Creating a Spring Boot Configuration Server Using a Database
Not many people talk about how to create a Spring Boot configuration server with a database as opposed to a file system or git repository. But here's how to do it.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeYou can find many articles on the internet about creating a Spring Boot configuration server using either a file system or git repository, but this is not true for a configuration server based on a database. In this article, I am going to discuss reasons to use a database as a configuration server and demonstrate how to create it using Spring Boot.
Storing configurations on a database seems to be a better idea than storing it on either a file system or git. Because it is less trackable, it is less secure. I admit that git has security and tracking options, but they seem to be complicated for a developer. However, tracking a database table is just creating a trigger for updates, and securing a database is not an issue for a developer. Again, changing a value in a database table is just so simple and easy to commit; however, it can be a cumbersome task to make a change in a git repository.
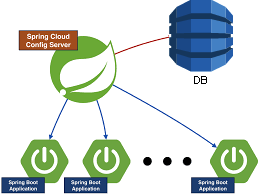
The overall architecture is as follows:
Once you have created your Spring Boot project from the Spring initializer, you need to add the following dependencies to your pom.xml file:
...
<!-- CONFIG SERVER -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- /CONFIG SERVER -->
<!-- JDBC -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ulisesbocchio</groupId>
<artifactId>jasypt-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-jdbc</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.zaxxer</groupId>
<artifactId>HikariCP</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<!-- Your database driver dependencies here -->
</dependency>
<!-- /JDBC -->
...Next, you will need to create a table in your database to store the configuration:
CREATE TABLE my_properties
(
application VARCHAR(200),
profile VARCHAR(200),
label VARCHAR(200),
KEY VARCHAR(200),
value VARCHAR(200)
) Finally, you will need to configure your configuration server with a application.yml file as shown below:
...
spring:
cloud:
config:
server:
jdbc:
sql: SELECT KEY, VALUE from MY_PROPERTIES where APPLICATION=? and PROFILE=? and LABEL=?
order: 1
datasource:
url: <your db url here>
driver-class-name: <your databases driver class here>
username: <your user to database>
password:
hikari:
maximum-pool-size: 10
connection-timeout: 5000
profiles:
active:
- jdbc
...Now, you can test your configuration server with a configuration client.
Here is a sample project.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments