Data Vault Data Model: An Efficient and Agile Approach for Data Warehousing
The Data Vault data model offers a unique and robust solution to these challenges, making it an increasingly popular choice among organizations.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the dynamically evolving field of data warehousing, traditional approaches often face challenges when it comes to flexibility, scalability, and adaptability. The data vault data model offers a unique and robust solution to these challenges, making it an increasingly popular choice among organizations.
The data vault data model is a design pattern that provides a structured and scalable foundation for building data warehouses. It is specifically designed to handle large volumes of data, offer agility in modeling changes, and ensure data integrity.
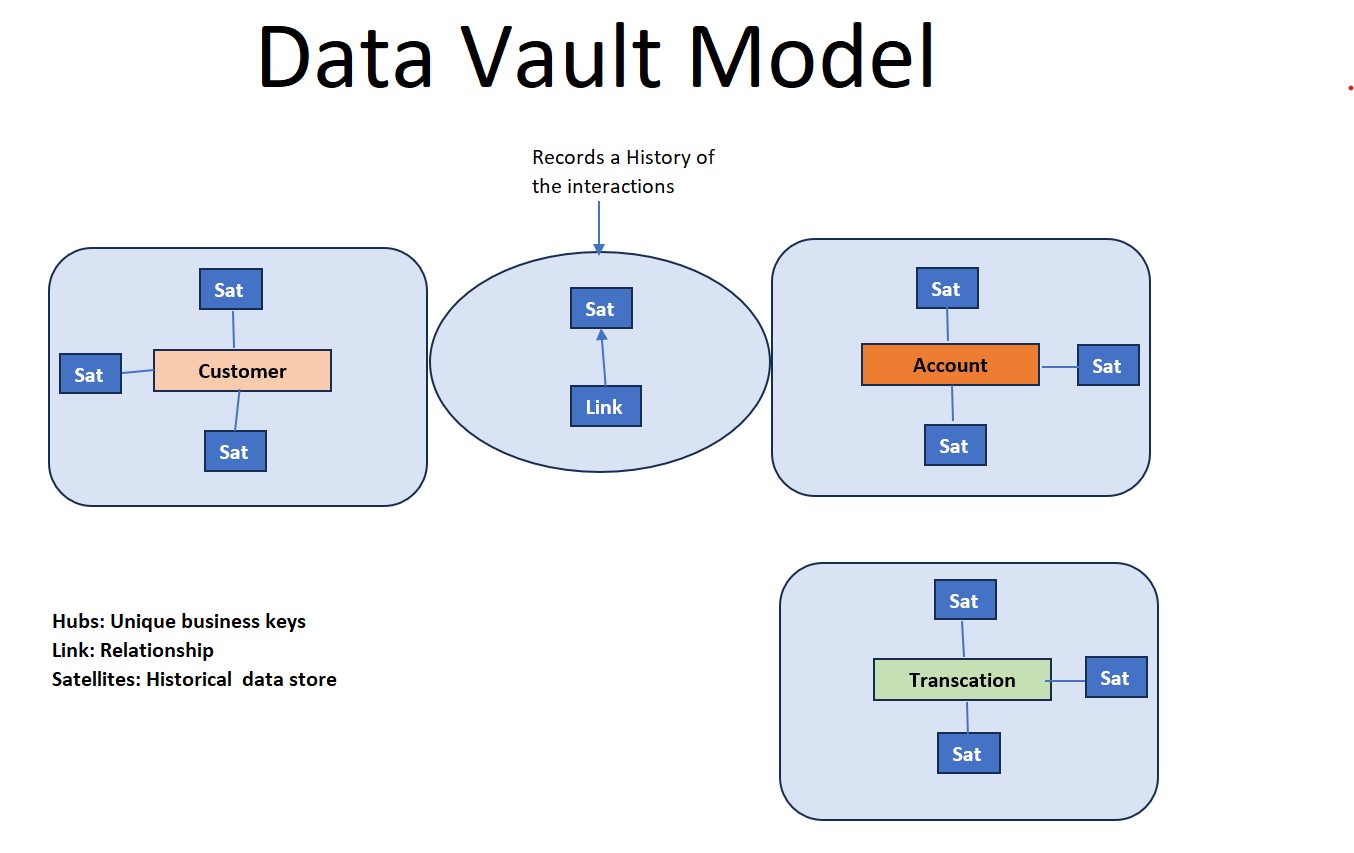
Unlike traditional approaches like the star schema or snowflake schema, the data vault model is built on three core components: hubs, links, and satellites. These components work together harmoniously to create a flexible and adaptable data structure.
Hubs
The hubs represent core business entities or concepts. They act as the primary keys for these entities and contain only unique business keys. Hubs help minimize redundancy and provide a scalable structure that can be easily expanded when new entities are introduced.
Links
Links connect the hubs and represent the relationships between different entities. Links are the glue that holds the data warehouse together, ensuring a clear and consistent view of the relationships between data points.
Satellites
Satellites contain additional descriptive information about the hubs. They hold attributes such as historical data, changes over time, or additional contextual data. Satellites are attached to hubs and links, providing a comprehensive and detailed view of the data.
The data vault model offers several advantages over traditional approaches:
Scalability
The data vault model is highly scalable and can handle large volumes of data with ease. As businesses generate more and more data, Data Vault can accommodate the increasing data load without requiring major redesigns or changes to the existing structure.
Flexibility
One of the key strengths of the data vault model is its flexibility. It allows for easy modifications and enhancements to the data model without affecting the existing structure or requiring extensive rework. This flexibility is crucial in today's rapidly changing business environment, where data requirements can evolve rapidly.
Historical Data Storage
The use of satellites in the data vault model allows for the storage of historical data. This feature enables businesses to analyze and track changes over time, facilitating better decision-making and trend analysis.
Data Integrity
The data vault model ensures data integrity by adhering to strict rules and constraints. Its design principles focus on maintaining the accuracy, consistency, and completeness of data, reducing the risk of data anomalies or discrepancies.
Incremental Loading
Data vault supports incremental loading, meaning that it can be updated incrementally without needing to reload the entire dataset. This feature simplifies data integration, as new data can be easily added without disrupting the existing structure.
Implementing the data vault model does come with some challenges. It requires a thorough understanding of the business domain and a disciplined approach to modeling. Additionally, it may require specialized tools and technologies to fully leverage its potential.
Conclusion
The data vault data model offers an efficient and agile approach to data warehousing. Its scalable and flexible design enables organizations to adapt to evolving data requirements and handle large volumes of data. With its data integrity and historical data storage capabilities, the data vault model empowers businesses to make better-informed decisions and unlock the full potential of their data.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments