Why Using Generative AI for OKRs Is Generally a Bad Idea
You may want to think twice before jumping on the AI hype train for your OKRs. Security concerns and algorithmic bias can cause your OKRs to cause more harm than good.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSetting objectives and key results (OKRs) is a powerful way to align an organization's efforts toward a common goal. However, as the amount of data and complexity of objectives increase, it can become challenging to set effective and achievable goals. One solution that has gained popularity in recent years is to use generative artificial intelligence (AI) to automate the OKR creation process. While this may seem like a convenient and efficient solution, it comes with significant security implications that organizations need to consider.
Generative AI for OKRs: The Basics
Generative AI is a type of machine learning algorithm that can create new data from existing data. In the context of OKRs, this means that the AI can generate new objectives and key results based on the historical data and patterns it has learned from an organization's past performance. This can save time and effort for managers who would otherwise need to manually analyze data and create objectives based on their insights.
The Potential Risks of Generative AI for OKRs
While the use of generative AI may seem like an effective way to automate the OKR creation process, it comes with significant risks that organizations need to consider. Here are some of the most notable risks:
Security Risks
One of the most significant risks of using generative AI for OKRs is the potential for data leaks and breaches. Generative AI algorithms work by analyzing large amounts of historical data to identify patterns and relationships. This means that any sensitive or confidential data that an organization has collected over time could be accessed by the AI. If this data is not properly secured, it could be shared or leaked across user accounts. According to Cyberhaven, the average company leaks confidential material to ChatGPT hundreds of times per week, with up to 11% of the data employees paste into ChatGPT being confidential.
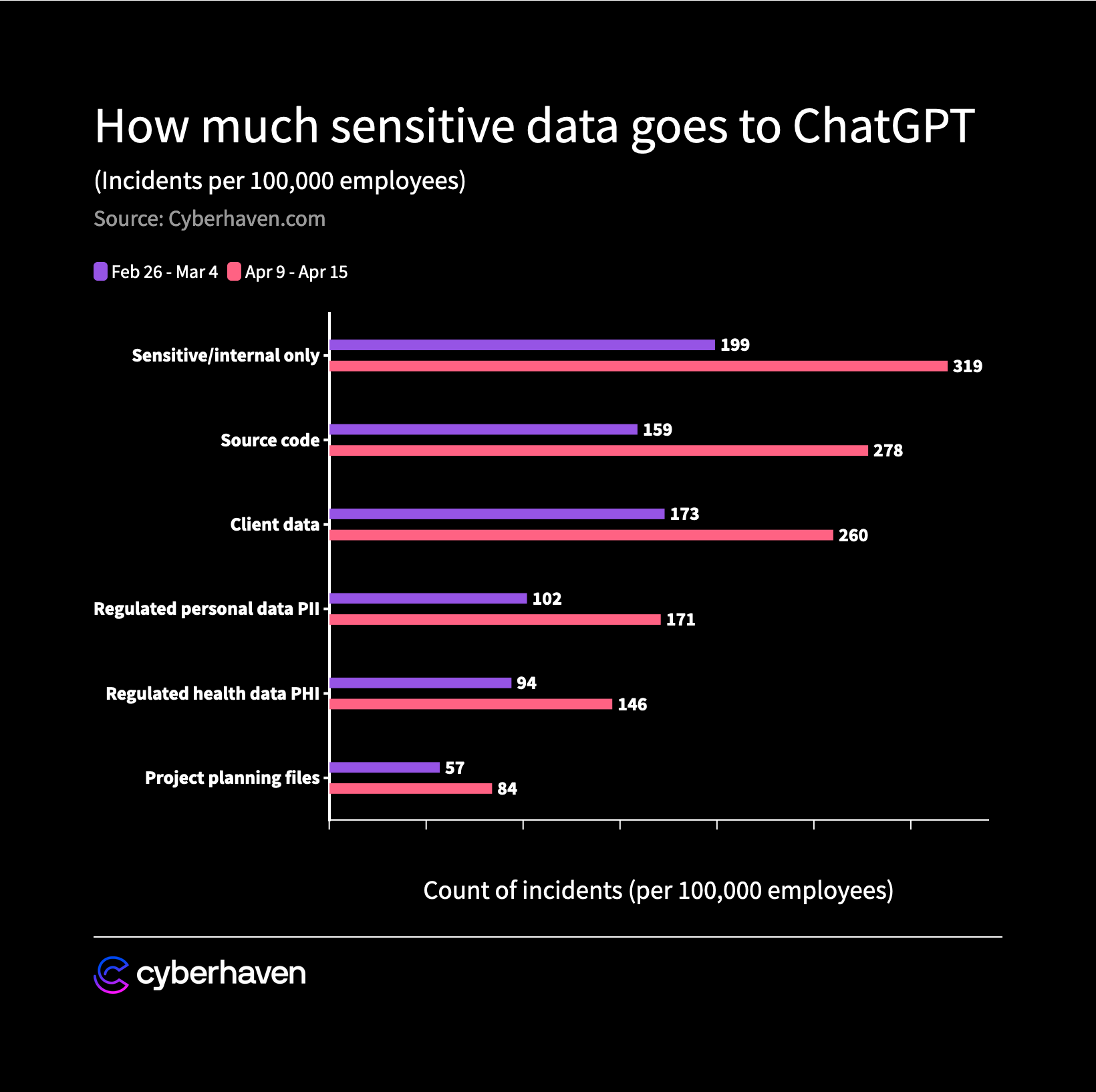
Suppose Company A uses a generative AI model to set its OKRs. Company A's AI model is highly sophisticated and well-designed, and it relies on a large amount of training data to generate its recommendations. However, the model has a serious flaw in its security protocols, which allows someone like Company B to access their prompt data.
Now, let's say that Company B, a direct competitor of Company A, becomes aware of this security flaw and decides to exploit it. Company B gains access to Company A's prompt information and begins to extract data from it. As a result, Company B is able to view all of the OKRs that Company A is generating, including those that are highly sensitive and confidential.
Company B can now use this information to gain a competitive advantage over Company A. For example; Company B may be able to figure out what types of new products that Company A is pursuing, what goals it is setting, and what metrics it is using to measure success. This information can help Company B to tailor its own strategies to better compete with Company A.
As you can see, this scenario illustrates the security risks that can arise when using generative AI for OKRs. Even if the AI model itself is well-designed, flaws in security protocols can expose sensitive data and give competitors an unfair advantage. This isn't a hypothetical scenario; this is happening today with tools like ChatGPT.
It's crucial for companies to take a proactive approach to security and to implement robust security measures to protect their IP and data.
Bias and Inaccuracy
Generative AI is only as good as the data it is trained on. If the data is biased or inaccurate, the AI will produce biased or inaccurate results. This is a significant risk for organizations that rely on OKRs to make critical business decisions. If the AI generates biased or inaccurate objectives or key results, it could lead to poor performance and lost opportunities.
Lack of Transparency
Generative AI is often referred to as a "black box" because it is difficult to understand how it arrives at its results. This lack of transparency can make it challenging for managers to evaluate the objectives and key results generated by AI. If managers cannot understand how the AI arrived at its results, they may be hesitant to trust them, which could lead to a lack of buy-in and participation in the OKR process.
The Importance of Data Security
Given these risks, it is crucial for organizations to take data security seriously when considering the use of generative AI for OKRs. To avoid data breaches or leaks, organizations need to ensure that all data is properly secured and that access is tightly controlled. This includes data used to train the AI, as well as any data generated by the AI.
In addition, organizations should consider working with AI vendors that prioritize data security and provide transparency in their algorithms. By working with vendors that prioritize data security, organizations can reduce their risk of data breaches and leaks and ensure that their OKRs are accurate and unbiased.
Conclusion
Generative AI has the potential to streamline the OKR creation process and provide valuable insights for organizations. However, the security implications of using generative AI for OKRs are significant and cannot be ignored. Organizations that are considering using generative AI for OKRs must take data security seriously and ensure that all data is properly secured and controlled. By doing so, organizations can reduce their risk of data breaches and leaks and ensure that their OKRs are accurate and unbiased.
Published at DZone with permission of James Bohrman. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments