Maximizing Business Benefits: Building Microservices Architecture in Azure
The Azure platform offers managed services, infrastructure, and end-to-end developer tools that can be used to create microservices applications.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeTransitioning from monolithic architecture to microservices brings about significant advantages for businesses. While monolithic structures have their simplicity, they come with limitations such as complex updates, manual testing requirements, and difficulties in scaling. This is where microservices shine, offering a more efficient way to develop, protect, and market applications.
According to a report by Nginx, 36% of commercial organizations have already adopted microservices, with another 26% exploring their potential. Microservices, since their launch in 2011, have gained rapid acceptance across various industries and company sizes.
Microsoft defines microservices as an architectural strategy where each fundamental function or service is built and deployed independently. Microservices are loosely coupled, allowing components to work independently. If one component fails, it doesn't lead to the failure of the entire app, enhancing overall productivity.
Benefits of Microservices
- Agility: Microservices enable updating features without redeploying the entire application, providing agility in development.
- Small teams: Compact enough for small teams to build, test, and deploy, promoting agility over large, dispersed teams.
- Technology blend: Teams find it easy to learn new technologies that align with their software or application needs.
- Fault isolation: Individual microservices' failure doesn't affect the entire program, as they run independently, handling errors effectively.
- Scalability: Microservices offer greater flexibility in scaling compared to complete programs, optimizing resource utilization.
- Data isolation: Changes in a single microservice are simpler than altering an entire program, facilitating easy schema upgrades.
Steps for Building Microservices in Azure
Domain Analysis
Clearly outlining the roles and responsibilities of each subsystem within the microservices structure is essential to prevent concealed dependencies or close connections between services.
Microsoft emphasizes that microservices should primarily focus on business functions, avoiding involvement in technical tasks such as data access, analytics, or communications. The Azure design pattern encourages users to employ a domain-driven design (DDD) framework in defining the business challenge, often referred to as the "bounded context," that a microservice aims to address. Each microservice should be developed with a distinctly defined and constrained context, independent of reliance on other microservices.
Azure Compute Options
Azure presents three computing options for microservices, each presenting distinct advantages and disadvantages:
Service Orchestrator—Leveraging Azure Service Fabric
This option provides highly scalable collections, functioning as high-performance, scalable cloud applications resembling standalone computer applications. It is particularly suitable for developing stateful services.
Container Orchestrator—Employing Azure Kubernetes Service
This choice facilitates efficient resource segregation among various workloads and seamless mobility between physical resources. It is ideal for creating microservices with high scalability and reliability requirements.
Function-As-A-Service—Utilizing Azure Functions
This option abstracts infrastructure management, leading to reduced operating costs in various scenarios. It is the most fitting selection for small services handling streaming events.
API Designing
Several key considerations should be taken into account when crafting APIs for your microservices architecture:
REST vs. RPC
In the realm of public APIs, prioritize REST over HTTP, reserving RPC for internal APIs. RPC boasts swift serialization and the largest payload size, making it preferable for back-end APIs that facilitate microservices connections. To maintain a streamlined communication process and avoid noisy APIs, strive to minimize communication.
Languages
Note that REST APIs are versatile and support any language, whereas RPC API frameworks are restricted to Java, Python, C++, and C#. Be mindful of these language limitations when selecting the appropriate API framework for your microservices.
The Formal Definition of APIs
For seamless integration with automatically generated client code, documentation, and security rules, it is essential to formally define your APIs. Open API is recommended for REST APIs, while the Interface Definition Language (IDL) is suitable for RPC APIs.
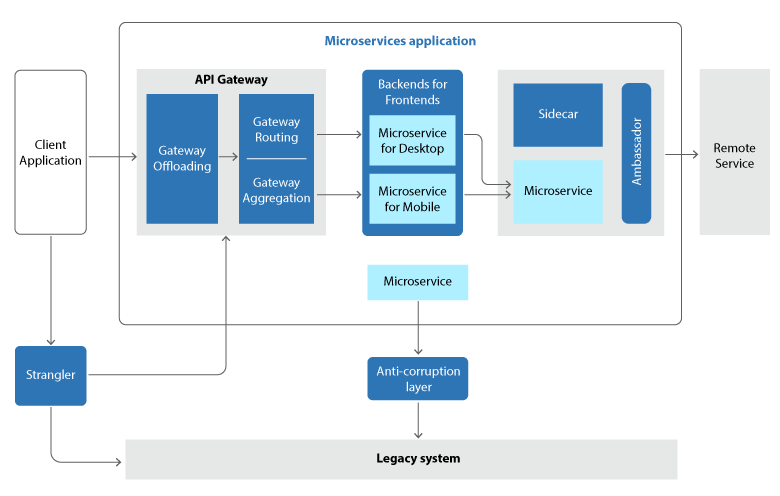
API Gateway
REST establishes a uniform interface based on HTTP verbs, fostering advancement and ensuring specific semantics for idempotency, side effects, and response codes. It governs stateless communication, enhancing scalability.
On the other hand, RPC is more focused on operations or commands, potentially leading to the design of chatty APIs as RPC interfaces resemble local method calls. Careful consideration is warranted when designing the interface to mitigate potential challenges.
Design Patterns
Select design patterns like Ambassador, Anti-corruption layer, Bulkhead, Back-ends for front-ends, Gateway aggregation, Strangler, and Sidecar.
The global microservices market size is projected to reach $8,073 million by 2026 at a CAGR of 18.6%.
— Allied Market Research
How Microservices Work With DevOps
Managing microservices can be complex due to the numerous moving parts involved. To simplify this, it's essential to incorporate DevOps, a collaborative approach that combines various tasks like IT operations, development, quality assurance, and security. This integration promotes flexibility and teamwork, allowing these different aspects to collaborate toward a common goal.
DevOps is especially beneficial when working with microservices because of their smaller size and easier deployment. This combination is often considered optimized for continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD). By deploying microservices with DevOps practices, you can efficiently operate within a microservices architecture, ensuring smoother deployment, monitoring, and lifecycle automation for better software development.
In summary, transitioning to a microservices architecture on Azure provides businesses with agility, smaller development teams, and flexibility. Azure offers compute options tailored to specific needs, including scalability and cost-effectiveness. When creating APIs, considerations such as REST vs. RPC and language support are crucial. Implementing DevOps alongside microservices streamlines deployment and fosters collaboration.
Extensive experience in microservices applications ensures a smooth migration with expertise in various technologies and aligns tools and components with your application development, maximizing the return on investment.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments