Okta as Code: Identity Management in the Cloud Native Era
Okta has become the de facto way to manage administrative access to digital resources, and this is why it should be managed as code, like all cloud resources.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWe have previously written posts on how to manage uncodified legacy apps on different platforms like AWS. In this post, we'd like to look at the very popular Okta platform, which provides some of the largest companies in the world with cloud-based identity and access management (IAM) for secure authentication and authorization for applications, devices, and users.
Okta is likely the most popular choice for organizations that need to manage access to their digital resources across multiple applications and environments, as it provides a range of features that make it popular for authentication and authorization, such as:
- Single sign-on (SSO)
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- User management
- Integration with a wide range of APIs and SDKs.
In this post, we'd like to dive into why managing Okta configuration as code, like any other cloud application, should be a best practice. The diversity of challenges codifying your Okta will help you overcome, and how to get started migrating your manual config to as-code config in Okta.
Manually Configuring Okta Gone Wrong
Okta is a forward-thinking cloud-based IAM platform and was built with extensible APIs to enable it to align with IaC best practices. However, the teams that usually manage Okta implementations are largely from the IT domain and have fewer DevOps. Either are less familiar with this approach to configuring Okta or don't have the domain expertise to do so.
Let's get started by going through some of the challenges Okta-as-Code can help overcome and good ways to get started with codifying your Okta operation.
Policy as Code for Okta: Misconfiguration Prevention
Like any other cloud asset, Okta, too, can be prone to human misconfigurations and errors, which is why the world of cloud and containers has endless amounts of tools to help identify and mitigate such errors before being deployed to production. However, since Okta is often manually configured, there aren't even the same safeguards for rollback, history tracking, revisions, and more.
By configuring Okta manually and not as code, you lose the opportunity to apply CI/CD to your code, PR/MR workflows, gating, and the guardrails available in these processes for reviewing your code, ensuring its quality, and then deploying to production. There are countless horror stories on the internet of manual configurations gone wrong, with no ability to roll these back or recover the previous state when manually configured. Even Okta, due to its high level of security, does not have any way to recover the accounts of admins who mistakenly deploy misconfigurations that cannot be reverted through git practices.
Once you have defined policy best practices in your organization, it is important to apply these globally to your entire cloud and SaaS-based operation, whether it's DevOps tools or IAM platforms. This is where IaC can help level up your Okta operation.
Leveraging IaC for your Okta configuration will enable you to gain the known benefits Git makes possible, including history tracking, change management, revision approval workflows, and CI/CD gating for your Okta configurations. In addition to this, you can take this one step further and apply the relevant policies to your code in your CI/CD pipelines, fail/pass build based on configuration checks, and much more before deploying to production.
One more critical inherent value made possible through IaC is the ability to create a backup of your configuration in Git. Aside from change management, this can also be a distributed, highly-available form of disaster recovery in the event of a ransomware attack or a hostile takeover of the admin account, which can reduce stress in a high-stress scenario.
ClickOps Doesn't Scale: IaC to the Rescue
Once you choose to configure your Okta as code, there are immediate benefits you derive in the form of automation, on top of the safety and guardrails these make possible. In addition, as noted above, Okta comes with out-of-the-box SSO, MFA, user management, and integration with third-party software.
Let's provide a quick overview of how this works.
For SSO, Okta enables users to authenticate themselves once and gain access to multiple applications without the need to enter separate credentials for each one. This reduces the risk of weak or reused passwords and simplifies the user experience.
In addition, most large enterprises today require at the very least 2FA, if not MFA, for accessing company resources. Okta supports a range of MFA methods, including SMS, voice, push notifications, hardware tokens, and biometric factors. This adds an extra layer of security to the authentication process, making it more difficult for attackers to gain access to sensitive resources.
When it comes to user management, Okta allows administrators to manage user accounts and permissions across multiple applications and environments from a single console. This simplifies the process of provisioning and de-provisioning users and helps ensure that access is granted and revoked in a timely manner.
Finally, Okta provides a range of APIs and SDKs that make it easy to integrate with other applications and platforms. This allows organizations to leverage their existing technology investments while adding an additional layer of security to their authentication and authorization processes.
As you can see, that is a very wide range of mission-critical capabilities that security-minded enterprises today require to be able to properly manage access and authorization at scale. However, doing this manually for just tens of users sounds ludicrous, so let's not talk about hundreds, thousands, and even tens of thousands of employees.
By codifying your Okta config, you can also apply automation to your processes around onboarding, revising, and removing users, changing their access to different applications, adding applications, and removing OAuth access, just to name a few of the common activities constantly performed by administrators on a daily basis for organizational asset safekeeping. Without automation, this becomes a nearly impossible feat––and also loses the ability to track changes and history over time or any other critical information with regards to managing critical company assets.
Okta Config as Code in Action
All of this is why the Okta Terraform provider has millions of all-time downloads and tens of thousands monthly. In the example below, we'll demonstrate how you can quickly take your manual Okta config and convert it to Terraform code to be able to have the power of Git coupled with the automation your cloud-based IAM requires.
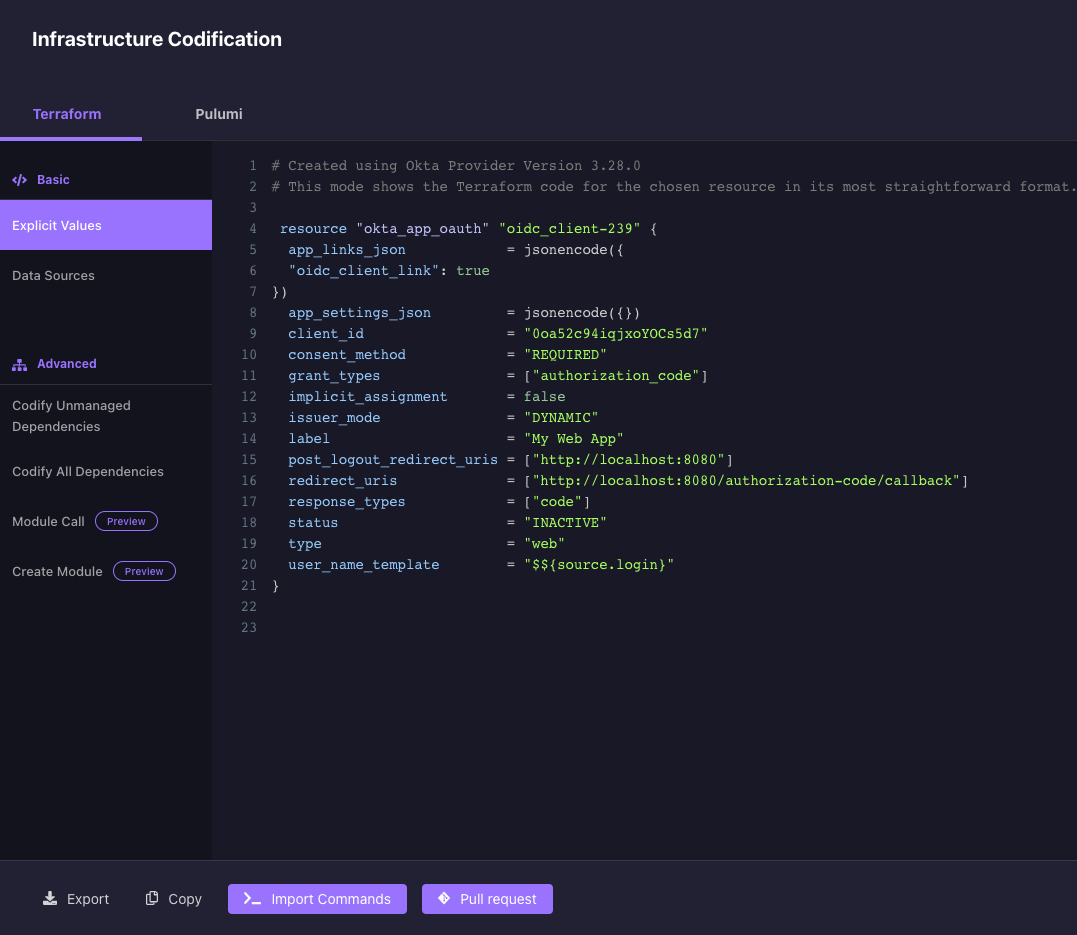
Treat Your Okta Like All Your Cloud Assets
Overall, Okta's popularity for authentication and authorization is driven by how it changed cloud-based IAM for the better with its ease of use, flexibility and integration features for the diversity of applications used today, and robust security features. By helping organizations improve their security posture and streamline their access management processes, it has become the nearly de facto tool for any organization that needs to manage access to their digital resources.
With such scale and adoption, Okta can benefit from applying the same as-code best practices from other disciplines and cloud worlds, which is possible due to its open APIs that are quite powerful. Many organizations have learned to leverage Terraform to codify their Okta configurations, and those who have not yet should most certainly get started with doing so. Okta as code will enable greater safety, guardrails, recovery, tracking, and change management alongside greater scale and automation. With today's tooling, Terraform providers, and more, you can quickly migrate your existing configurations to code, providing your organization with greater confidence and security in your IAM operation.
Published at DZone with permission of Eran Bibi. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments