Creating Application using Spring Roo and Deploying on Google App Engine
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSpring Roo is an rapid application development tool that helps you in rapidly building spring-based enterprise applications in the java programming language. Google app engine is a cloud computing technology that lets you run your application on Google's infrastructure. Using Spring Roo, you can develop applications that can be deployed on the Google app engine. In this tutorial, we will develop a simple application that can run on the Google app engine.
Roo configures and manages your application using the Roo shell. Roo shell can be launched as a stand-alone, command-line tool, or as a view pane in the Springsource tool suite ide.
Create it Fast and Effectively
Most who create applications want to make them fast, and they want to make them effectively. What this means is that if they can figure out a way to create something that will both work for their users and also provide them with the speed of transaction that they need, then it is entirely possible that this will be precisely what they need to do in order to get the best results.
Most are looking to Google search as a great way to get their apps out into the world, and it seems like this is as good of a place as any to start. Pushing out apps that can help the general population get the help they need with various projects means working with the most popular search engines in the world to make it happen. Thus, you should look to develop apps that work on Google in order to get the kind of results that you require.
Prerequisite
Before we can start using the Roo shell, we need to download and install all prerequisites.
Download and install SpringSource Tool Suite 2.3.3. m2. Spring Roo 1.1.0.m2 comes bundled with STS. While installing STS, the installer asks for the location where STS should be installed. in that directory, it will create a folder with the name "roo-%release_number%" which will contain roo stuff. add %spring_roo%/roo-1.1.0.m2/bin in your path so that when you can fire roo commands from the command line.
Start STS and go to the dashboard (help->dashboard)
Click on the extensions tab
Install the "google plugin for eclipse" and the "datanucleus plugin".
Restart STS when prompted.
After installing all the above we can start building the application.
Conferenceregistration.roo Application
Conference registration is a simple application where speakers can register themselves and create a session they want to talk about. So, we will be having two entities: speaker and presentation. Follow the instructions to create the application:
Open your operating system command-line shell
Create a directory named conference-registration
Go to the conference-registration directory in your command-line shell
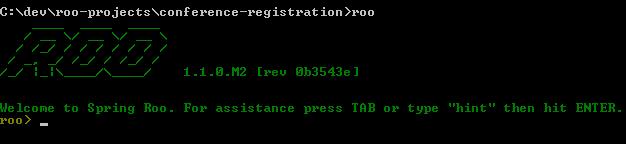
- Fire Roo command. You will see a roo shell as shown below. Hint command gives you the next actions you can take to manage your application.
![roo_shell]()
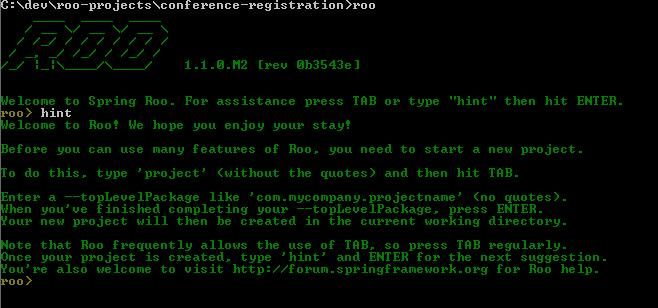
- Type the hint command and press enter. Roo will tell you that first you need to create a project and for creating a project you should type 'project' and then hit tab. Hint command is very useful as you don't have to cram all the commands; it will always give you the next logical steps that you can take at that point.
![hint_command]()
Roo hint command told us that we have to create the project so type the project command as shown below
project --toplevelpackage com.shekhar.conference.registration --java 6This command created a new maven project with the top-level package name as com. Shekhar.conference.registration and created directories for storing source code and other resource files. In this command, we also specified that we are using Java version 6.
- Once you have created the project, type in the hint command again, Roo will tell you that now you have to set up the persistence. Type the following command
persistence setup --provider datanucleus --database google_app_engine --applicationid roo-gae
This command set up all the things required for persistence. It creates persistence.xml and adds all the dependencies required for persistence in pom.xml. We have chosen the provider as DataNucleus and the database as google_app_engine because we are developing our application for google app engine and it uses its own data store. Applicationid is also required when we deploy our application to the Google app engine. Now our persistence setup is completed.
8. Type the hint command again, Roo will tell you that you have to create entities now. so, we need to create our entities' speaker and presentation. To create a speaker entity, we will type the following commands
entity --class ~.domain.speaker --testautomatically field string --fieldname fullname --notnull field string --fieldname email --notnull --regexp ^([0-9a-za-z]([-.\w]*[0-9a-za-z])*@([0-9a-za-z][-\w]*[0-9a-za-z]\.)+[a-za-z]{2,9})$ field string --fieldname city field date --fieldname birthdate --type java.util.date --notnull field string --fieldname bio
The above six lines created an entity named session with different fields. In this, we have used notnull constraint, email regex validation, date field. Spring Roo on the app engine does not support enum and references yet which means that you can't define one-one or one-to-many relationships between entities yet. These capabilities are supported on spring MVC applications but spring MVC applications can't be deployed on app engines as of now. Spring Roo Jira has these issues. They will be fixed in future releases(hope so :) ).
9. Next create the second entity of our application presentation. To create a presentation entity type the following commands on Roo shell
entity --class ~.domain.presentation --testautomatically field string --fieldname title --notnull field string --fieldname description --notnull field string --fieldname speaker --notnull
The above four lines created a jpa entity called presentation, located in the domain sub-package, and added three fields -- title,description and speaker. As you can see, the speaker is added as a string (just enter the full name). Spring Roo on google app engine still does not support references.
10. Now that we have created our entities, we have to create the face of our application i.e. user interface. currently, only GWT-created UI runs on the app engine. so, we will create GWT user interface. To do that type
gwt setup
this command will add the GWT controller as well as all the UI required stuff. This command may take a couple of minutes if you don't have those dependencies in your maven repository.
11. Next you can configure the log4j to debug level using the following command
logging setup --level debug
12. Quit the Roo shell
13. You can easily run your application locally if you have maven installed on your system, simply type "mvn gwt:run" at your command line shell while you are in the same directory in which you created the project. This will launch the GWT development mode and you can test your application. Please note that applications do not run in the Google chrome browser when you run from your development environment. So, better run it in firefox.
14. To deploy your application to the Google app engine just type
mvn gwt:compile gae:deploy
it will ask you for app engine credentials (email id and password).
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments