JSF Versus JSP: Which One Fits Your CRUD Application Needs? (Part 1)
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Freewe make decisions every day; everything we say and do is the result of a decision, whether we make it consciously or not. no matter how big or small is the choice, there's no (easy) formula for making the right decision. the best decision is the one you adopt after you approach the situation from as many perspectives as possible and then choose a course of action that seems reasonable and balanced at that time.
this article aims to help those of you that were/are/will be challenged to choose between jsp and jsf for developing a crud application, all the words written inside it being accompanied by valid code snippets and samples.
content of jsf versus jsp debate consists of the following:
- overview over the differences between the two technologies
- architectural differences between applications developed with each of them
- step by step implementation of an application with jsf/jsp ; the application(s) will be built over the same database and addressing the same purpose.
requirements:
-
an ide
- java ee 6.0 or higher
- maven 2.0 or higher
- jsf2.0 or higher
differencies between jsf and jsp
javaserver faces (jsf) is a web application framework that is based in java. its main objective is to simplify development integration of user interfaces that are web based. it is a request driven model view controller based on component driven ui design model, which uses xml –view templates or facelet views. requests ran through the jsf are processed by the facesservlet. this component loads the view template that is required, builds a component tree, processes events, and renders the response –which is usually in html.
javaserver pages (jsp) is a java based technology specifically used to help software developers serve dynamically generated web pages (such as html and xml) as well as other document types suitable to the development of interactive web content. it was specifically created in order to provide developers the ability to program java web applications.
|
jsf |
jsp |
|
jsf is a web application that is used to simplify development integration of web based user interfaces. |
jsp is a java based technology used specifically in order to help software developers create dynamic web pages. |
|
jsf contains multiple core features, including, but not limited to, managed beans, a template based component system, and two xml based tag libraries. |
jsp must be compiled in java bytecode in order to function properly.jsp must be compiled in java bytecode in order to function properly. |
|
jsf is a framework.
controller:facesservlet |
jsp is not a request driven model view controller, but jsp is accessed by the dynamically generated web pages like html or xml. |
|
jsf supports validator and conversion,ajax. |
jsp does not. |
personal recommendations and observations:
1. learn jsp first, and then jsf; you have to understand the past to see what future holds to you. jsf is popular within nowadays applications implementations, but make sure you understand the components that make jsf a powerful tool.
2. jsp+servlet are best suited for service-oriented applications and need to control function of presentation through dispatching requests.
3. jsf and facelet are more appropriate for generating mark-up like xhtml, and generally used for presentation-oriented applications.
4. jsf enables development of an web application with only model objects (javabeans) and views (jsp/xhtml pages).
5. in a jsp/servlet application the following will be necessary : a lot of code to control, preprocess, postprocess, gather data, validate, convert, listen, etc the http request and response.
architectural overview of applications developed with jsf and jsp
as a developer, before you start coding, you are responsible to examine the ways in which you can design the project. specifically, you need to outline the responsibilities among functional components, and determine how they will interact with each other. as stated in the previous topic, both jsf and jsp have in common a the mvc (model-view-controller) paradigm so let's examine how an application that uses it is looking for each of them.
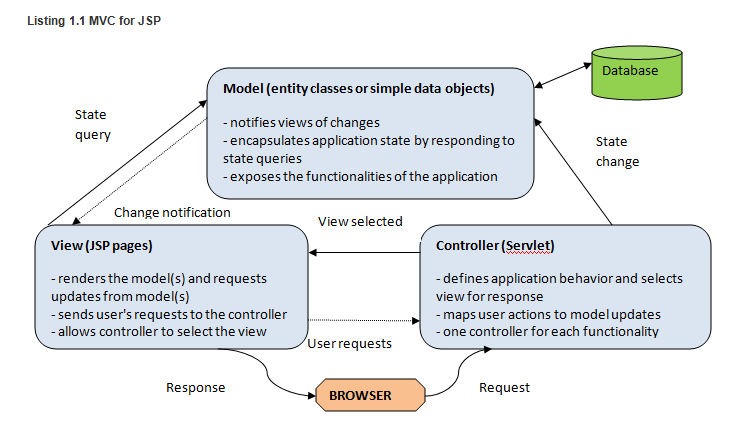
adopting the mvc design pattern for your application based on jsp (and not only) provides you with the following benefits:
- separation of design concerns : because of the decoupling of presentation, control, and data persistence and behavior, the application becomes more flexible; changes to one component have minimal impact on other components. new views can be created without needing to rewrite the model.
- more easily maintainable and extensible code : good structure can reduce code complexity. as such, code duplication is minimized.
- promotes division of tasks : developers with different skill sets are able to focus on their favorite skills and collaborate through clearly defined interfaces.
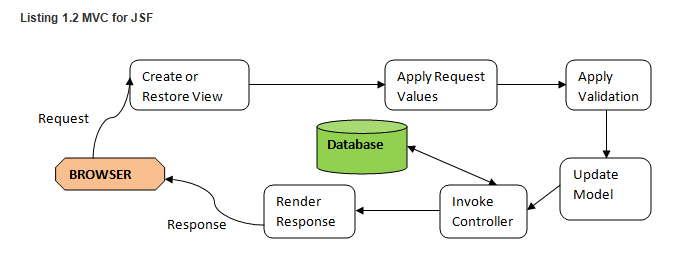
when using javaserverfaces2.0 or higher, a request-response cycle goes through six lifecycle phases ( according to specifications), defined as follows:
- create or restore view : restores or creates a server-side component tree (view) in memory to represent the ui information from a client.
- apply request values : updates the server-side components with fresh data from the client.
- process validations : performs validation and data type conversion on the new data.
- update model values : updates any server-side model objects with new data.
- invoke application : invokes any application logic needed to fulfill the request and navigate to a new page if needed.
- render response : saves state and renders a response to the requesting client.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments