the Development environment undergoes testing and validation.
5. Deployment to Test
If testing in the Development environment is successful, the pipeline triggers the deployment to the ECS cluster in the Test account using the same Blue/Green strategy.
6. Testing in Test
The application undergoes further testing in the Test environment.
7. Manual Approval
After successful testing in the Test environment, the pipeline triggers an SNS notification and requires manual approval to proceed.
8. Deployment to Production
After the approval, the pipeline triggers the deployment to the ECS cluster in the Production account using the Blue/Green strategy.
9. Final Testing in Production
The application undergoes final testing in the Production environment.
10. Completion
The pipeline completes, and the new version of the application is running in the Production environment.
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve explored the strategic approach to deploying Docker images across multiple AWS accounts using a combination of ECS, CodePipeline, CodeDeploy, and the reliability of Blue/Green deployment strategies, all through the power of AWS CloudFormation. This methodology not only enhances security and operational efficiency but also provides a scalable infrastructure capable of supporting growth. By following the steps outlined, organizations can fortify their deployment processes, embrace the agility of Infrastructure as Code, and maintain a robust and adaptable cloud environment.
Implementing this guide's recommendations allows businesses to optimize costs by utilizing AWS services such as Fargate and embracing DevOps practices. The Blue/Green deployment strategy minimizes downtime, ensuring resources are utilized efficiently during transitions. With a focus on DevOps practices and the use of automation tools like AWS Code Pipeline, operational overhead is minimized. CloudFormation templates automate resource provisioning, reducing manual intervention and ensuring consistent and repeatable deployments.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments