Trying to Understand How WhatsApp Uses Encryption
It turns out that the encryption used by WhatsApp is built on elliptic curves. They can be a little complicated to explain but this article contains excellent information about it.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
By now all of the security-minded users have upgraded to the current version of WhatsApp, which supports end-to-end encryption.
End to end encryption, as the name suggests is a way of encrypting communication between two parties such that a third party, or even Whatsapp themselves, cannot decrypt/read the communication.
For a while now, I have been trying to understand the algorithm from the white paper which Whatsapp has published and I apparently realized that explaining the algorithm in simple terms seems almost impossible.
The setup includes a handful of encryption keys. Like any other communication systems, the ‘signal’ protocol uses a combination of asymmetric and symmetric key cryptographic algorithms. The symmetric key algorithms ensure confidentiality and integrity whereas the asymmetric key cryptographic algorithms help in achieving the other security goals namely authentication and non-repudiation. In symmetric key cryptography, a single key is used for encryption of the data as well as decryption. In asymmetric key cryptography, there would be two separate keys. The data which is encrypted using the public key of a user can only be decrypted using the private key of that user and vice versa.
Whatsapp uses the Curve25519 based algorithm. The history of Curve25519 is worth noting as it was introduced after the concerns over allegations that certain parameters of the previously prevalent P-256 NIST standards have been manipulated by NSA for easier snooping. Elliptic Curve Diffie Hellman algorithm is a mathematical algorithm which helps two communicating entities to agree upon a shared secret without actually sending the actual keys to each other.
To understand the article and the method which they use, it is necessary to have a basic understanding of advanced cryptographic algorithms. So if you are not aware of ECDH, AES, SHA etc, this article may not entertain you. The following video by Robert Pierce beautifully explains the ECDH algorithm.
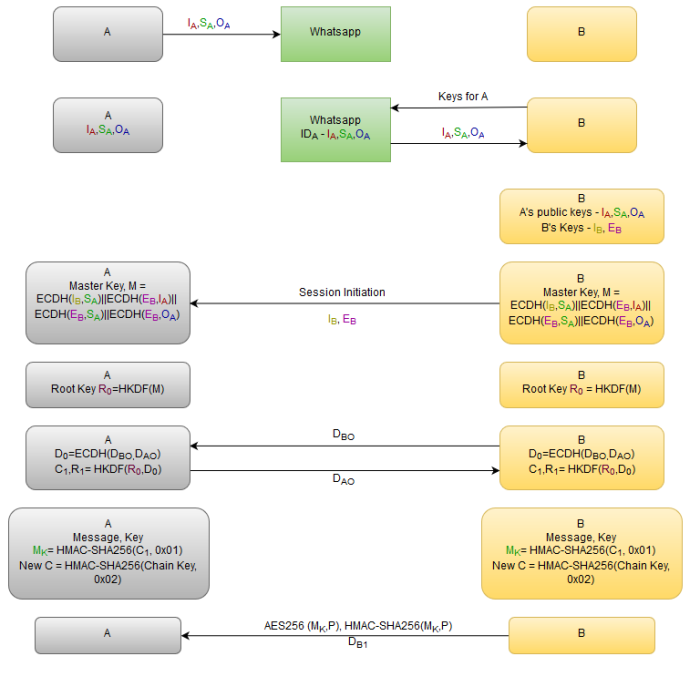
In the following flow chart, all the key exchanges which occur when a user installs WhatsApp up until a message is sent to another user. Message key is a one-time usable key and the process is repeated from the step where the new chain key is calculated.
Communicating Entities

Asymmetric Keys

Symmetric Keys/ Pseudo Random Numbers

Cryptographic Functions

Step By Step Process of Whatsapp End to End Encryption
Published at DZone with permission of Traven West, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments