Observability Architecture: Financial Payments Common Observability Elements
Explore open-source cloud-based 011y financial payments architecture with a logical diagram that captures the elements of a successful payment solution.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeCloud-native technology has been changing the way payment services are architected. In 2020, I presented a series of insights from real implementations adopting open-source and cloud-native technology to modernize payment services. The series consisted of six articles and covered architectural diagrams from logical and schematic to detailed views of the various use cases uncovered.
The architectures presented were based on open-source cloud-native technologies, such as containers, microservices, and a Kubernetes-based container platform. The major omission in this series was to avoid discussing any aspect of cloud-native observability. This series will take a look at fixing that omission with an open-source standards-based cloud-native observability platform that helps DevOps teams control the speed, scale, and complexity of a cloud-native world for their financial payments architecture.
The introductory article (part one, linked in the "Series Overview" section at the conclusion of this post) covered the baseline architecture, defined the payments project, and shared the planning for this series in adding observability to the logical and physical architectures. In this article, we'll explore the logical diagram that captures the elements of a successful payment solution.
Background of Generic Architectures
Before diving into the common elements, please understand that this is a collection of identified elements uncovered in multiple working implementations. These elements presented here are, then, the generic common architectural elements identified and raised up to a generic architecture.
The intent was to provide architectural guidance and not in-depth technical details. The assumption is that you're smart and can figure out adapting it to your own architecture. You're more than capable of slotting in the technologies and components you've committed to in the past where applicable. The goal here is to describe generic components and outline a few specific cases enabling you to make the right choices when applying to your own architecture.
Feel free to comment or contact me directly with your feedback.
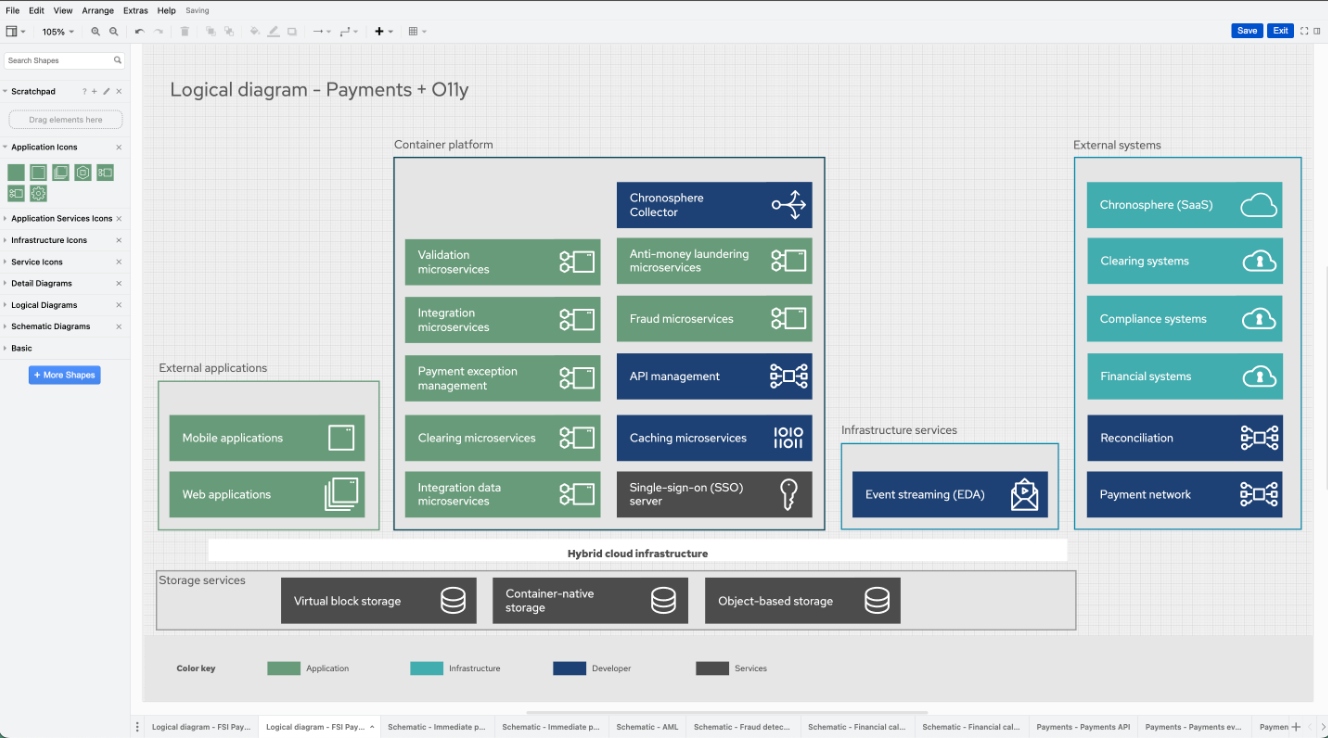
In the article "Payments Architecture - Common Architecture Elements," I toured the generic architecture and outlined the common elements of payments architecture. In this article, I'll focus on introducing the logical view of only the component layers where I'm adding cloud-native observability elements to the solution.
Container Platform
In this section, I want to focus on the new addition of cloud-native observability components in the container platform logical view.

Modern financial organizations are not only modernizing payments offerings with the use of cloud-native technologies and containers, but they are also finding out that cloud-native observability can be challenging for both their engineering and observability teams. They are not only building, testing, and deploying, but also having to contend with cloud-native complexity, data cardinality explosions, security, and more as they attempt to keep their solutions both running and cost-effective.
Within this view of the container platform, you find an addition - a Chronosphere Collector element - that ensures your microservices, applications, APIs, integration points, caching, and other services are providing their metrics and tracing data to your observability platform.
Using open source standards and protocols from the CNCF projects Prometheus and OpenTelemetry, it's collecting telemetry data and metrics data, and routing them to an external Chronosphere observability platform. This provides for a very easy transition for organizations that might have started their cloud-native observability journey using open-source projects and standards.
In upcoming articles in this series, I'll share the specific ways you can deploy and leverage the Chronosphere Collector element in a container environment. I'll also present several specific use cases and provide schematic diagrams that detail the physical architectures for those use cases.
External Systems

The elements found in the external systems capture the various regional or local needs for a payments solution. Many are not under the full hosted control of the financial organization, and this is where you find the SaaS solution for your observability needs.
Many organizations start off their cloud-native observability journey with do-it-yourself (DIY) solutions that, over time due to the payments solution success, grow into a resource burden in management, infrastructure, and observability data complexity.
The managed Chronosphere observability platform allows you to host your cloud-native observability needs, unplugging from your DIY infrastructure, and redirecting your open-source standards ingestion of metrics and telemetry data. Your engineering and observability teams are still using the same open-source tooling, query languages, and visualization that they are well versed in from their experiences with CNCF projects such as Prometheus and OpenTelemetry.
Using the Payments Project
The architecture collection provided insights into all manner of use cases and industries researched between 2019-2022. The architectures each provide a collection of images for each diagram element as well as the entire project as a whole, for you to make use of as you see fit.
If we look at the financial payments project, you'll see a table of contents allowing you to jump directly to the topic or use case that interests you the most. You can also just scroll down through each section and explore at your leisure.
Each section provides a short description covering what you see, how it's important to the specific payments topic listed, and a walk through the diagram(s) presented. You can download any of the images to make use in any way you like. At the bottom of the page, you will find a section titled Download Diagrams.
If you click on the Open Diagrams link, it will open all the available logical, schematic, and detailed diagrams in the diagram tooling we used to create them. This makes them readily available for any modifications you might see fit to make for use in your own architectures, so feel free to use and modify them!
Finally, there is a free online beginners guide workshop available focused on using diagram tooling, please explore to learn tips and tricks from the experts.
Series Overview
The following overview of this o11y architecture series on adding cloud-native observability to your financial payments architecture can be found here:
- Financial payments introduction
- Financial payments common observability elements (this article)
- Adding observability to immediate payments example
- Adding observability to financial calculations example
Next in this series, adding cloud-native observability to an immediate payments example.
Published at DZone with permission of Eric D. Schabell. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments