Blockchain Document Signing Platform: Offering Security to Confidential Documents
Get the security your documents need.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
The document signing process plays a crucial role, as it guarantees the creation of binding obligations between the signing parties.
The sales contract looks legalized, have all the parties signed it? Is it the reviewed and latest version? Can it be proved that the document has not been altered before you signed? Is it possible to prove the document you received is identical to the one you viewed earlier?
Though many online document signing solutions provide secure electronic signatures, it is entirely different from the digital signatures. An electronic signature can be a scanned image of a handwritten signature, but a digital signature uses mathematical algorithms to prove authenticity.
Plenty of digital signing services like Docusign and Echosign already exist that can help to sign legal documents.
All such document signing platforms allow users to sign documents securely. Additionally, they provide cloud storage for the signed documents.
You may also like: A Guide to Digital Signature Algorithms.
Since you need to blindly trust third-parties for storing your documents, these services appeal more to enterprises than the average users.
With Blockchain Document Signing, there is no need to blindly trust third-parties, neither for timestamping nor for storing signatures.
It can be possible to replace a third-party and prevent anyone from going back and track records in case of manipulation or disputes by building a blockchain document signing platform.
This article is intended for understanding the impact of blockchain technology on the document signing process.
Let’s first discuss the challenges in the current system and why it needs to be transformed with blockchain.
Challenges With the Existing Document Signing System
PDFs were designed to share richly formatted documents with enterprises or individuals. It became an international standard in 2008 as Adobe and other companies added security features into PDF files.
The security features of the PDF included password protection, digital signatures, and encryption. Digital signatures were added to PDF to verify who created and encrypted it.
Depending on the hashgraph algorithm used in the PDF files, it is not challenging to sabotage the document's protection. Schellekens, PDF expert at iText Software in Ghent, Belgium says that it is possible to change the document content and date/time stamp of a PDF document.
According to Schellekens, the PDF specification comprises the concept of an ID-tuple, which includes timestamps for when the file was created and updated.
But the protection only applies to the entire document, not to its various parts. Suppose a document has to be signed by multiple parties. As not all certificate authorities save their private keys with equal vigilance, there is no surety of who modified the document, at what times, and in which order.
Signature to a digital document should be made serially, one at a time. But the PDF specification does not enable a document to be signed in parallel by multiple parties and then combined together.
Blockchain can enter the document signing industry by creating timestamps and allowing multiple signatures. By using private keys between the signer and recipient, documents can be managed securely by approved parties.
We shall now discuss why blockchain is beneficial for signing the documents.
Why Blockchain for Document Signing?
Blockchain technology allows for a linking of a group of records, called blocks into a chain that is protected and encrypted against tampering.
Blockchain uses the concept of a hash, which is like a fingerprint for every block.
Every time a block is added to the chain, a hash gets generated for it. Tampering with any block causes the hash address to change.
As a result, all blocks containing the previous hash become invalid.
Now, let’s understand where blockchain comes into play in document signing.
A hash is calculated for the original version of a PDF file, and the value gets stored in the blockchain.
Authorized parties can verify that copies of the document are legitimate by matching their version’s hash with that of the original version’s hash stored in the blockchain.
In the case of multiple copies with different signatures, parties can use the blockchain document signing platform to look at the timestamps associated with the document’s metadata.
Blockchain can save an accurate time stamp/date and the identity of the person who signed the document. So, it can become possible for multiple parties to sign a document through a legally and secure binding process.
How the Blockchain Document Signing Platform Could Work
Stakeholders who can be involved in the blockchain document signing ecosystem:
- Users: To manage and sign the contracts using the platform.
- Admin: To view users and analytics reports.
Step 1: Users sign up to the platform
Users who want to use blockchain document signing platform to sign the documents or get them signed by multiple parties, sign up to the platform.
They need to provide their government-approved identity while registering on the platform. A hash corresponding to the identity information gets stored on the blockchain to verify the users when signing the document.
After signing up, users can sign in to use the platform for document signing without the involvement of third parties required to bring trust to the system.
Step 2: Users Upload the Document to the Platform
Users can upload the document that they need to get signed by the signer to the platform. Documents can be uploaded as pdf and doc files.
Also, they can store the signed documents to manage the files and saving the record in the blockchain.
A hash would be stored for every document a user uploads to the platform, ensuring who has uploaded the document, when it has been uploaded, and who all have signed the document.
Step 3: Users Add the Recipients Who Have to Sign Documents
Users can have the ability to add all signatories (recipients) who will be signing the documents.
They can add as many signers as many they want.
Signers would get a signing request on their emails and they need to enter their email ids and a verification code received in the mailbox to the platform for signing the documents.
Once the signers sign the document, users get a notification and the transaction corresponding to the signing would be saved on the blockchain. Signers can either draw the signature or use the government-approved signature system for signing a document.
Transactions saved for the signing of documents would maintain the history of signing records that cannot be altered or deleted. Also, users can add spectators who would receive the documents as a cc in their emails.
Step 4: Users Create the Signature and Sign the Document
Users who want to get the documents signed or signers who have to sign the documents can either create a signature by drawing it or adding a government-approved signature to the platform.
Every time a user creates or modifies the signature, the transaction gets saved on the blockchain to ensure the authenticity of the signature.
With the blockchain as a backend component, it can be ensured that the records stored are immutable and traceable.
Therefore, the signing records can be traced back anytime to resolve disputes or conflictions.
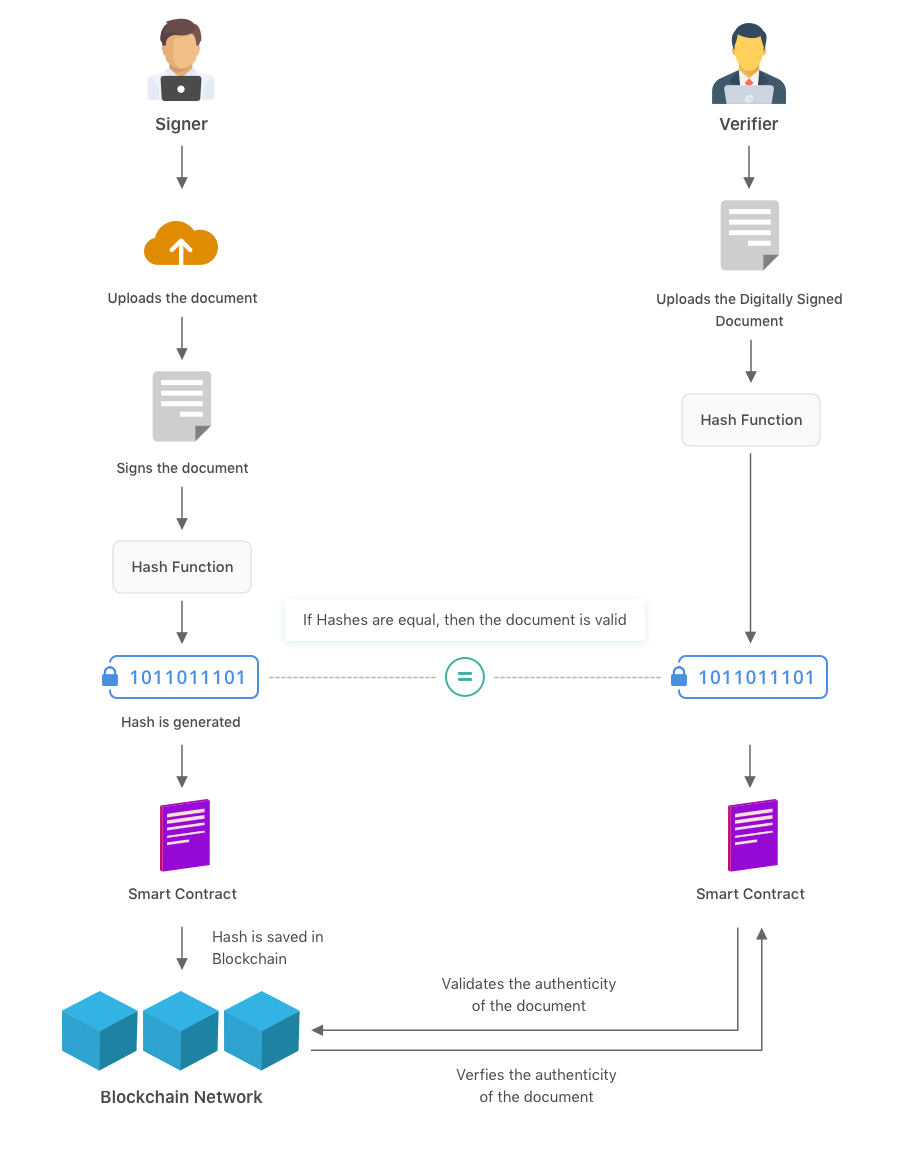
Step 5: Document Authenticity and Validation
After the document gets signed by all entities, a hash is generated on the blockchain. Any user with the signed document can check the authenticity of the document on the platform.
Users can upload the signed document on the blockchain document signing platform. If the hash comes out to be the same after uploading a signed document as that of the hash generated at the time of signing, then the document would be validated.
If the hash is not the same, there could be chances of manipulation or alteration in the signed document.
Since the blockchain document signing platform would be completely decentralized, the role of admin could be limited to managing the subscriptions of the users and analytics reports.
On-chain and Off-chain entities
The following are the details that would be stored on-chain:
- User ID.
- Document.
- Document Signatures.
- Finalized Document Hash.
- User subscription details.
The following are the details that would be stored off-chain:
- User information.
- Roles.
- Notifications.
- Document and Document Transaction ID.
- Subscriptions Plans.
- Invoices.
- Transactions.
- Logs.
Examples of Blockchain Document Signing Platforms
BlockSign
Blocksign is a blockchain-based platform for legally signing any document, contract, or agreement. It allows users to sign any document by uploading it and adding a signature to it. When the signatures on the document are found to be real, a unique 32-digit string gets stored in the blockchain for each signature.
OpenSig
OpenSig is an open digital signature scheme, which enables you to sign any digital document digitally and verify their authenticity and integrity later. The digital signature gets published on the publicly-owned decentralized ledger, blockchain with the time-stamped record.OpenSig v1.0 currently uses the Bitcoin Blockchain to allow blockchain document signing.
Blockchain offers enormous opportunities to the document signing industry with its features like trust and traceability. The proof of signature in the blockchain is not controlled by any single entity.
Members of the blockchain document signing platform instead act as public notaries or witnesses to attest the signature. A blockchain-based signing platform also provides users with access to the document and the ability to quickly confirm the authenticity of a signature.
Published at DZone with permission of Akash Takyar. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.


Comments