Migrating Spring Java Applications to Azure App Service (Part 1: DataSources and Credentials)
This tutorial demonstrates lift and shift in the cloud by migrating a Java legacy application and removing credentials from the code.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeOriginally published July 23, 2019
Running on the cloud is not only for cool new applications following 12-factor principles and coded to be cloud-native. Many applications could be converted to be cloud-ready with minimal adjustments — just to be able to run in the cloud environment. In the following few articles we will demonstrate how to address the most common migration items in legacy Spring applications — handling JNDI, and credentials, externalizing configuration, remote debugging, logging, and monitoring.
This article demonstrates how to migrate Java Spring/Hibernate applications using JNDI settings to cloud environment, externalize configuration, and how to keep credentials out of code by using Azure Managed Service Identity.
How Azure App Service Hosts Java
Azure App Service supports multiple application runtimes — Java, Node, Python, .NET and others. On Azure App Service Windows service, HTTP requests reach IIS on an App Server worker instance and is processed by theHttpPlatformHandlermodule. This module is described in detail in Microsoft docs. The role of HttpPlatformHandleris to start and manage an HTTP listener process on the localhost and proxy traffic to it. HTTP listener could be any process handling web requests. For a Java application we will configure Tomcat to process the requests.
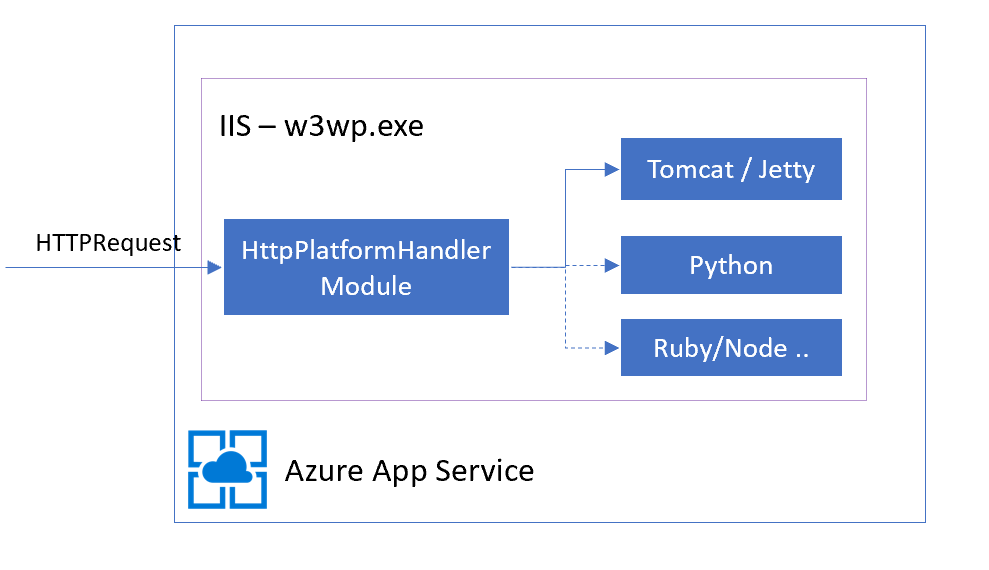
Azure App Service has necessary Java tools such as the JDK and Tomcat application server and configuration files installed and managed on the host. For example, managed Tomcat files are installed under D:\Program Files (x86)\apache-tomcat-x.x.xx\conf. Example of web.config that uses Tomcat as runtime:
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<handlers>
<remove name="httpPlatformHandlerMain" />
<add name="httpPlatformHandlerMain" path="*" verb="*" modules="httpPlatformHandler" resourceType="Unspecified"/>
</handlers>
<httpPlatform processPath="%AZURE_TOMCAT7_HOME%\bin\startup.bat" requestTimeout="00:04:00" arguments="" startupTimeLimit="60" startupRetryCount="3" stdoutLogEnabled="true">
<environmentVariables>
<environmentVariable name="CATALINA_OPTS" value="-Xms1024m -Xmx1024m -Dport.http=%HTTP_PLATFORM_PORT% -Dsite.logdir=d:/home/LogFiles/ -Dsite.tempdir=d:/home/site" />
</environmentVariables>
</httpPlatform>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>Spring/Hibernate JNDI DataSources for Azure SQL server
Majority of the legacy Spring Applications use Hibernate to implement data access. Hibernate is using container-managed JNDI DataSources in Tomcat application Server and referencing them as resources in descriptors.
There are few options to configure JNDI for the web application running under Tomcat (Tomcat JNDI):
- Application context.xml — located in app
META-INF/context.xml- define Resource element in the context file and container will take care of loading and configuring it. - Server.xml — Global, shared by applications, defined in
tomcat/conf/server.xml - Server.xml and context.xml — defining Datasource globally and including ResourceLink in application context.xml
When deploying Java application on Azure App Service, you can customize out-of-the-box managed Tomcat server.xml, but is not recommended as it will create a snowflake deployment. The right way is to define JNDI Datasource on the Application level.To do that add file META-INF/context.xml to the application.
The example used in this article posted in GitHub and context file is added to main/webapp/META-INF/context.xml and is defining connection to Azure SQL server:
<Context>
<Resource auth="Container"
driverClassName="com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver"
maxActive="8" maxIdle="4"
name="jdbc/tutorialDS" type="javax.sql.DataSource"
url="${SQLDB_URL}" />
</Context>To avoid putting credentials and environment specifics inside the application and in source control, the actual URL and username/password are referenced by environment variable which is set during application deployment.
Include SQL Server Driver libraries in pom.xml :
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.sqlserver</groupId>
<artifactId>mssql-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>7.2.0.jre8</version>
</dependency>and update Hibernate to use SQL Server dialect in resources\META-INF\persistence.xml
<property name="hibernate.dialect" value="org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServerDialect" />Spring Application Deployment
There are a number of options to create and deploy WebApp in Azure App Service. We will use a portal for simplicity. In Azure portal create WebApp + SQL and configure Tomcat and JDBC settings
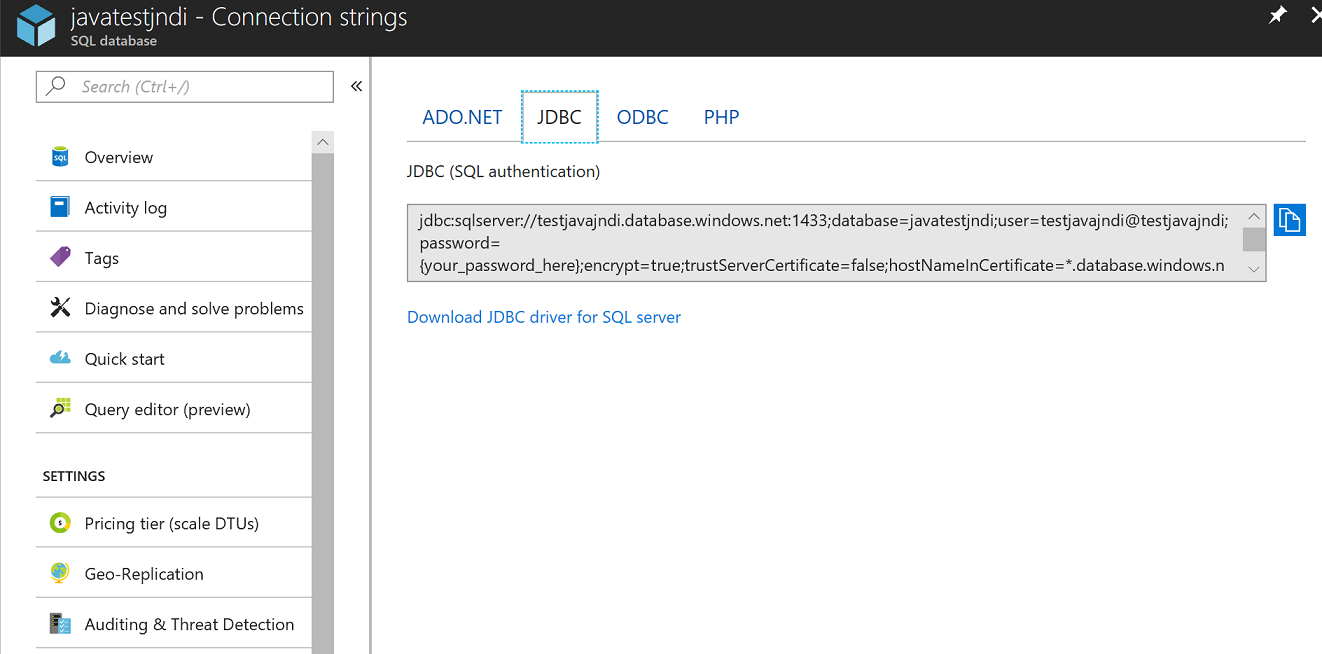
Copy Database connection String from Azure SQL JDBC tab
Add Azure SQL connection string to AppService/ApplicationSettings, so that it will be available to the Java application as an environment variable to be used in context.xml
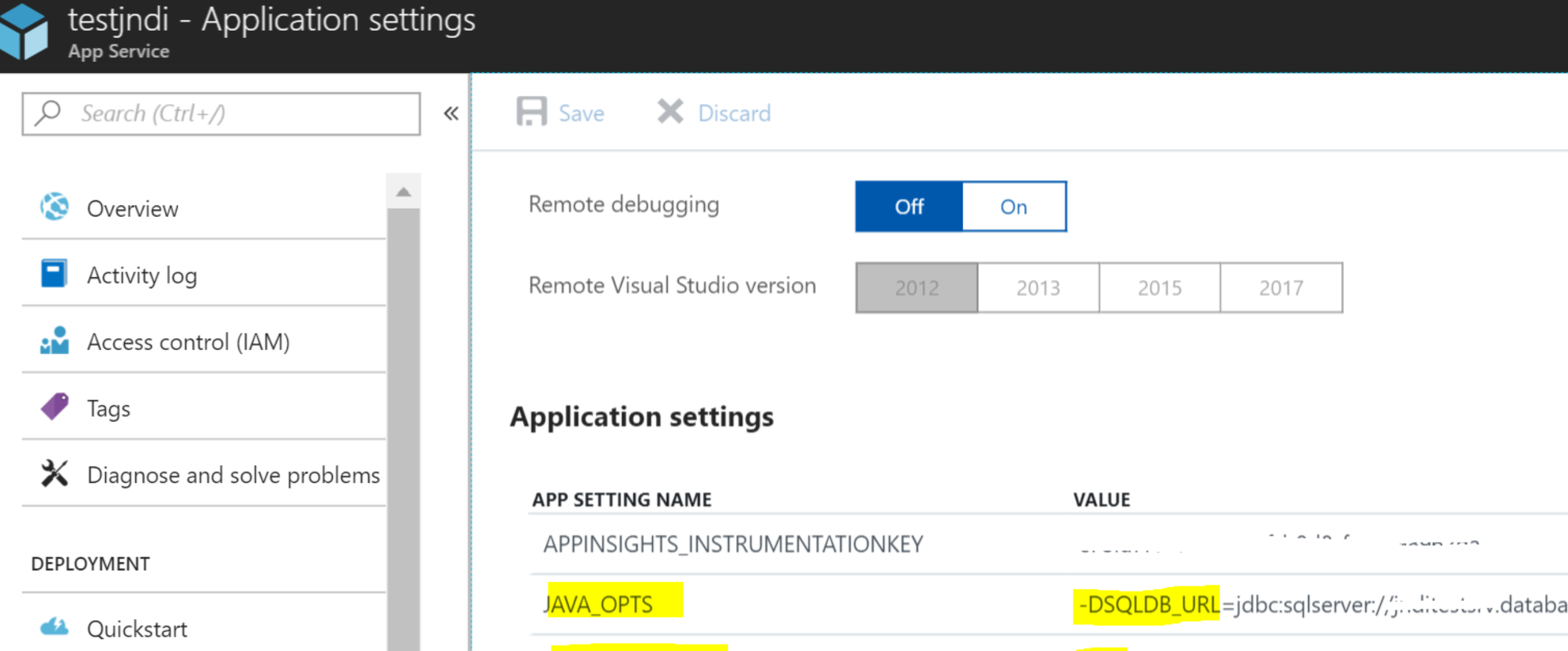
To make the environment variable available to Tomcat process on startup it should be passed as a parameter in JAVA_OPTS . As a result of the sample setting above variable SQLDB_URL will be available to the Tomcat application and bound in Datasource definition in context.xml.
Maven Deployment
Build and deploy the application using the Maven plugin or ftp. To use the Maven plugin:
- Setup authentication in
.m2/settings.xmlas described in this article and reference it as shown in lines 6-8 below. - Add following definition in pom.xml (pointing to server authentication) defining all the app service settings:
<plugin>
<groupId>com.microsoft.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-webapp-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1</version>
<configuration>
<authentication>
<serverId>azure-auth</serverId>
</authentication>
<!-- Web App information -->
<resourceGroup>testjavajndi</resourceGroup>
<appName>testjavajndi</appName>
<!-- <region> and <pricingTier> are optional. They will be used to create new Web App if the specified Web App doesn't exist -->
<region>canadacentral</region>
<pricingTier>S1</pricingTier>
<!-- Java Runtime Stack for Web App on Windows-->
<javaVersion>1.8.0_181</javaVersion>
<javaWebContainer>tomcat 7.0.81</javaWebContainer>
<stopAppDuringDeployment>true</stopAppDuringDeployment>
<appSettings>
<property>
<name>JAVA_OPTS</name>
<value>-DSQLDB_URL=jdbc:sqlserver://server.database.windows.net:1433;database=sqldb;authentication=ActiveDirectoryMSI;encrypt=true;trustServerCertificate=false;hostNameInCertificate=*.database.windows.net;loginTimeout=3</value>
</property>
</appSettings>
<!-- WAR deployment -->
<deploymentType>war</deploymentType>
<!-- Specify the war file location, optional if the war file location is: ${project.build.directory}/${project.build.finalName}.war -->
<warFile>${project.build.directory}/${project.build.finalName}.war </warFile>
<!-- Specify context path, optional if you want to deploy to ROOT -->
<path>/tutorial-hibernate-jpa</path>
</configuration>
</plugin>To build and deploy, run:
mvn clean package
mvn azure-webapp:deploy- war file will be deployed to d:/home/site/wwwroot/webapps/tutorial-hibernate.war
Example output:
[INFO] --- azure-webapp-maven-plugin:0.2.0:deploy (default-cli) @ tutorial-hibernate-jpa ---
AI: INFO 25-03-2018 19:31, 1: Configuration file has been successfully found as resource
[INFO] Start deploying to Web App testjavajndi...
[INFO] Authenticate with ServerId: azure-auth
[INFO] [Correlation ID: 462a8a7f-c2ec-40c8-a43b-80be705225b8] Instance discovery was successful
[INFO] Updating target Web App...
[INFO] Copying 1 resource to C:\projects\tutorial-hibernate-jpa\target\azure-webapps\testjavajndi\webapps
[INFO] Starting uploading directory: C:\projects\tutorial-hibernate-jpa\target\azure-webapps\testjavajndi --> /site/wwwroot
[INFO] [DIR] C:\projects\tutorial-hibernate-jpa\target\azure-webapps\testjavajndi --> /site/wwwroot
[INFO] ..[DIR] C:\projects\tutorial-hibernate-jpa\target\azure-webapps\testjavajndi\webapps --> /site/wwwroot/webapps
[INFO] ....[FILE] C:\projects\tutorial-hibernate-jpa\target\azure-webapps\testjavajndi\webapps\tutorial-hibernate-jpa.war --> /site/wwwroot/webapps
[INFO] ...........Reply Message : 226 Transfer complete.
[INFO] Finished uploading directory: C:\projects\tutorial-hibernate-jpa\target\azure-webapps\testjavajndi --> /site/wwwroot
[INFO] Successfully uploaded files to FTP server: waws-prod-yt1-005.ftp.azurewebsites.windows.net
[INFO] Successfully deployed Web App at https://testjavajndi.azurewebsites.netNavigate to https://<appname>.azurewebsites.net/tutorial-hibernate-jpa/create-user.html to test the app.
Get Credentials Out of the Code — Managed Service Identity
The solution above showed how to deploy a Java Spring application and connect it to Azure SQL DataSource. It requires managing credentials, although they are externalized from the code but still need to be managed and entered in application settings. This problem could be solved through the magic of Azure AD authentication and MSI (Managed Service Identity) More details about MSI are available here. Authentication flow is depicted below:
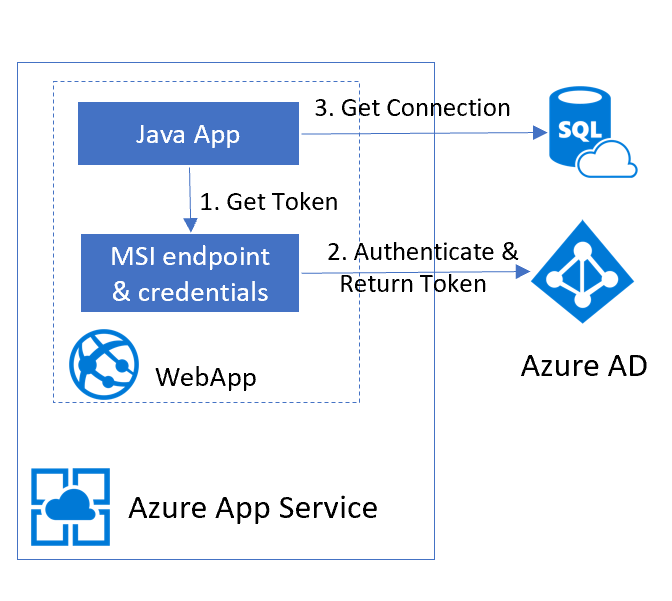
In summary, Managed Service Identity is Azure AD identity assigned to the service and fully managed by Azure. Once enabled on App Service, it makes local endpoint available to the Web Applications to fetch the Azure AD token (supported by injected credentials). This token could be used to authenticate to other services that support Azure AD authentication, such as Azure KeyVault and Azure SQL.
July 2019 Update: JDBC driver starting from version 7.2.0 supports MSI based Authentication natively, as descibed in Connect using Azure AD authentication and implemetation no longer requires custom libraries.
Enable Managed Service Identity in App Service
Steps to enable MSI in AppService:
- Assign MSI identity to Azure App Service — Azure will assign and inject AD credentials
az webapp identity assign --resource-group <resource_group> --name <app_service_name>
az ad sp show --id <id_created_above>- Grant MSI identity access to Azure SQL DB (it could be assigned to AD group or admin user)
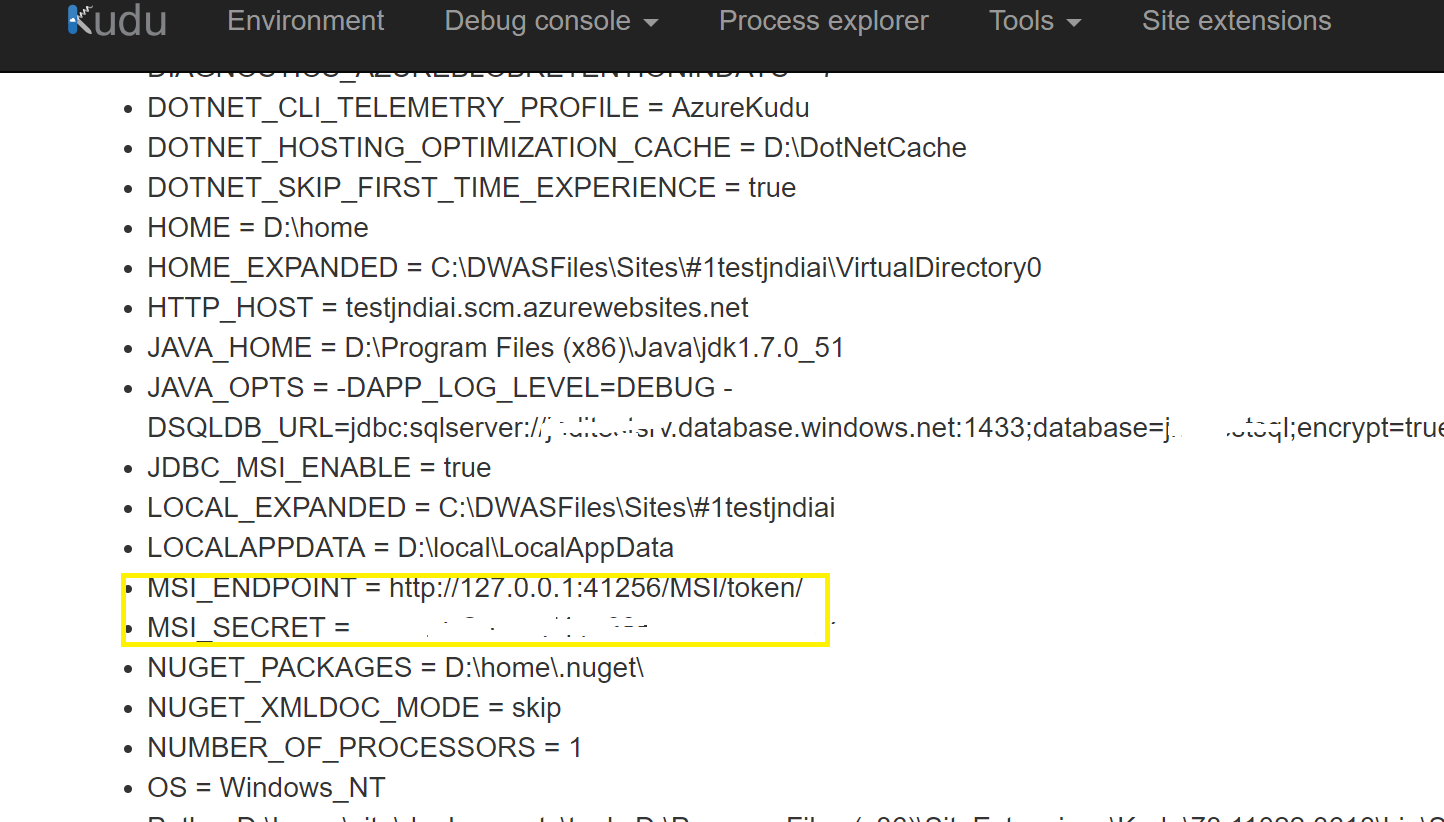
az sql server ad-admin create --resource-group <resource_group> --server-name <sql_server_name> --display-name <admin_account_name> --object-id <id_created_above>Verify using Kudu console thatMSI_ENDPOINTandMSI_SECRETvariables are injected by Azure
Connect JDBC With MSI Authentication
To use Azure MSI with JDBC driver set flag authentication=ActiveDirectoryMSI in connection URL using maven plugin ot Azure portal to set AppService settings:
<appSettings>
<property>
<name>JAVA_OPTS</name>
<value>-DSQLDB_URL=jdbc:sqlserver://<dbsrv>.database.windows.net:1433;database=<dbname>;authentication=ActiveDirectoryMSI;encrypt=true;trustServerCertificate=false;hostNameInCertificate=*.database.windows.net;loginTimeout=30;</value>
</property>
</appSettings>Build and deploy application, it's that simple now.
mvn clean package
mvn azure-webapp:deployJDBC driver will establish connection by getting AAD access token from the MSI endpoint and use it to connect to SQL server. It will also automatically refreh the token when it expires!
Summary
In this article, we have demonstrated how to take legacy Java Spring application and apply one of 12 factor principles by extracting configuration from code and providing it in environment variables. We have also shown how to get credentials out of the code by using Azure Managed Service identity.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments