Spring Bean Lifecycle: Using Spring Aware Interfaces
Learn more about using Aware interfaces to access Spring bean lifecycle events.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
Spring Aware interfaces allow you to look into the inner workings of the Spring Framework. Through Spring Aware interfaces, you can access the Spring context, or Spring bean lifecycle events.
Your Spring beans might require access to framework objects, such as ApplicationContext, BeanFactory, and ResourceLoader. To gain access, a bean can implement one of the many Aware interfaces of the Spring Framework.
Want to learn more about various aspects of the Spring bean lifecycle? Check out this post: Working With Resources in Spring!
When a bean implements an Aware interface, the Spring Framework injects a particular framework object to the bean through a callback-style method. The object Spring injects depends on the interface which the bean implements. For example, if the bean implements the ApplicationContextAware interface, Spring will inject an ApplicationContext object into the bean.
In this post, we will learn about the Spring aware interfaces, particularly ApplicationContextAware, BeanFactoryAware, and BeanNameAware interfaces.
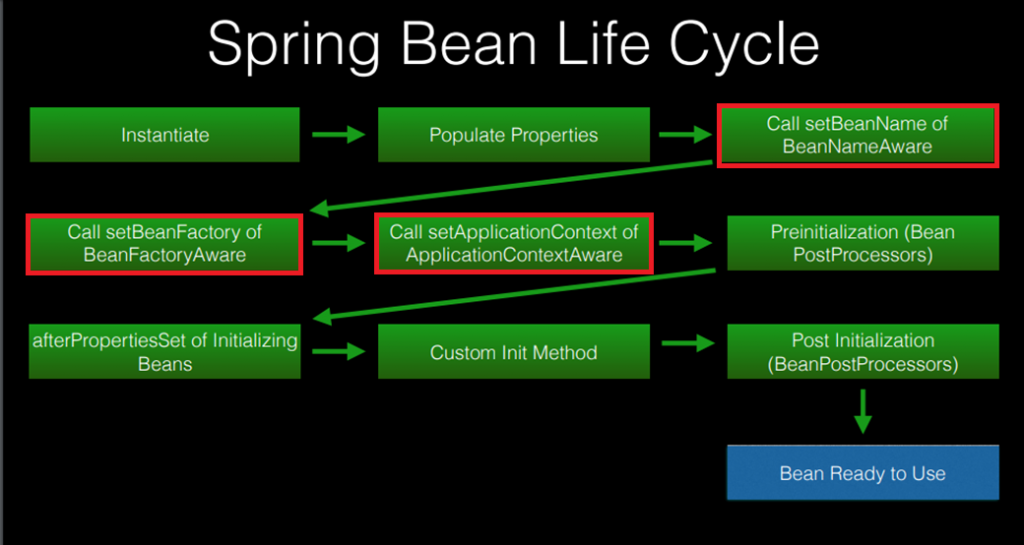
In the bean lifecycle, the Spring Framework calls the aware interface methods after populating bean properties and just before pre initialization with BeanPostProcessor.
The ApplicationContextAware Interface
In Spring beans, you might require access to the ApplicationContext. For example, if your bean needs to look up some other beans. Similarly, if your bean needs access to some application file resource in your bean or even publish some application events, you need access to the ApplicationContext.
Spring provides an ApplicationContextAware interface that allows beans access to the ApplicationContext. This interface provides a single setApplicationContext method.
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext)
throws BeansExceptionThe following code shows the use of ApplicationContextAware.
package guru.springframework.springawaredemo.awareimpls;
import guru.springframework.springawaredemo.domain.User;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
public class ApplicationContextAwareImpl implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
User user = (User) applicationContext.getBean("user");
System.out.println("User Id: " + user.getUserId() + " User Name :" + user.getName());
}
}The preceding code is of a bean that implements ApplicationContextAware. The code overrides the setApplicationContext() method to lookup another bean with the id user using the injected ApplicationContext.
The BeanFactoryAware Interface
Beans might need access to the bean factory that created it, say to call any service from the bean factory.
Should you need to obtain a reference to the bean factory, implement the BeanFactoryAware interface. This interface provides the setBeanFactory() method.
void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory)The preceding setBeanFactory() is a callback that supplies the owning factory to the bean instance.
Here is an example of a bean that implements the BeanFactoryAware Interface.
package guru.springframework.springawaredemo.awareimpls;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
public class BeanFactoryAwareImpl implements BeanFactoryAware {
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(beanFactory.getBean("user"));
}
}The BeanNameAware Interface
The BeanNameAware interface is implemented by beans that need access to its name defined in the Spring container. This interface provides the setBeanName() method.
void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory)The preceding setBeanFactory() is a callback that supplies the name of the bean.
Here is an example of a bean which implements the BeanNameAware Interface.
package guru.springframework.springawaredemo.awareimpls;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
public class BeanFactoryAwareImpl implements BeanFactoryAware {
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(beanFactory.getBean("user"));
}
}Summary
Although I covered only three, there are additional aware interfaces. The Aware API documentation provides complete details.
One interface I would like to specially mention is the ResourceLoaderAware interface. Implement this interface if a bean needs to load resources present in the classpath or file system. On implementing ResourceLoaderAware, your bean is notified of the ResourceLoader (typically the ApplicationContext) that it runs in. This is an alternative to a full ApplicationContext dependency via the ApplicationContextAware interface.
I’ll be writing a detailed post on ResourceLoaderAware that you can check out.
As an end note, I’m not particularly fond of the aware interfaces. Implementing them ties your application to the Spring Framework, thus inverting the whole inversion-of-control concept. In an ideal world, your application should not be aware of being managed by an ApplicationContext at all or tied to any framework objects.
Also, note that ApplicationContextAware is the legacy version that has been around at least since Version 2.0. @Autowired ApplicationContext applicationContext and @Inject ApplicationContext applicationContext are the newer mechanisms but they work in pretty much the same way. Although the newer ones require lesser typing of code, I’d probably go with ApplicationContextAware, because it semantically makes clear what it is about.
The source code for this post can be found here on GitHub.
Further Reading
Defining Bean Dependencies With Java Config in Spring Framework
Published at DZone with permission of John Thompson, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments