AI Agents For Automated Claims Processing
AI agents streamline workflows by autonomously processing claims, detecting fraud, ensuring compliance, and enhancing decision-making with real-time insights.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAgent-grounded models live for quite some time. They are generally enforced as computer simulations. An AI agent is a software operation that engages with its surroundings, collects information, and utilizes that data to negotiate predefined objectives. AI agents:
- Are software programs that accomplish jobs autonomously or semi-autonomously
- Run independently to design, implement, and optimize workflows
- Have proper boundaries to help execute tasks properly
- Help in driving better decision-making and functional effectiveness
- Can enable personalization
- Help in performing tasks accurately and consistently
- Manage and optimize complex systems
- Monitor and analyze security pitfalls in real time, delivering proactive measures to prevent breaches and guarantee data protection
- Increase productivity by reasoning, planning, and self-checking, releasing users from certain tasks
Business Case for AI Agents Usage
Today, CXOs see the IT budget as an area of overspending and are continuously looking for ways to reduce costs and time [1].
The global AI in the insurance market size was valued at $2.74 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $45.74 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 32.56% from 2022 to 2031 [2].
Driving business outcomes with AI agents requires strategy and collaboration from enterprise brigades. The following strategy-level questions help to understand the enterprise readiness for the AI agent implementation.
Business
- How does the AI agent align with the enterprise's overall business goals and strategic objectives?
- Does the enterprise have a governance framework in place to manage the deployment and ethical use of AI agents?
- Is there a top management-level charter for AI agents tied to one or more of the drivers?
- Does the enterprise have a published business strategy for AI agents?
- How does the AI agent enhance existing processes and support enterprise strategy?
- Is there an internal business case built? If so, at what level?
- What strategies do enterprises have in place to identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with AI agents?
- How does the enterprise manage the organizational changes required for the adoption of AI agents?
- What key performance indicators (KPIs) will be used to measure the success and impact of AI agent initiatives?
Technology
- Is the current IT infrastructure capable of supporting the computational demands of AI agents?
- Does the workforce possess the skills to use AI agents, and what are the implications for talent acquisition and upskilling?
- Are data management practices robust enough to handle the data requirements and ensure data quality for AI agents?
- How are enterprises addressing security and compliance concerns related to the deployment of AI agents?
Automated Claims Processing With AI Agents
Consider a scenario where an AI agent streamlines claims processing operations. The process steps are described below.
Claim Submission
- A patient visits the hospital, doctor, or diagnostic center called a healthcare provider for a medical service.
- After the treatment, the healthcare provider submits a claim electronically to the payer, covering details like patient information, treatment provided, and costs incurred.
Initial Claim Review
- The AI agent receives the electronic claim and begins the initial review.
- The AI agent checks the claim for completeness, ensuring all required information is included and correctly formatted.
Data Verification
- The AI agent cross-references the submitted claim data with the patient’s insurance plan details and medical history.
- The AI agent verifies the validity of the claim by checking for any inconsistencies or discrepancies, such as duplicate claims or services not covered by the policy.
Fraud Detection
- Using LLMs, the AI agent analyzes the claim for any fraud.
- Fraud can be of various types, including high cost, repeated claims for the same service, or suspicious billing codes.
Policy Compliance Check
- The AI agent ensures that the claim complies with the patient’s insurance plan terms and conditions.
- It checks the coverage limits, co-payment requirements, and any applicable deductibles.
Approval and Reimbursement
- If the claim passes all the checks, the AI agent automatically approves it.
- The AI agent calculates the reimbursement amount based on the policy terms and initiates the payment process.
- The patient is notified about the claim approval and expected reimbursement.
Escalation for Manual Review
- If the AI agent identifies any issues or uncertainties during the review process, it escalates the claim to the agent for further investigation.
- The agent reviews the flagged claim, makes any necessary corrections or decisions, and updates the system.
Continuous Learning
- The AI agent uses feedback from the manual review process to continuously improve its algorithms and decision-making capabilities.
- It learns from past claims to enhance accuracy and efficiency in future claims processing.
AI Agent-Based Automated Claims Processing Architecture
The following illustrates the use of AI agents for automated claims processing.
Input Data Sources
The data sources provide the insight required for automated claims processing. Various data sources are submitted: claims by the patients and real-time data from various sources covering patient information and treatment performed by the providers. These data sources are structured, semi-structured, and unstructured, as well as multi-model data covering images, text, video, audio, etc.
AI Agents
AI agents process data coming from input data sources. It performs activities like claims review, fraud detection, policy compliance check, claims approval, claims reimbursement processing, and any escalations.
All these formatted outputs are interpretable by LLMs. The AI agents analyze the response received from the LLMs and pass it on to tools to perform additional actions and convert them into coherent responses.
Tool Integration
It enables the agent to connect with other applications, databases, and automation tools to extend its functionality. Tool integration is achieved through API and third-party integration. Agents integrate with fraud detection systems, patient recognition systems, payment processing systems, claims processing systems, and reimbursements.
Memory
It helps AI agents to consider data storage, learning repositories, and historical data. Key memory management characteristics include scalability, privacy, consistency, and adaptability.
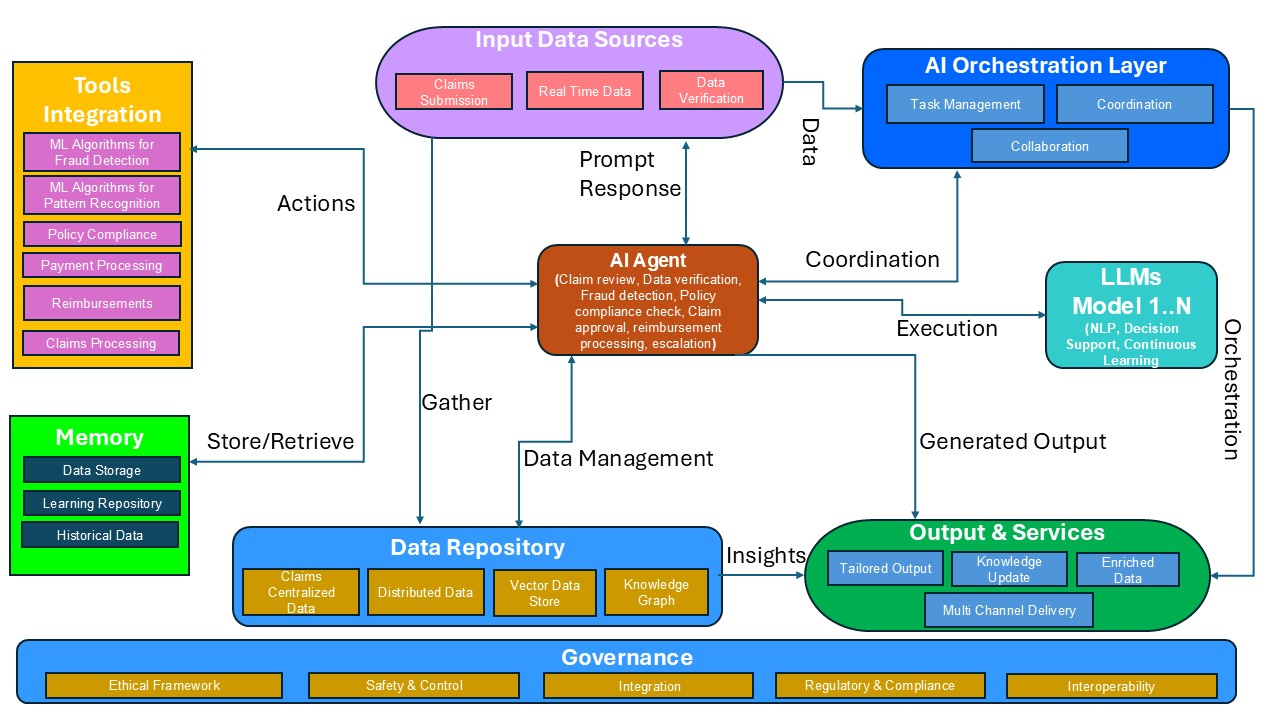
AI Orchestration
It involves managing the coordination and interaction between multiple AI agents to achieve automated claims processing. The key components of the AI orchestration are task management, coordination, and collaboration.
Data Repository
It facilitates efficient data management by utilizing claims, centralized data, and distributed data.
Output
It consists of AI insights that are transformed into personalized, context-aware results. These results are continuously updated. The system's knowledge base is also refreshed in the process.
Governance
The AI architecture integrates essential governance and safeguards to ensure safety, compliance, and ethical AI deployment. It ensures that AI agents operate safely, securely, and within regulatory boundaries.
Conclusion
AI agent-based claims processing solution is a game-changer for the medical insurance industry. This helps players modernize their business processes and stay competitive. The innovative solution reduces operational costs, provides a better customer experience, and enhances efficiency, allowing faster claim resolutions.
AI agents help provide enhanced fraud detection and minimize revenue leakage to payers. They also provide a better customer experience in terms of real-time support that enhances patients’ satisfaction levels.
References
- AI in Insurance Market Size, Share, Competitive Landscape and Trend Analysis Report
- Generative AI Playbook For Architects, IT Leaders & CXOs – Part 1
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Tanay Srivastava, Director, Tricon Solution LLC, for giving the required time and support in many ways in bringing up this Comprehensive Guide as part of Technical Services efforts.
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this article/presentation are those of the author, and Tricon Solutions LLC does not subscribe to the substance, veracity, or truthfulness of the opinion.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments