Simplified Blockchain Part One: Theory
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeBlockchain in Two Words
You can interpret blockchain as a distributed database, each node of which is launched on the client side. All nodes synchronize (validate and confirm) all transactions among themselves. Every deployed smart contract (code and variables) stays there forever with its unique id. Initially, blockchain was created as a way to store information about sending/receiving money between clients. New blockchain systems are significantly different — they let users deploy and execute functions + variables, also known as smart contracts. Smart contracts turned these databases into real, stateful servers.
Classical Server vs Blockchain Network
To simplify your understanding of blockchain, check out the figure and table below:

| Classic Java EE server | Blockchain network | |
| Is it decentralized? | No. Can be clustered (but still not decentralized) | Yes it's decentralized and all nodes synchronize the same state. |
| Is it possible to redeploy artifacts? | Each component (java class eg jar/war/ear) can be redeployed | Every new component (smart contract) is persisted forever with it's unique hash. Every new deploy create new version of the component |
| What I need to do to hack the application? | Put troyan inside deployed component/crack database/social engineering (bride server administrator) | In the best case you need to replace (half + 1 node) |
| Can persiste a lot of data? | Yes, often servers tons of hdd/ram memory | Each node has to replicate all the data. Big size nodes became useless quickly. Rather looks like text/transaction storage |
| Is it possible to brut force security once you have source code? | Depends on security implementation. Often it's possible. | No chance. To brutforce regular Ethereum account private key - billion years |
Key Advantages of Blockchain
Code can be trusted:
1. Each transaction executed on blockchain being verified by (half + 1) node. To falsify it, you need to falsify more than half of the nodes. This is practically impossible.
2. Each contract (also known as a class in Java) has its unique hash and can't be redeployed. An executed contract is the right contract you execute.
3. All transactions (a.k.a. blocks) in blockchain have a specific hash that is compatible with the next and previous transactions. Quite similar to GIT. So no transaction can be injected somewhere in the middle.
So if we deploy the same code twice, we can see unique transaction hash and unique contract address.
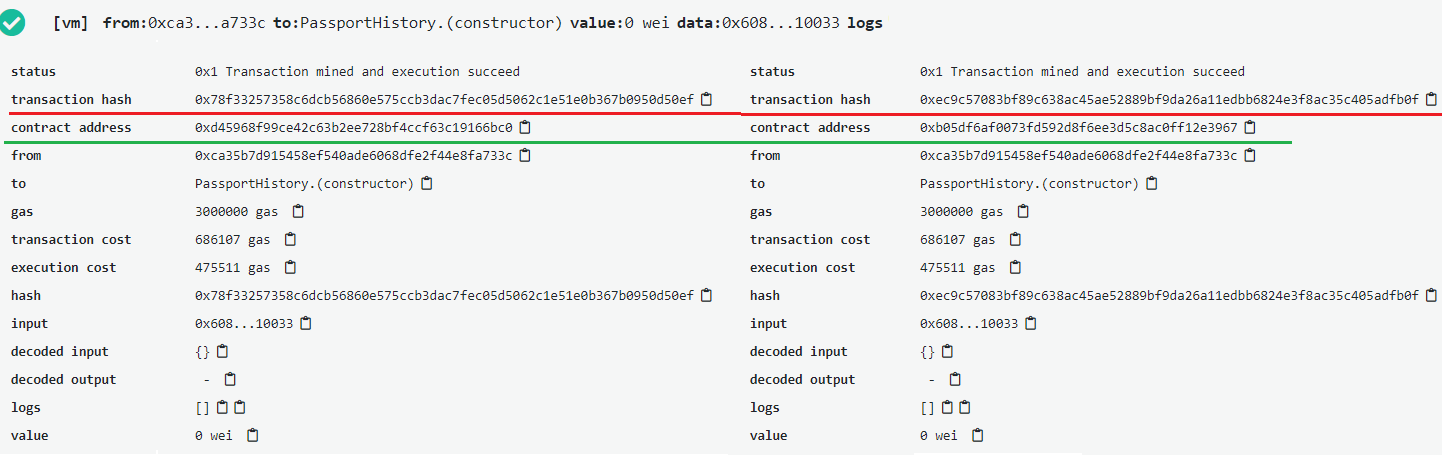
Access is invulnerable
Each contract is being executed by account (built in feature). Ethereum account key has 256 bit complexity. Brute force of such key takes more than a billions years.
When Blockchain Is Useful
Because of this, two advantages blockchain platforms can be used as trusted, incorruptible third-party player eg:
- Casino: blockchain protects casino by holding a bet and protect player from game falsification.
- Signing juridical contact: blockchain helps to sign contract by both sides in one single action and store that contract without any possible change. So you do not need the presence of a lawyer/realtor as evidence of the authenticity of the contract.
- Government systems: blockchain systems protected from any falsification (even bribed internal employees) and stays completely invaluable to attacks even if application been stolen.
Implementing Passport Office System on Blockchain
In Sweden, their national passport service is based on blockchain systems. Let's create the same simplified service using Ethereum in the next article.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments