Hybrid and Federated Cloud Computing
Clouds are growing more complex and interconnected. This overview covers the benefits and uses for cloud bursting, cloud brokerage, and multi-tier clouds.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreePlenty of enterprises today are in different stages of cloud adoption. New market trends and evolving business models are renovating the entire computing industry to focus more on a variety of cloud services from different providers that bring value to customers. Those enterprises are endeavoring to adopt the hybrid cloud ecosystem model, which encompasses administration of their traditional workloads as well as the workloads that are distributed across various clouds. The increasing prominence of hybrid cloud environments in industry's transformation is leading businesses to accentuate on innovative platforms, partnerships, agreements, regulations, designs, and federations.
Cloud federation provides a platform for fabricating a hybrid cloud ecosystem in a seamless manner with no vendor locks, giving customers a magnitude of players to choose from based on their budgets and investment plans. It also encourages users to switch from one platform to another with minimum risk and O&M costs.
Here's my favorite definition of cloud federation, as suggested by Reuven Cohen of Enomaly (from Cisco’s Cloud Computing Primer):
“Cloud federation manages consistency and access controls when two or more independent geographically distributed clouds share either authentication, files, computing resources, command and control, or access to storage resources."
In simple terms, it is cloud interoperability – communication and information exchange among different clouds in a reliable and streamlined fashion.
Let's cover some common models for cloud federation and their benefits:
Cloud Bursting Model
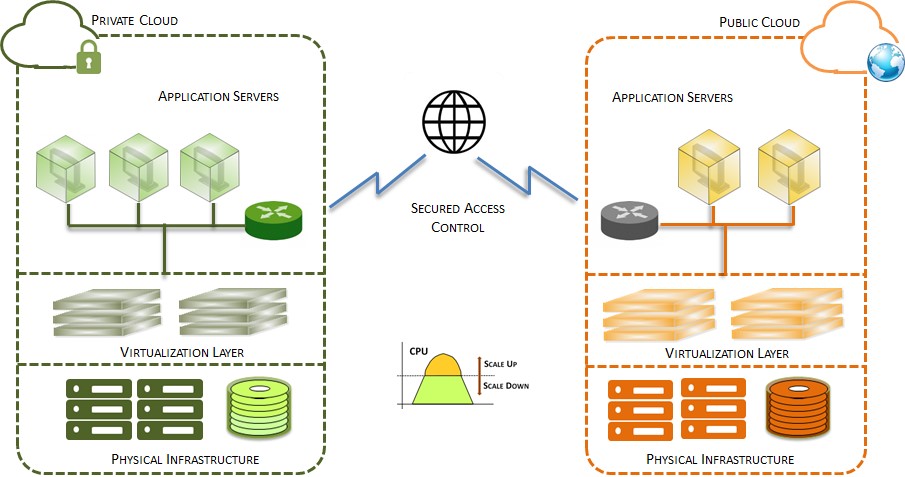
Cloud bursting is an application deployment model in which an application runs in a private cloud or data center and bursts into a public cloud when there is a necessity to meet peak demands or computing capacity spikes. Cloud bursting is best suited for minimum sensitive and non-critical applications with similar deployment and delivery infrastructure platforms across clouds.
Cloud Brokerage Model
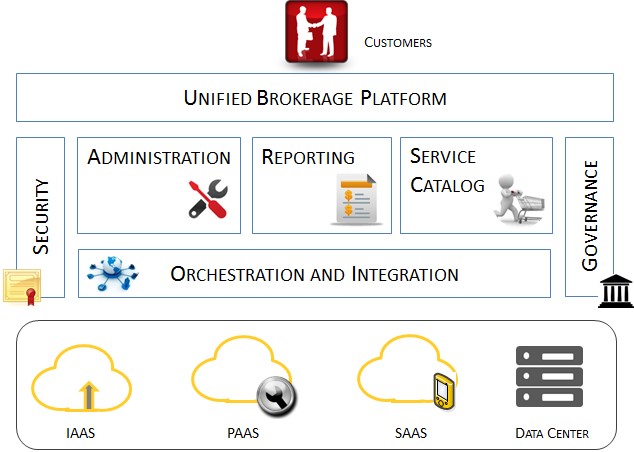
A cloud broker provides a unified platform to manage various clouds through a single sign-on and federated identity system with better cost, performance, and reliability optimization. The brokerage service removes the complexity of managing various provider platforms and simplifies the “several” into a single unified offering for consumption. The unified platform also assists the service consumers to compare various cloud services, choose appropriate cloud and deploy solution and services. The consumer would only subscribe to the service and pay for what he consumes. The major hitch with this model is that the service consumer has to heavily dependent on the cloud broker for all the operations and support.
Aggregated Cloud Architecture
There is a subtle difference between the cloud bursting and aggregated cloud models. The resource sharing in the case of aggregated clouds is between partners to meet peak demands. It enables distribution and management of complex IT services across diverse administrative domains and platforms. The main advantage over the cloud burst model is to accomplish advanced interoperation support, access control, resource monitoring, and secured cross-site operations among the partners.
Multi-Tier Cloud Architecture
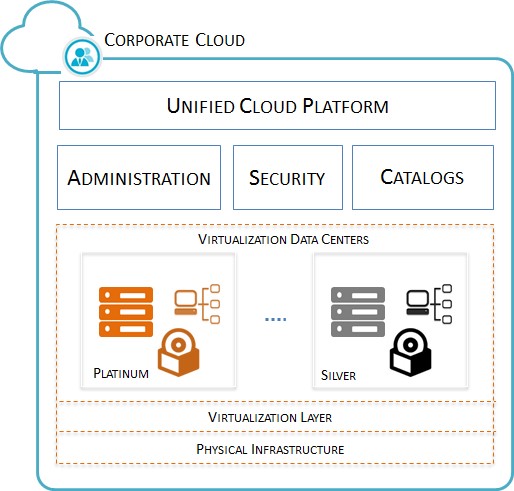
A multi-tier cloud is a unified platform fabricated to provide a wide variety of cloud services levels with a tiered pricing model. Each tier has dedicated resources and pre-defined regulatory policies and agreements. The tiers range from high-priced quality services to low-cost services. This is just like economy and business class flight tickets offered for air travel. Just as business class customers get more privileged services and treatment than economy class, similarly, tier 1 domain cloud services get better superiority services.
Application components can be arranged with lower-priority service levels assigned to lower-value components. Businesses can take calculated risks by applying lower-priced services to particular components and still use higher-priced services to support more critical areas of the enterprise.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments