An Introduction to RESTful APIs
REST refers to a stateless software architecture that provides many underlying characteristics and protocols that govern the behavior of clients and servers.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeToday, almost every application on the internet does need to provide interoperability as a basic feature. At any given moment, applications are communicating with other applications (for example, a mobile application communicating with a web application). Thus, it is important that all applications should be able to communicate with other applications without depending on the underlying operating system and the programming languages. Web services are used to create such applications.
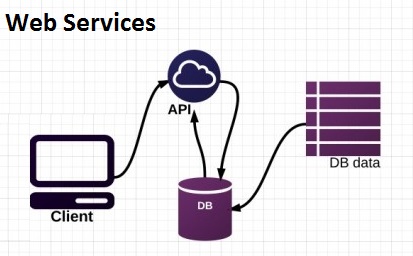
Web Services
A web service is a collection of standards and protocols that applications and systems use for exchanging data over the internet. A web service could be written in any programming language and is OS-independent.
For instance, an application built in PHP running on a Linux server can communicate with an Android application built using Java and running on an Android operating system.
What Is REST?
REST stands for Representational State Transfer. It is a stateless software architecture that provides many underlying characteristics and protocols that govern the behavior of clients and servers.
What Is Meant by RESTful?
An API that has following features is known as RESTful API:
Client-server architecture: The client is the front-end and the server is the back-end of the service. It is important to note that both of these entities are independent of each other.
Stateless: No data should be stored on the server during the processing of the request transfer. The state of the session should be saved at the client’s end.
Cacheable: The client should have the ability to store responses in a cache. This greatly improves the performance of the API.
Learn how to secure REST APIs with client certificates.
What Is a RESTful API?
A RESTful API (also known as a RESTful web service) is a web service implemented using HTTP protocol and the principles of REST. It is a collection of resources that employ HTTP methods (GET, PUT, POST, DELETE).
The collection of the resources is then represented in a standardized form (usually XML) that can be any valid Internet media type, provided that it is a valid hypertext standard.
Popular RESTful API request formats:
REST
XML-RPC
Popular RESTful API response formats:
REST
XML-RPC
SOAP
PHP
Why Use a RESTful API?
A RESTful API is used to make applications distributed and independent over the internet with the aim of enhancing the performance, scalability, simplicity, modifiability, visibility, portability, and reliability of the application. DZone’s previously covered securing Spring Boot applications with Keycloak’s REST API.
Real-World RESTful API Examples
All the most popular websites and social media offer RESTful API. Several popular examples include:
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments