Protecting Your React.js Source Code With Jscrambler
Source code protection is recommended by the OWASP and NIST as a way to prevent reverse-engineering and tampering attacks. Here's how to protect the source code of React.js apps.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeReact.js is one of the most popular JavaScript libraries. The 2019 "State of JavaScript" survey puts React as the front-end framework of choice, with 72% of responders stating that they have used it and would use again.
With its elegant programming style, rich package ecosystem and good documentation, React has found its way into powering the applications of large enterprises. Specifically, the developer survey found that 18% of responders who are using React work for companies with over 1000 employees.
As we know, the very nature of JavaScript means it can't be encrypted and can easily be accessed on the client-side or even tampered with.
Because React powers enterprise-grade applications, it requires an enterprise-grade security solution such as Jscrambler.
This tutorial will explain how to integrate Jscrambler seamlessly into React's build process in just a few minutes. You'll learn how to protect your React source code with the most advanced polymorphic obfuscation techniques, along with code locks and self-defensive capabilities.
Pre-Requisites
Only two things are needed to properly integrate Jscrambler into the React build process: creating a React app and configuring Jscrambler. We will highlight both below.
How to Create a React Application
For the purposes of this tutorial, we will be using a create-react-app boilerplate app. To get started, we will need to install it using npm:
xxxxxxxxxx
npm i -g create-react-app
This will download create-react-app and install it globally with all the required dependencies for the latest React version.
Now, we're ready to create our boilerplate app, which we'll use as the basis for this tutorial. Start by creating this new app with the following command:
xxxxxxxxxx
create-react-app react-jscrambler-boilerplate
After the installation finishes, we can run our newly created boilerplate app:
xxxxxxxxxx
cd react-jscrambler-boilerplate
npm start
Our new React app will run on development mode and appear at localhost:3000. Check if everything is in place before moving to the next step. For further help on getting started with create-react-app, see the official documentation.
The base project structure of our React application is as follows:
xxxxxxxxxx
react-jscrambler-boilerplate/
|-- package-lock.json
|-- package.json
|-- yarn.lock
|-- build/
| |-- static/
| | |-- css/
| | |-- js/
| | |-- media/
|-- node_modules/
|-- public/
|-- src/
package.jsoncontains all the configurations which are related to npm such as dependencies, version and scripts.The
srcdirectory features all the source code of the application. The sources are then built and packed into thebuilddirectory. This is where our protected HTML and JavaScript files will be placed after the build.
How to Configure Jscrambler
If you haven't created a Jscrambler account yet, be sure to do so before moving forward.
All of Jscrambler's configuration will reside inside a single file: .jscramblerrc. As such, we will need to create this file to specify which transformations we wish to use.
The quickest way to achieve this is via the Jscrambler Web App. Once there, create a new app. Now, in the Application Modes tab, select the Language Specifications and application type. Next, select the transformations you want (check the Templates and Fine-Tuning tabs). In this tutorial, we'll be selecting the Obfuscation template. If you need help with these steps, please refer to our guide.
Now, we simply have to download a JSON file with all this configuration, which will be used only for quickly getting the required settings.
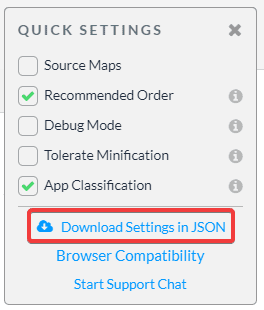
Now, let's create a new file named .jscramblerrc on the React project’s root folder. Open the jscrambler.json file we just downloaded and copy all its contents to the .jscramblerrc file. After that, we just have to add two new sections to .jscramblerrc, which are filesSrc and filesDest (see below). Your final .jscramblerrc file should look like this:
xxxxxxxxxx
{
"keys": {
"accessKey": <ACCESS_KEY_HERE>,
"secretKey": <SECRET_KEY_HERE>
},
"applicationId": <APP_ID_HERE>,
"filesSrc": [
"./build/**/*.html",
"./build/**/*.js"
],
"filesDest": "./",
"params": [
{
"name": "whitespaceRemoval"
},
{
"name": "identifiersRenaming",
"options": {
"mode": "SAFEST"
}
},
{
"name": "dotToBracketNotation"
},
{
"name": "deadCodeInjection"
},
{
"name": "stringConcealing"
},
{
"name": "functionReordering"
},
{
"options": {
"freq": 1,
"features": [
"opaqueFunctions"
]
},
"name": "functionOutlining"
},
{
"name": "propertyKeysObfuscation"
},
{
"name": "regexObfuscation"
},
{
"name": "booleanToAnything"
}
],
"areSubscribersOrdered": false,
"applicationTypes": {
"webBrowserApp": true,
"desktopApp": false,
"serverApp": false,
"hybridMobileApp": false,
"javascriptNativeApp": false,
"html5GameApp": false
},
"languageSpecifications": {
"es5": true,
"es6": false,
"es7": false
},
"useRecommendedOrder": true,
"jscramblerVersion": "6.<X>"
}
Because we got this information directly via the Jscrambler Web App, our accessKey, secretKey and applicationId fields are already filled. If you wish to retrieve them manually, refer to our guide.
It's important to note that the params section specifies the transformations that will be used to protect your React app. These can be hand-picked by you, by selecting them in the Web App or setting them manually. You can find documentation on all the available transformations here.
You can also change filesSrc to match the files you need/want to protect. For our example — and all React apps — we recommend protecting the .html and .js files. Certainly, with a better understanding of the project, you may identify what’s critical and essential protecting.
By using filesDest: './', the files we send to protect will be overwritten by their protected version.
Integrating Jscrambler in the Build Process
Using the CLI is likely the most common way of generating your build. We will use our boilerplate app to showcase how to integrate Jscrambler into the build process.
The first step of our integration with Jscrambler is installing the Jscrambler API Client. Simply run:
xxxxxxxxxx
npm i jscrambler --save-dev
To integrate Jscrambler in our application's build process via the CLI, we need to create a CLI hook in the scripts section of package.json. The section should look like this:
xxxxxxxxxx
"scripts": {
"start": "react-scripts start",
"build": "react-scripts build && jscrambler",
"test": "react-scripts test",
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
},
The specific "build": "react-scripts build && jscrambler" hook will trigger the jscrambler command after the build process is finished.
In order for this command to be executable, we need to make sure that the .jscramblerrc file that we created before is in our project's root folder.
We are now ready to protect our code and build our application via the CLI:
xxxxxxxxxx
npm run build
This will create the protected production files on build/static/.
And you're done! Now all your HTML and JavaScript files are protected with Jscrambler against code theft and reverse-engineering. Remember that you can always fine-tune your protections to manage eventual performance hits. If that's the case, be sure to follow our tutorial.
Note: If you have ejected your project, you can also protect the files using the Jscrambler webpack plugin.
Testing the Protected React App
As a final step, let's check if the app is running successfully with the newly-protected source code. Start by installing the required dependencies:
xxxxxxxxxx
npm i -g serve
Next, let's simply deploy the app build files to a local development server:
xxxxxxxxxx
serve -s build
Now, as you should be able to see on the terminal, you can run this server on two ports. One which is publicly available, and another which is specific to your machine.
Open the provided URL and your app will start in the browser.
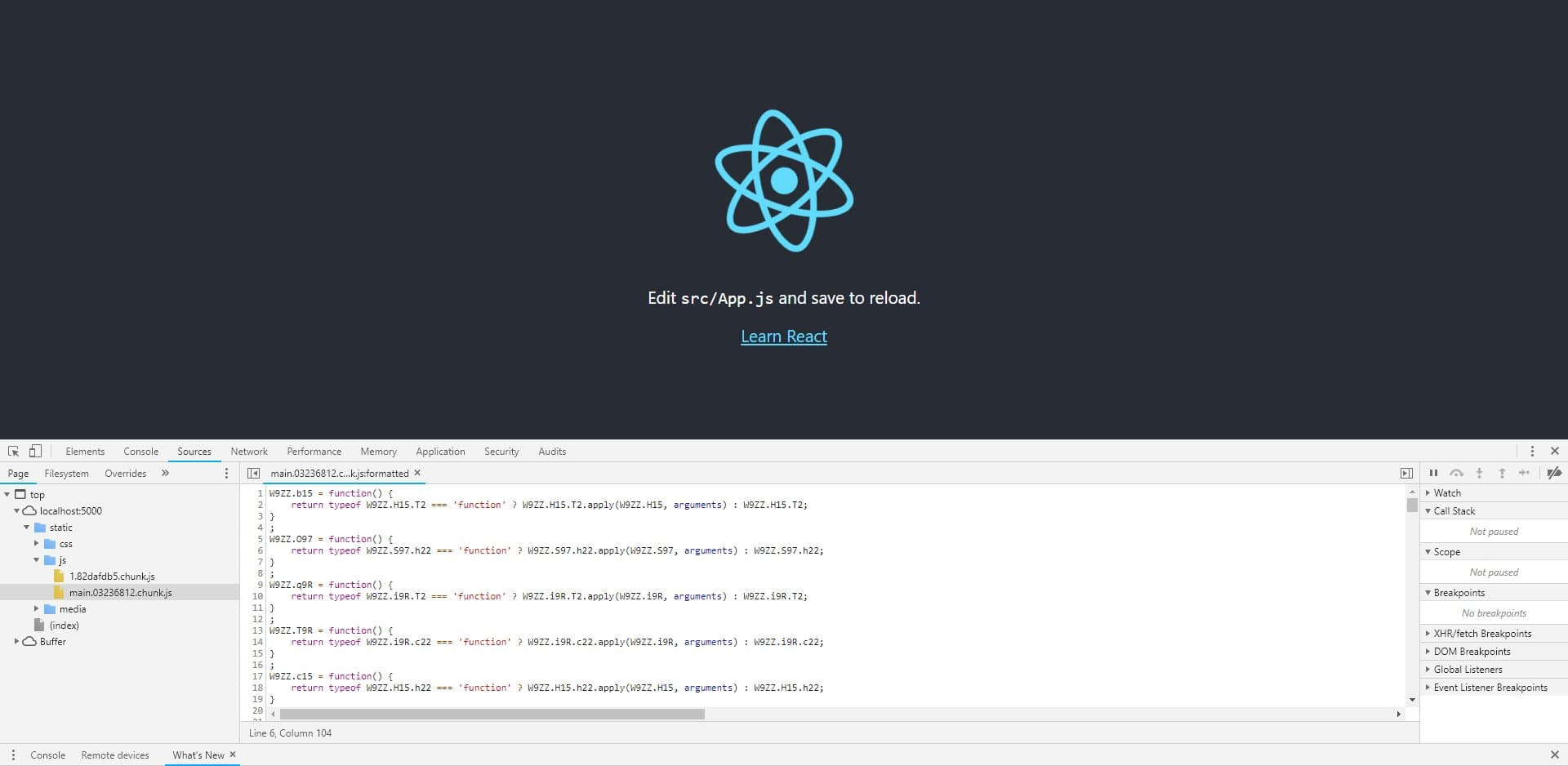
You can now check what your protected files look like. This can be achieved simply by opening the browser's debugger and opening the files from the "Sources" tab. The protected code should look like this:
Conclusion
There are no doubts that React is a crowd favorite, from individual developers to large enterprises.
If you're building React applications which have sensitive logic, want to prevent reverse-engineering, licensing violations, and tampering, a security solution such as Jscrambler is a must.
Integrating Jscrambler into React's build process is simple and enables protecting your code with the most sophisticated polymorphic obfuscation, code locks, and self-defensive capabilities.
Published at DZone with permission of . See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments