Project Management Methodology: A Beginner's Guide
Using a specific methodology can help a Project Manager steer a project in the right direction and work in a structured manner.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeProject management is a very popular subject all over the world. Learning project management is not a simple task, and it involves taking help from the best practices and experiences of experts. This article is based on research and best practices being done by various project managers. This article is useful for beginners who want to start a career in project management. It covers the most popular project management methodologies.
Before going in depth about the methodologies, it should first be understood that what the term “methodology” is actually all about.
A methodology is basically a body of procedures, methods, and practices. They solely belong to those working in a specific discipline. Every Project Manager needs to steer projects in the right direction. So, these methodologies help them to work in a structured manner.
What Are Project Management Methodologies?
In this guide, we will go through the most popular project management methodologies.
Agile Methodology
Agile is the most commonly used methodology in software development. The purpose of Agile is to ensure the regular delivery of the product to the customer. It is different from traditional methodologies such as Waterfall because there is no clarity defined about the end product at the onset. Agile consists of a prioritization process with nonstatic requirements like regular communication, flexibility, and constant change.
Although it is a very popular among software developers and very powerful approach to other types of projects, as well. In agile, the development process is broken up into Sprints with chunks of milestones.
Neil Killick, a passionate technology professional, shares his views about Agile as follows:

Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall is the most widely used methodology in project management. It is being used commonly in software development and the construction industry. It is a traditional methodology. It works in a sequential manner. Waterfall suggests that one task must be completed before the next begins. It is basically a connected sequence of tasks that ultimately lead to a deliverable. Waterfall methodology is ideal for construction projects or projects in which the milestone is a physical object.
These are the phases of Waterfall:
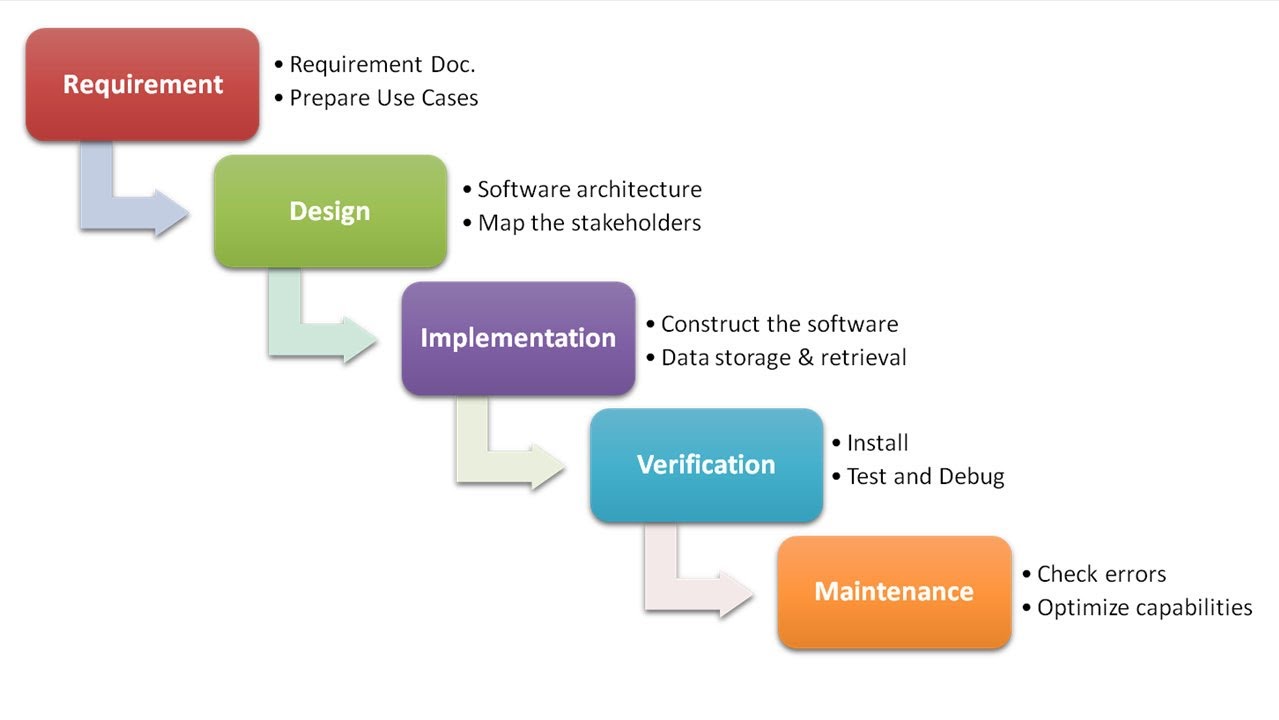
The Waterfall method is usually divided into various versions, but the following are a few original high-level phases:
- Design.
- Requirements specification.
- Integration.
- Construction (coding).
- Installation.
- Maintenance.
- Testing and debugging.
Pam Rotella, a health freedom activist, has this to say about Waterfall:

Scrum Methodology
Scrum methodology is basically a type of Agile in which there is a focus on 30-day Sprints and Scrum sessions on a monthly basis. This methodology works best for teams who feel difficulty in prioritizing tasks, as all of them have their own significance. Adopting Scrum can massively increase the productivity of the team.
In scrum methodology, there is no job title of Project Manager — it's Scrum Master. The Scrum Master's responsibility is to ensure smooth communications and tackle every hindrance that affects team performance.
This methodology is highly suitable for specific type of environments. These environments include:
- Dedicated environment. This is an environment with 100% dedicated team members. Dedicated means that they should not be working as shared resources.
- Unlimited support environment: This environment implies that there is no time and budget constraint.
RAD (Rapid Applications Development)

This is another widely used methodology of software development. It utilizes prototyping and structured techniques for designing the annual system. It involves a cycle of models in the process.
RAD methodology has been criticized by many Project Managers because they claim that short interactions create hurdles to developing an in-depth methodology.
NPI Methodology
 NPI stands for New Product Introduction. It is quite an unpopular methodology but is still followed by many organizations. It is not a complete project management methodology. It lacks a few necessities for a project’s success such as WBS (work breakdown structure). This methodology is mostly used in product based companies.
NPI stands for New Product Introduction. It is quite an unpopular methodology but is still followed by many organizations. It is not a complete project management methodology. It lacks a few necessities for a project’s success such as WBS (work breakdown structure). This methodology is mostly used in product based companies.
PER Methodology
PER stands for Package-Enabled Re-engineering. It implies the business traditional approach to project management.
PRINCE2 Methodology

PRINCE2 stands for Projects in Controlled Environments. PRINCE2 methodology is a standard used by the government of United Kingdom. It is used and recognized in public as well as private organizations. It gives greater control over the team and helps manage risks.
It is different from PMI’s publication PMBOK in this regard, as PMBOK is a collection of best practices, not a methodology. PMBOK 5th Edition is recommended to prepare for the PMI certifications.
Kanban Methodology
 In this methodology, project progress is displayed on a board. Stickies are very common in this regard. They generally move from left to right and are categorized as tasks in progress, tasks recently completed, and tasks in the queue.
In this methodology, project progress is displayed on a board. Stickies are very common in this regard. They generally move from left to right and are categorized as tasks in progress, tasks recently completed, and tasks in the queue.
Kanban makes it easy to visualize what work has being going on and what’s next.
Kanban methodology works best for small teams. Also, individuals consider the use of personal Kanban boards as an effective use of this methodology.
Six Sigma Methodology

This methodology was originally developed by Motorola. Six Sigma is a data-driven and disciplined methodology. This methodology was developed for eliminating the causes of defects. However, many professionals don’t think it as a methodology.
Six Sigma is actually based on DMAIC-S, which stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. Its purpose is basically to synergize the organization. The DMAIC cycle is used for optimizing, improving, and stabilizing designs and processes.
Outcome Mapping

Outcome mapping basically comprises of two phases: a record keeping phase and a design phase. This approach is widely used in developing countries for charitable projects. Outcome mapping was designed by the IDRC (International Development Research Center).
Outcome mapping is different from other methodologies as it focuses only on behavioral change rather than measurable deliverables.
Critical Path Method (CPM)
CPM was first developed in the 1950s. It is based on the fact that tasks can't be initiated until the previous ones are completed. A critical path is plotted among these dependent tasks.

The critical path method helps Project Managers in prioritizing and allocating resources for getting the most important work done and rescheduling the low-priority work.
CPM is related to CCPM (Critical Chain Project Management) methodology. In CCPM, resources required for completing tasks are the main focus. It involves building the project schedule in the beginning and sticking to it under all circumstances. It also involves reserving resources for high-priority tasks. Time buffers are also made in the project schedule. It helps in meeting deadlines.
PMBOK Methodology
Many Project Managers believe that PMBOK is not solely a methodology. As PMI claims, PMBOK is a collection of best practices, not a collection of processes. This methodology basically works by breaking down the project into five process groups, as shown below.

Extreme Programming (XP) Methodology
 XP is an offshoot of Agile. It is designed to improve the quality of the software and the company's tendency to adapt to the customer needs. XP uses iterations, Sprints, and consistent collaboration with the stakeholders. Change may happen in a Sprint. If some task has not been initiated, then it can be swapped by a similar task.
XP is an offshoot of Agile. It is designed to improve the quality of the software and the company's tendency to adapt to the customer needs. XP uses iterations, Sprints, and consistent collaboration with the stakeholders. Change may happen in a Sprint. If some task has not been initiated, then it can be swapped by a similar task.
Adaptive Project Framework (APF) Methodology
 Traditional methodologies are not sufficient to manage most IT projects because of uncertainty and changing requirements. This is where APF completely fits the bill.
Traditional methodologies are not sufficient to manage most IT projects because of uncertainty and changing requirements. This is where APF completely fits the bill.
It works with RBS (Requirements Breakdown Structure) to define strategic goals based on features, functions, and product requirements. The project then proceeds in various iterative stages. At the end of every stage, the previous outcomes are evaluated for improving performance and practices. Stakeholders also have the right to make changes in project scope at the beginning of every iteration stage.
Change Management Methodologies
 These methodologies are best utilized when a project is undergoing rapid changes. It focuses on planning for risks and then controlling the outcomes.
These methodologies are best utilized when a project is undergoing rapid changes. It focuses on planning for risks and then controlling the outcomes.
Event Chain Methodology (ECM)
The basic idea of ECM is that there exists a potential risk that mostly lies outside the project scope. It is important to plan for unexpected events that can ultimately affect the project’s success.
Extreme Project Management (XPM)
XPM helps in managing massive change. It is actually the opposite of Waterfall. This methodology enables you to make changes in the budget, plan, and even the final milestones to best fit the changing demands. This methodology is usually adapted for managing projects with smaller timelines.
Lean Methodology
 Lean is a type of process-based methodology. It deals with business process management. The purpose of Lean is to focus on streamlining and cut down the waste. It involves the creation of work process breakdown for eliminating delays and bottlenecks. Lean’s methodology objective is to deliver customer more with less human resource and time.
Lean is a type of process-based methodology. It deals with business process management. The purpose of Lean is to focus on streamlining and cut down the waste. It involves the creation of work process breakdown for eliminating delays and bottlenecks. Lean’s methodology objective is to deliver customer more with less human resource and time.
PRiSM Methodology
PRiSM stands for Projects Integrating Sustainable Methods. It is used for managing change and ensuring environmental sustainably into processes. The basic purpose of PRiSM is to finish projects with a reduction of the organization’s social impact.
Benefits Realization Methodology
This methodology focuses on the satisfaction of customers by ensuring deliverables. It is not only about the on-time delivery of a product within the allocated budget but also about delivering value to stakeholders.
Crystal Methodology
In this methodology, processes are comparatively given a low priority. This methodology focuses on team member skills, team communication, and team interactions. They are under the roof of Agile.
Dynamic Systems Development Model (DSDM)
It is actually a descendant of RAD methodology. It totally focuses on active user involvement in the project lifecycle.
Feature-Driven Development (FDD)
FDD focuses on feature-driven delivery cycles. It is all about concentrating on simple and well-defined processes.
Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL)
ITIL is actually the collection of best practices in project management. This methodology focuses on organizational management-level processes.
Joint Application Development (JAD)
JAD focuses on the involvement of clients from initial stages. JAD sessions are held between the client and the project team for getting input from the client. These sessions are conducted throughout the entire project lifecycle.
Rational unified process (RUP)
RUP methodology is all about focusing on the positive aspects of modern software development methodologies and providing them in a single package. RUP was the first methodology which recommended an iterative approach to software development.
Spiral Methodology
Spiral is actually the extended version of Waterfall methodology, which contains prototypes. This methodology is preferred in large projects as a replacement to Waterfall.
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
SDLC is a conception model utilized in software development projects. It may be a combination of two or more project management methodologies for the best results. SDLC focuses on documentation process along with strict guidelines.
Conclusion
The above-discussed methodologies are very useful in their specific environments, but selecting the best methodology is typically a tricky task. However, an experienced Project Manager can pick the best one according to the scope of a specific project.
There are hundreds of factors that must be considered when selecting a right methodology. A Project Manager must consider all the weaknesses and strengths before selecting the methodology best suited for a project.
This tweet from Mr. James Townsend, an Entrepreneur at Infostrat, is perfect to conclude this topic:

Don’t forget to share your valuable experience and knowledge with the community. Which methodology do you use? Share it in the comments section.
Published at DZone with permission of Atif Qureshi. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments