How AI Search Solves the Problem of Working With Unstructured Data
Up to 90% of business data is unstructured. AI search uses NLP and semantic understanding to interpret user intent and find conceptually similar content.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAre you struggling with unstructured data, like support tickets, employee feedback, and documents? Many businesses face this challenge, leading to wasted time and missed insights. Unstructured datasets make up up to 90% of all enterprise-generated data, yet most systems are optimized for structured, field-based records. AI-powered search can interpret intent and context, find conceptually similar content, and improve results over time based on user behavior. Today, we’ll explore how AI search can transform the way you interact with data.
What’s Unstructured Data and Why It’s Hard to Work With?
Unstructured data refers to any information that doesn’t have a predefined format and does not conform to fixed schemas of databases. Common examples in enterprise environment include:
- Text-heavy documents: Emails, meeting notes, support tickets, contracts, and project briefs
- Files and reports: PDFs, Word documents, PowerPoint presentations, and scanned forms
- Multimedia content: Customer call recordings, interview videos, and voice memos
- Collaboration tools: Slack/Teams messages, comment threads, and internal wikis
Unlike structured data — such as a CRM system’s "Customer Name" field — unstructured content doesn’t have fixed labels. As a result, traditional database queries can’t easily retrieve it, leading to several challenges:
- Keyword search falls short: Users must guess the exact phrasing (e.g., searching for "order delay" won’t surface an email saying "shipment stuck in customs").
- No consistent formatting: A contract clause may appear in a PDF, an email attachment, or a scanned handwritten note, each requiring different extraction methods.
- Lack of metadata and context: Without AI, a customer complaint buried in a support ticket won’t be tagged unless manually labeled.
- Scalability issues: Manual categorization and tagging become slow at large scale — imagine HR reviewing hundreds of resumes or legal teams parsing years of contracts.
When employees can’t quickly find the information they need, businesses suffer:
- Slower decision-making: Sales reps waste time searching for client details instead of closing deals
- Increased errors: Misinterpreted notes or overlooked contract terms lead to compliance risks
- Frustration and inefficiency: Employees spend up to 30% of their time searching for information
- Missed opportunities: Hidden insights in customer feedback or employee surveys go unused
AI to the Rescue: Solving Issues with Unstructured Data
When traditional search becomes ineffective, AI-powered search changes the game. It can understand context, intent, and relationships within data. Let’s explore how it works and why it outperforms conventional approaches.
How AI Search Processes Unstructured Data
AI-driven search relies on several advanced technologies to make sense of unstructured content:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) helps understands user intent. For example, a user's query — "Find customer complaints about late deliveries" — retrieves emails, support tickets, and notes even without exact keywords.
- Vector Embeddings and Semantic Search. An AI-based system converts text from unstructured datasets into numerical vectors, which allows it to capture meaning rather than rely solely on word matching. AI search enables similarity-based retrieval to find documents with related ideas, even if the phrasing differs (“order delay” vs. “shipment backlog”).
- Machine Learning for Continuous Improvement. AI software can learn from user interactions to prioritize relevant results over time. It automatically tags and categorizes documents — for example, grouping contracts by clause type.
- Multimodal Processing. AI software can extract text from images, PDFs, and scanned documents (OCR) and transcribe and index audio/video files for searchability.
AI-Powered Search vs. Traditional Search
|
Feature |
Traditional Search |
AI-Powered Search |
| Matching Method | Exact keywords or tags | Semantic understanding |
| Handling Synonyms | No (requires exact terms) | Yes (understands related terms) |
| Context Awareness | Limited | High (understands intent) |
| Learning Ability | Static algorithms with limited or no learning capabilities; updates require manual intervention | Learns and improves over time based on user behavior and feedback via machine learning |
| Multimedia Support | Rare (text only) | Yes (PDFs, audio, etc.) |
Transforming Business Outcomes with Server-Side AI Search
Integrating a semantic search engine on the server side allows organizations to extract value from unstructured data. By moving beyond literal keyword matching to a deeper conceptual understanding, businesses can convert unstructured text into a dynamic, intelligent asset that drives both growth and operational efficiency.
The real estate sector offers a compelling example of this transformation. Let’s see how a modern property platform uses server-side AI semantic search to make property discovery more intuitive and aligned with user intent.
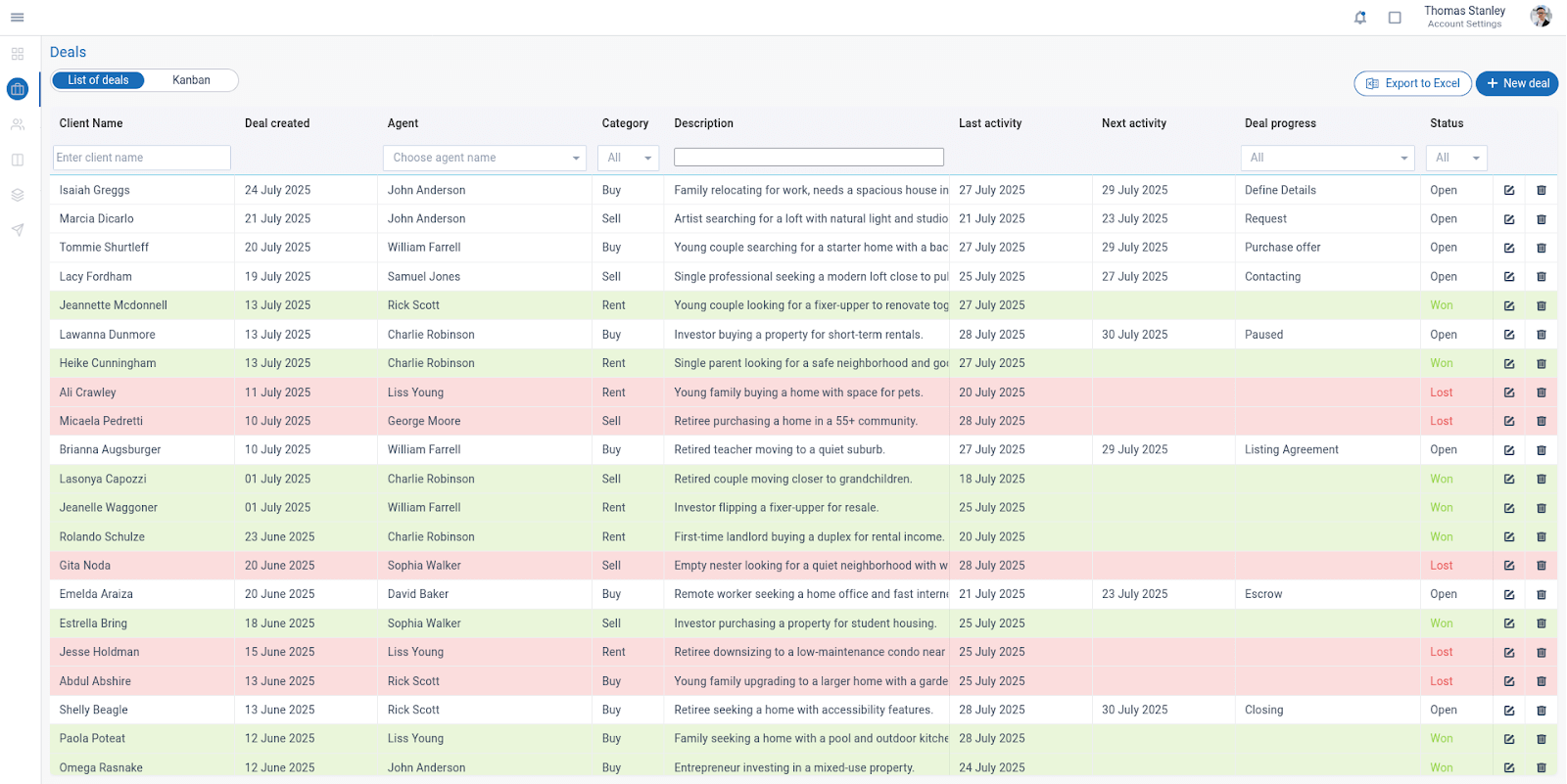
From Query to Match: How Our AI Search Validates Results
Vector-Based Matching
- Converts user queries and property descriptions into mathematical vectors
- Finds conceptual matches even without exact keyword overlap
- Example: Searching "education" returns properties mentioning "family seeking home near top-rated schools" and "investor purchasing a property for student housing"
Intelligent Threshold Filtering
- Applies similarity threshold to ensure relevant results
- Automatically excludes matches below a confidence level
- Example: A query for "quiet neighborhood"triggers matches such as:
- "Retired teacher moving to a quiet suburb" (84% match)
- "Empty nester looking for a quiet neighborhood with walking trails" (77% match)
- "Single parent looking for a safe neighborhood and good schools" (76% match)
Contextual Understanding
- Interprets related concepts through embedding relationships
- Recognizes "kids" → family amenities, playgrounds, safety features
- Identifies "investment potential" → rental yields, appreciation areas
How Semantic Search Powers Property Discovery
This AI-powered property search directly addresses critical pain points for real estate businesses:
- Capturing buyer intent beyond keywords. Many homebuyers use vague phrases like "good schools" or "quiet area" that traditional searches miss. The AI solution matches "family-friendly neighborhood" to listings mentioning "top-rated elementary school" or "playground access" even when exact terms differ. The business impact: 30% more relevant leads by understanding implicit requirements.
- Reducing missed opportunities. Valuable properties are often buried due to keyword mismatches (e.g., "serene" vs "quiet"). The AI solution surfaces conceptually aligned listings, increasing agent productivity by eliminating manual matchmaking.
- Converting ambiguous queries. Investors may search for "high-growth areas" while listings describe "appreciation hotspots" or "development zones." Vector relationships connect these terms, leading to faster deal flow through precision matching.
AI Search Query Examples Across Industries
Customer Support
AI search uncovers recurring support issues by recognizing patterns across channels, regardless of how customers describe their problems. This enables faster troubleshooting and better product insights.
Query: "Find tickets mentioning API integration issues"
What AI Search Does:
- Retrieves support tickets, forum posts, and chat logs
- Understands related terms like "API connection errors," "webhook failures," or "authentication problems"
- Groups similar cases for trend analysis
Traditional Search Limitation: Fails if the ticket says "system won’t connect" without the exact term "API."
Legal Department
Legal teams save time reviewing contracts and compliance documents by having AI identify relevant clauses and terms, even in PDFs or scanned documents — without manual tagging.
Query: "Show contracts discussing 2024 delivery terms"
What AI Search Does:
- Analyzes PDFs, scanned agreements, and email attachments
- Identifies clauses about "delivery timelines," "shipment deadlines," or "FOB terms"
- Filters by year even without manual metadata
Traditional Search Limitation: Cannot parse handwritten edits or complex legal phrasing without exact matches.
Sales & Marketing
Sales and marketing teams can get a clearer view of customer sentiment around campaigns and launches by analyzing unstructured feedback across channels.
Query: "Find customer feedback about the new service launch in April"
What AI Search Does:
- Aggregates surveys, social media mentions, and support tickets
- Detects sentiment (e.g., "loved the update" vs. "had issues with the rollout")
- Focuses on April-timeframe discussions, even if undated, using contextual clues
Traditional Search Limitation: Requires pre-tagged categories and dates, missing informal feedback.
Enterprise-Wide Real-World Example
A travel-fintech firm, Super.com, integrated an AI-powered enterprise search (powered by Glean) across Slack, Confluence, GitLab, and Google Drive to manage its remote-first workflow. The solution:
- Saved over 1,500 employee hours per month
- Reduced onboarding effort by 20%
- Supported AI-driven, personalized task lists and email drafts
- Ensured rigorous access controls to maintain security boundaries
AI-Powered Search: Advantages and Limitations
Advantages of Adopting AI-Based Search for Unstructured Data
- Employee time savings: AI search enables instant, context-aware retrieval, eliminating manual digging through emails, documents, and legacy systems. Automated tagging and categorization reduce administrative overhead, while unified search across CRM, HRM, and ERP systems cuts time wasted switching between apps.
- Improved customer experience: Clients often repeat themselves when agents can't locate previous interactions. By linking all support tickets, calls, and emails to customer profiles, AI creates a complete interaction history. Companies using AI see significant increases in first-contact resolution rates.
- Reduced risk of data loss: AI software penetrates deep into attachments, images, and audio files to surface buried content. The system preserves decades of knowledge through intelligent organization and retrieval. Organizations maintain permanent access to historical IP — R&D notes from years past remain instantly discoverable.
Potential Challenges and Limitations of AI-Powered Search
- Data quality requirements: Common issues include poor OCR accuracy in scanned documents, inconsistent file formats (e.g., handwritten notes vs. digital PDFs), and duplicate or outdated versions of documents. Solutions include data cleansing, OCR enhancement, and metadata enrichment.
- Security and privacy considerations: Accidental exposure of confidential information can occur through broad search results. Over-permissioned access is another risk. Mitigation strategies include role-based access controls and redaction capabilities for sensitive content.
- User training requirements: Employees accustomed to keyword searches may struggle with natural language queries or understanding semantic search capabilities. For example, a search for "drilling" could return unrelated results from oil industry reports and dental clinic records. A phased rollout and interactive tutorials help users adapt.
- Additional limitations: Language support limitations for multilingual organizations; computational costs for processing large document volumes; integration complexity with legacy systems.
Unlocking Tomorrow’s Insights Today: The AI Search Revolution
As Artificial intelligence models grow more sophisticated, we’ll see systems that don’t just find documents — they'll anticipate user needs. They may surface relevant contracts before negotiations begin or highlight customer pain points before they escalate. Multimodal capabilities will bridge text, voice, and even visual data.
For businesses ready to begin this transformation, success lies in phased adoption paired with strategic data preparation. Companies can focus first on cleaning and connecting core data sources, then expand as users adapt to conversational queries and confidence-based results.
Published at DZone with permission of Sergey Laptick. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments