Order in Chaos: Python Configuration Management for Enterprise Applications
Explore a systematic approach to dealing with configurations in Python including tools, best practices, and real-world examples.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeImportance of Configuration Management
In enterprise applications, configuration management is the most underrated operator that keeps everything integrated and running smoothly. It acts as a backstage manager ensuring all lights are in place, theatrical queues are ready, and the show can go on without a hiccup. Especially, while dealing with multi-environment deployments, with tight-knit CI/CD processes, one wrong configuration can pose an application-wide shutdown risk.
Multi-environment enterprise applications carry their own set of challenges and managing configs is no exception. We all have heard the famous “But, it was working on my machine!” excuse more times than daily salutations.
In a large-scale Python application, inconsistent, or poorly managed configurations can lead to:
- Downtime: One misconfigured environment variable can ensure an application-wide shutdown!
- Bugs: Inconsistent environment-specific configurations can and will make sure you lose sleep trying to debug a “403: Forbidden” error.
- Developer headaches: All of the above costs a lot of resources.
In conclusion, without proper configuration management, applications can end up in a soup no one wants to touch.
Strategizing Configuration Management: 3 Golden Rules
Following these 3 principles can help you build a more efficient and robust configuration management strategy:
1. Don’t Repeat Yourself (DRY)
To ensure consistency and easy maintainability, centralize your configurations. If different components of your application use the same value that has scattered initializations across your codebase, it is a good candidate for a centralized configuration key-value pair.
2. Keep It Simple
Configurations should be as straightforward as possible. If someone needs a doctorate to understand configuration files, you’re doing it wrong. Maintainability is driven by simplicity.
3. Keep It Secure
Never use hardcore sensitive information like API Keys, passwords, or PII data in your code. Always use environment variables (at the very least) or dedicated secrets management tools (recommended) like Secrets Manager/HashiCorp Vault to keep this information safe.
Python’s Jukebox of Config Management Tools
Python offers various config management tools in the form of various libraries and modules to make lives easier.
- configparser: A go-to for managing Windows-like INI files which is simple, effective, and great for small-scale applications. The main downside is that there is no type safety. In simple terms, it means every value you provide in the INI file, is read as a string.
- json and YAML: JSON and YAML, being more human-readable, are perfect for complex applications with nested configurations. Just like INI files, JSON and YAML do not ensure type safety/validations.
- dotenv: Uses .env files for managing environment variables. The only downside here is that everything is stored in plaintext. This is a likely candidate for medium-sized applications.
- Settings Class - Pydantic and dynaconf:
pydanticoffersSettingsclass which endures validation out of the box, ensuring the configurations are always type-checked and validated.dynaconfoffers an additional advantage by allowing multi-layered configurations with support for multiple file formats
Writing a Sample Configuration With the Settings Class
See the following sample to define the various settings or configuration parameters and their validations.
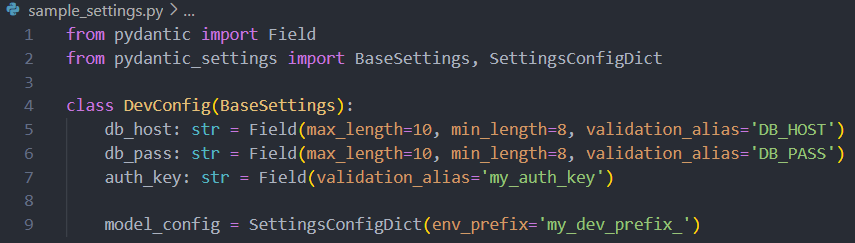
When creating a model that inherits from BaseSettings, the model initializer will make an attempt to determine the values of any fields not provided as keyword arguments by accessing the environment. In cases where the corresponding environment variable is not set, default values will be utilized.
This makes it easy to:
- Create a clearly defined, type-hinted application configuration class.
- Automatically read modifications to the configuration from environment variables.
- Manually override specific settings in the initializer where desired (e.g., in unit tests).
As you may see here, we define the Config class but do not assign any values. The reason is that we have the flexibility here to read from either an environment file or read it from a much more secure cloud-based secrets management tool.
Conclusion
Here is a small comparison table to help you choose the best fit for your needs.
| Tool | Suited For | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
configparser |
Simple INI style configs |
Small applications with straightforward settings |
| JSON/YAML |
Complex, nested configurations |
Applications with a need for human-readable and easy-to-manage configurations across multiple environments |
dotenv |
Environment variable management |
Application that prefers the old way of environment variable-specific config management |
|
Pydantic |
Type-safe, validated configs with environment variable support |
Large-scale enterprise applications that require robust validations with multi-environment support |
|
|
Multi-layered configs with support for various file formats |
Projects that require extensive config management with support for multiple file formats |
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments