A Guide to Resolving the Cross-Database Query Problem with A Single SQL Statement
Look at a guide to resolving the cross-database query problem with a single SQL statement.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeRecently, an e-commerce user experienced a sharp increase in access volume due to rapid business development, resulting in bottlenecks in database capacity and performance. To reduce the database size and improve performance, the user decided to implement vertical sharding on the architecture. Sharding is performed by table, which results in less of an impact on applications and supports clear and simple sharding rules.
The user vertically divided data into three databases according to members, commodities, and orders. After the vertical sharding was performed, the data was distributed to different database instances, reducing the data volume in each database and increasing the number of instances. This process seems simple but is difficult to implement. This is because once sharding is introduced, a query originally implemented in one database instance will now be implemented across two database instances.
If there is only one database, you can query the data required by many lists and detail pages in the system by running the SQL JOIN statement to join tables. After sharding, the data may be distributed to different nodes or instances and the JOIN statement is unavailable across databases. If this is the case, a tough issue arises.
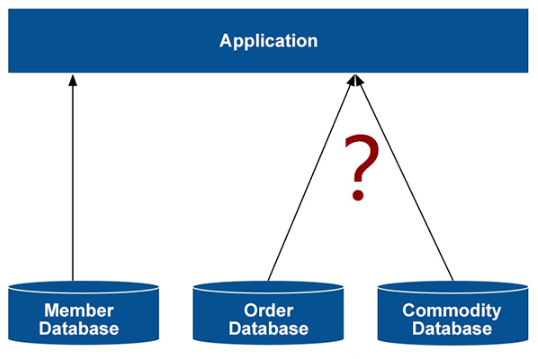
For example, if the sales order volume of a particular commodity category needs to be displayed in a business process but the order data and commodity data are distributed between two separate database instances, how can a joint query be implemented?
The first possible method is to reconstruct the existing business code by respectively querying the data from both databases and using the JOIN statement in the business code. However, this introduces the following issue: by using this method, the business code must be modified for a number of queries relevant to the business, making sharding extremely difficult to implement. In other words, this method is too complex and inefficient. Unfortunately, there is no efficient way to perform cross-database JOIN operations, and iterative queries must be performed one database after another. As a result, the query efficiency is low.
So, is there a solution for this tough issue?
Solution
This issue is actually a typical querying issue across database instances. Currently, Alibaba Cloud Data Management System (DMS) supports SQL queries across database instances. With DMS, you can use one SQL statement to resolve this issue. DMS not only meets the core demand of cross-database JOIN but also greatly simplifies the technical solution.
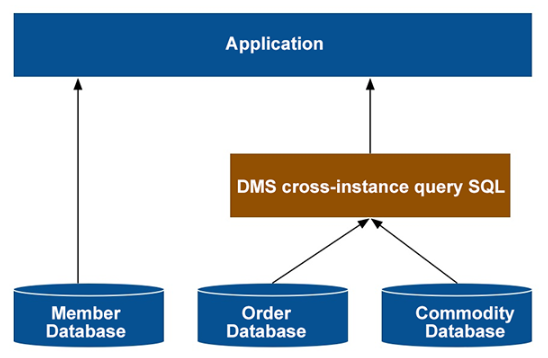

In addition to the case described previously, the cross-database instance query function provided by DMS can also meet any cross-database query requirements of businesses. For example, you can join online and historical databases to quickly retrieve complete data, join the databases of all cells in a cell architecture to query global data, and, for gaming businesses, join the user data in a MySQL database and the game equipment data in a MongoDB database.
Now, let's take a quick look at how to compose this SQL statement.
Data in the Commodity Database
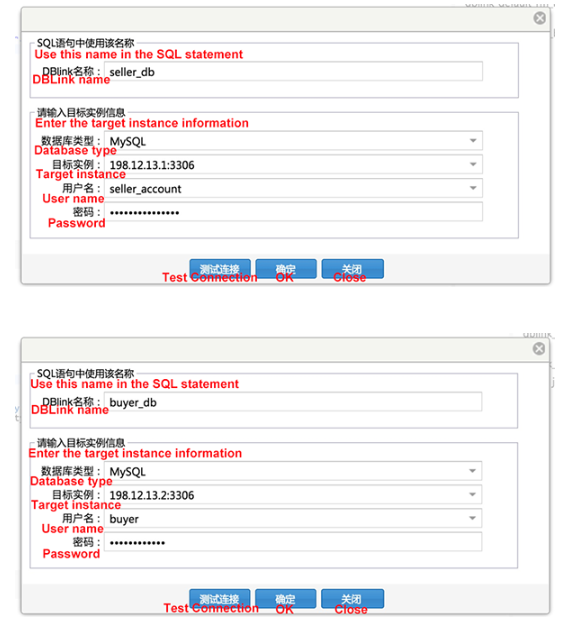
Instance connection address: 198.12.13.1:3306, database name: seller
Commodity table name: commodity
The table structure that contains part of all fields:
create table commondity(
id BIGINT(20), -- Commodity ID
name varchar(100), -- Commodity name
create_time TIMESTAMP , -- Commodity check-in time
categoryBIGINT(30), -- Commodity category
features text, -- Commodity description
param text), -- Commodity attributeData in the Order Database
Instance connection address: 198.12.13.2:3306, database name: buyer
Order table name: order_list
The table structure that contains part of all fields:
create table order_list(
id BIGINT(20), -- Order ID
buyer_id BIGINT(30), -- Buyer ID
create_time TIMESTAMP , -- Order creation time
seller_id BIGINT(30), -- Seller ID
commodity_id BIGINT(30), -- Commodity ID
status int(8) -- Order statusCreate DBLinks
Before composing the query statement, you must configure the DBLinks of the seller and buyer databases in DMS.
Compose and Run the Cross-Database Query Statement
After configuring the DBLinks, compose and run the SQL statement in DMS to query the order list of a commodity.
SELECT comomndity.catogary,
count(1)
from buyer_db.buyer.order_list
order,
seller_db.seller.commondity commondity
where order.commodity_id= commondity.id
GROUP BY commondity.catogary;The SQL syntax is fully compatible with the MySQL syntax except that the table name of the from clause is prefixed with "DBLink."
By using the cross-database query statement of DMS, you can easily solve the cross-database query issue after sharding without having to reconstruct the business.
What Is the DMS Cross-Database Query Function?
SELECT * FROM oracle.dsqltest.b oracle inner join
mysql.dsqltest.a mysql on oracle.id = mysql.id WHERE oracle.id=1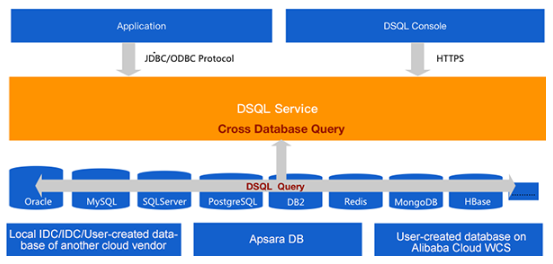
The cross-database instance query function of DMS was developed by Alibaba Group. This function has already served more than 5,000 developers to fully support Alibaba's online query requests across database instances. DMS supports online querying across heterogeneous databases and data sources including MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, and Redis. It provides a global data query capability for applications. You can use the standard SQL statements to implement queries across instances without converging data.
Note: Alibaba Cloud DMS is currently only available for Mainland China accounts.
Published at DZone with permission of Leona Zhang. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments