What Is Quick Sort in C Programming?
Due to its popularity and popularity over other sorting algorithms, quick sorting is a frequently used sorting algorithm.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeDue to its popularity and popularity over other sorting algorithms, quick sorting is a frequently used sorting algorithm. It then divides an array into two groups, one containing elements smaller than a chosen pivot element and the other containing elements larger than the pivot. After that, the algorithm repeats this process for each partition until the entire array is sorted.
Any situation that calls for sorting can benefit from quick sorting, including database applications, scientific computing, and web applications. It is frequently used when a sizable dataset needs to be sorted quickly and efficiently. The following are some specific use cases where quick sort is frequently employed:
- Array sorting in programming languages like Python, Java, and C.
- Database management systems' database record sorting.
- Sorting large datasets for scientific computing applications like data analysis and numerical simulations.
- Organizing search results in online applications and shopping carts.
Characteristics
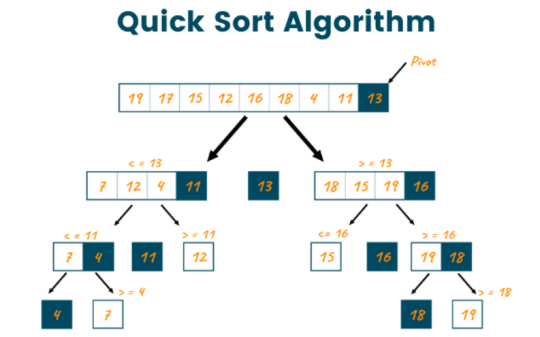
- According to a pivot element, which is typically the last element in the array, quick sort divides an array into two parts.
- The array is split into two partitions by placing all elements smaller than the pivot in one partition and all elements larger than the pivot in the other.
- This process is repeated by the algorithm for each division until the entire array is sorted.
- Quick sort has a worst-case time complexity of O(n2) if the data is already ordered or the pivot element is not carefully chosen.
Advantages
- Quick sort is effective for handling large datasets because of its fast average-case time complexity of O(nlogn).
- It is a straightforward algorithm that only requires a few lines of code to implement.
- Quick sort is appropriate for use on multicore and distributed systems because it is simple to parallelize.
- Because it uses in-place sorting, no additional memory is needed to store temporary variables or data structures.
Disadvantages
- If the data is already sorted or the pivot element is selected incorrectly, quick sort has a worst-case time complexity of O(n2).
- The relative order of equal elements in the sorted array is not guaranteed because it is not a stable sorting algorithm.
- Since it necessitates multiple passes through the data, quick sorting is not appropriate for sorting large datasets that do not fit in memory.
Conclusion
Quick sort is a well-liked and effective sorting algorithm that operates by dividing an array into two parts and carrying out the process iteratively on each partition until the entire array is sorted. It has an O(nlogn) average and best-case time complexity and an O(n2) worst-case time complexity. Despite having a higher worst-case time complexity than other sorting algorithms, quick sorting is frequently preferred because of its performance, simplicity, and ease of implementation.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments