Attribute Based Access Control for Mulesoft APIs
Let’s explore how ABAC could be implemented effectively for Mulesoft API gateway through a custom policy.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeHow can we automate the processes of API registrations and access controls to make it easier to manage at scale? Attribute-based access control (ABAC) has unique advantages over role-based access control (RBAC) for API gateway management, especially when it’s enabled with the OAuth2 JSON web token (JWT). Let’s explore how ABAC could be implemented effectively for Mulesoft API gateway through a custom policy.
Background
By default, the Mule Anypoint Platform comes with its own identify provider (IdP). This IdP is intended to help customers to jump-start their projects or create PoCs. It is not provided for production deployments, especially with a large number of client applications. For that purpose, Mule supports integration with external IdPs, such as Okta, OpenAM, etc.
Mule and External IdP Integration Solution
To access secured APIs, users or machines need to be registered with the external IdP either through Mule or at the IdP first, then request permissions for API accesses. OOB, Mule enables authorization and access control through RBAC. Authorizations to the APIs have enforced through Mule provided default policy - Client ID Enforcement Policy. For now, Mule can only be configured with a single external IdP since it’s configured at the organization level.
The main benefit of using an IDP configured through Mule is that many default policies are readily available to support OAuth2 token. However, there are scalability and configuration management issues. When the number of registered users/machines are more than a few hundred, managing the access rights to the APIs is overwhelming. It’s not uncommon for web applications to have users in hundreds of thousands. Also, Mule and the external IdP are tightly coupled since the client-ids need to be synced for the author and authN to work.
Identify Federation
Mule Identify federation enables external users created dynamically and map external user groups to predefined roles in Mule. However, you cannot grant the user access to APIs through roles in Mule at runtime since no roles with such permission exist. (Even you can define such roles, it’s too much burden to manage mappings from LDAP groups to Mule roles with permissions to access a large number of Mule APIs.)
ABAC addresses the concerns of automation of user registrations and API access control more elegantly by decoupling the two. Managing access rights of a large number of users/machines is the wrong approach since the users do not and should not care about API credentials after they have SSO through the federation.
Mule and External IdP Trust Solution
ABAC can be realized through Mule custom policy. Mule Anypoint Platform needs not to be configured with or restricted to a single IdP since they are loosely coupled through a trust relationship. The trust is established through Mule honoring the JWT tokens issued by the trusted IdPs. With ABAC, Mule can support more than one IdPs for authN and authZ/access control. Custom policies can be created to meeting your special requirements. The custom ABAC policy can be applied like those OOB Mule polices, such as JWT Validation and Client ID Enforcement.
OAuth2 Token – JWT
OAuth2/JWT is widely adopted to realized API gateway authN/authZ. It’s enabled by almost all cloud-based services/APIs access controls. JWT’s claim-based identifies attributes that can be used to enforce access controls at the API gateway.
ABAC Solution
Registration and access control are handled separately. 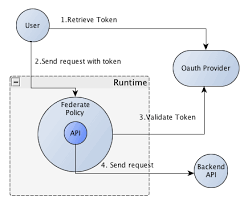
Before Diagram: Mule OOB Policy
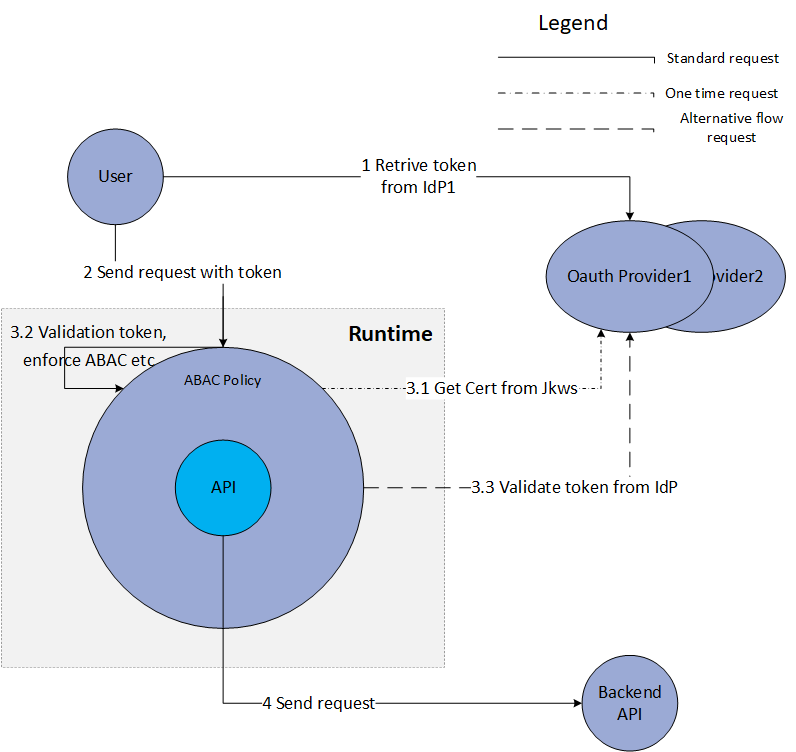 After Diagram: Custom Mule ABAC Policy
After Diagram: Custom Mule ABAC Policy
Registration
- Mule publishes a list of APIs and access info to external systems, including IdPs.
- Users/machines register with the external registration system together with API and permission info. The registered info can be stored and Idp repo or as LDAP attributes
- Note that registration happens at the external system alone. There is no need to sync the data back to APIGW. Thus, the two systems are loosely coupled.
Access Control
Assumptions:
- APIGW and IdPs agree on where to store and the format of access control data. It’s commonly stored in the JWT claim scope.
- APIGW has access to IdP certs used to sign the tokens. Normally IdPs publish the certs through JWKS endpoints.
- Users/machines acquire OAuth2/JWT tokens through OAuth2 or SSO mechanism.
Policy Enforcement
- Users/machines request APIGW for specific APIs with a JWT bearer token
- APIGW custom policy intercept the token and decode it into plain text JSON
- The policy inspects the issuer of the token from iss field to ensure it is issued by trusted IdPs
- The policy queries the related JWKS endpoint to get the published certs and cache the certs
- The policy finds the cert matching JWT’s kid field and validates the token
- The policy extracts scope from JWT claims field
- The policy enforces access control rules. This can be done at APIGW or with external services. The enforcements can be done with Coase-Grained Authorization with simple JWT scope values to accessed API matching or with Fine-Grained Authorization.
- Optionally remove the token from REST header before forwarding to backend APIs
- Optionally enrich REST requests/headers with JWT claims info.
- Note1: Access control enforcement (PEP) can be done at APIGW, IdP, or external systems. There are pros and cons to enforcing it at different points. Here it’s done at APIGW.
- Note2: In Mule, when applied to a proxy/API, the custom policy can’t figure out which proxy/API it is applied to dynamically. Because of this limitation with Mule, the proxy/API name to which the policy attached to need to be set at API Manger.
Sample JWT data:
{
"active": true,
"principal": "https://example.com/users/jdoe",
"scope": ["list:hello", "read:hello", "create:hello", "update:hello", "delete:hello","someScope"],
"clientId": "host123",
"expiresAt": "2019-05-30T10:15:30+01:00",
}
Note: sample borrowed from Oracle OCI authN and authZ to API deployment
Implementation References
Mule 3 JWT validation source is available at github, which can be converted to Mule 4. Token validation can also be implemented in Java separately from the policy. It can be unit tested and ported to other platforms. Mule 4 can’t invoke java directly. It needs to go Mule SDK extension for Java.
This is well documented by Mule. A Mule 4 policy project skeleton is available at github. For this sample project, the java implementation details were intentionally left out. There are many open-source JWT projects. Auth0 and jjwt are two popular ones.
Summary
This writing explained how to implement a custom ABAC policy for Mule APIGW. Its design and processes to enforce ABAC can apply technologies other than Mulesoft.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments