Minimal API Using .NET Core 6 Web API
This article will go over the purpose of minimal APIs in.NET Core 6, as well as how to implement them step by step.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWe will go over the purpose of minimal APIs in.NET Core 6, as well as how to implement them step by step.
Prerequisites
- .NET Core 6 SDK
- Visual Studio 2022
- SQL Server
Introduction
- Minimal APIs are used to create HTTP APIs with minimum dependencies and configuration.
- Mostly, it is used in microservices that have fewer files and functionality within a single file.
- But there are a few things that are not supported in minimal APIs, like action filters and built-in validation; also, a few more are still in progress and will get in the future by .NET Team.
Step-by-Step Implementation Using .NET Core 6
Step 1
Create a new .NET Core Web API.
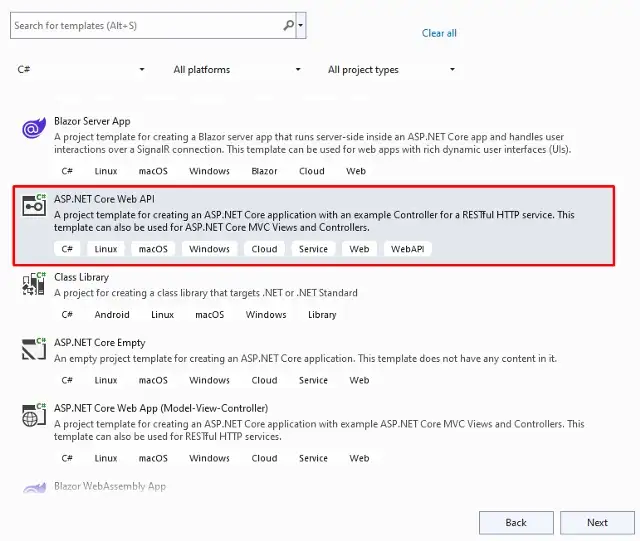
Step 2
Configure your project.
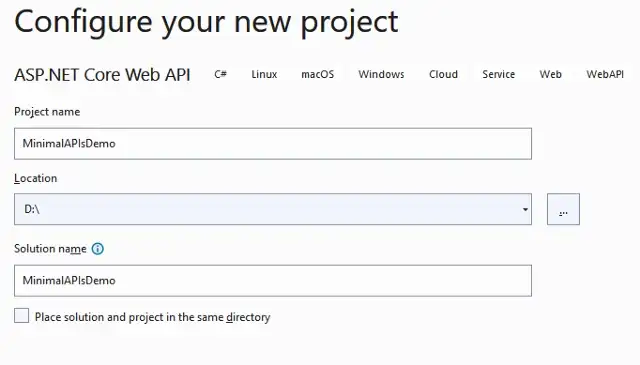
Step 3
Provide additional information as I showed below.
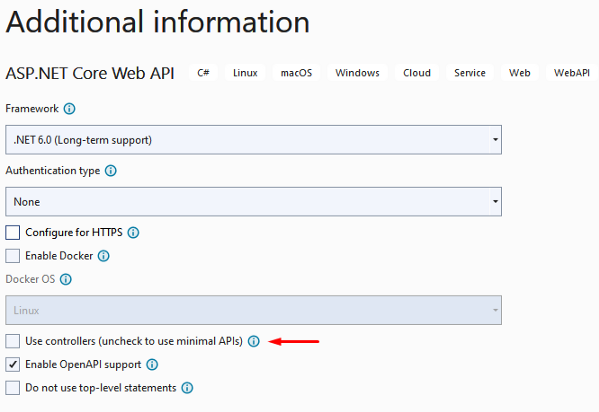
Step 4
Install the following NuGet packages.

Project structure:
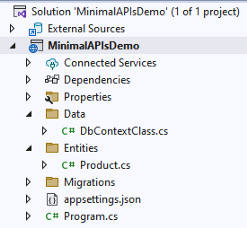
Step 5
Create a Product class inside the entities folder.
namespace MinimalAPIsDemo.Entities
{
public class Product
{
public int ProductId { get; set; }
public string ProductName { get; set; }
public string ProductDescription { get; set; }
public int ProductPrice { get; set; }
public int ProductStock { get; set; }
}
}Step 6
Next, create DbContextClass inside the Data folder.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using MinimalAPIsDemo.Entities;
namespace MinimalAPIsDemo.Data
{
public class DbContextClass : DbContext
{
protected readonly IConfiguration Configuration;
public DbContextClass(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder options)
{
options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"));
}
public DbSet<Product> Product { get; set; }
}
}Step 7
Register the Db Context service in the DI container inside the Program class, which is the entry point of our application.
builder.Services.AddDbContext<DbContextClass>();Step 8
Add the database connection string inside the app settings file.
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Data Source=DESKTOP;Initial Catalog=MinimalAPIDemo;User Id=sa;Password=database;"
}
}Step 9
Later on, add different API endpoints inside the Program class with the help of Map and specified routing pattern, as I showed below.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using MinimalAPIsDemo.Data;
using MinimalAPIsDemo.Entities;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddDbContext<DbContextClass>();
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
//get the list of product
app.MapGet("/productlist", async (DbContextClass dbContext) =>
{
var products = await dbContext.Product.ToListAsync();
if (products == null)
{
return Results.NoContent();
}
return Results.Ok(products);
});
//get product by id
app.MapGet("/getproductbyid", async (int id, DbContextClass dbContext) =>
{
var product = await dbContext.Product.FindAsync(id);
if (product == null)
{
return Results.NotFound();
}
return Results.Ok(product);
});
//create a new product
app.MapPost("/createproduct", async (Product product, DbContextClass dbContext) =>
{
var result = dbContext.Product.Add(product);
await dbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
return Results.Ok(result.Entity);
});
//update the product
app.MapPut("/updateproduct", async (Product product, DbContextClass dbContext) =>
{
var productDetail = await dbContext.Product.FindAsync(product.ProductId);
if (product == null)
{
return Results.NotFound();
}
productDetail.ProductName = product.ProductName;
productDetail.ProductDescription = product.ProductDescription;
productDetail.ProductPrice = product.ProductPrice;
productDetail.ProductStock = product.ProductStock;
await dbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
return Results.Ok(productDetail);
});
//delete the product by id
app.MapDelete("/deleteproduct/{id}", async (int id, DbContextClass dbContext) =>
{
var product = await dbContext.Product.FindAsync(id);
if (product == null)
{
return Results.NoContent();
}
dbContext.Product.Remove(product);
await dbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
return Results.Ok();
});
app.Run();Step 10
Run the following entity framework command to create migration and update the database.
add-migration "initial"
update-databaseStep 11
Finally, run your application.
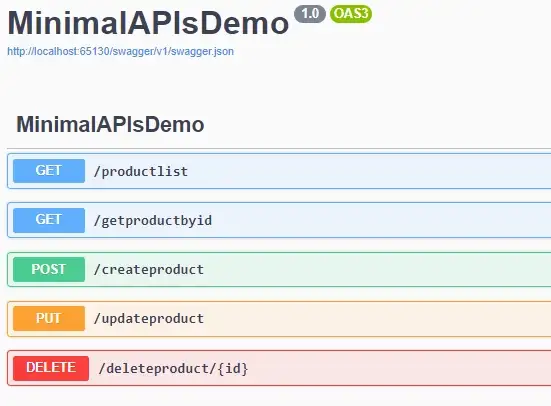
Conclusion
We discussed the minimal APIs and related topics using.NET Core 6 Web Application and Entity Framework with SQL Server.
Happy Learning!
Published at DZone with permission of Jaydeep Patil. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments