Designing Web Apps for High Availability in AWS
Create your web applications with high availability and redundancy aspects in mind while using Amazon AWS products.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeBefore the advancement of cloud technologies, building highly available web applications was considered a complex task. This is mainly due to the need for specialized hardware, middleware, and expertise which required higher costs both for development and operations.
If we consider a traditional 3-tier web application with a web server and a database server, it is suspected for single points of failures. Although it's possible to use fault-tolerant hardware, it is really expensive which makes it difficult to afford for a small business. However, it is still susceptible to scalability limitations which could potentially cause availability issues.
With the advancement of cloud computing, it is possible to build highly available applications for reasonable costs by utilizing excess capacity, elasticity, and middleware services.
The idea behind cost reduction is simple. Since cloud uses commodity hardware, the costs go down for the infrastructure with its economies of scale and automation. With elasticity and middleware services, it is possible to further reduce the costs by paying for on-demand usage with redundancy and horizontal scaling, rather than committing large servers upfront to support the peak load.
Redundancy in AWS
First of all, let us understand the level of redundancy provided by AWS. At the largest scale, there are multiple Regions with groups of data centers called Availability Zones. These Availability Zones are distant from each other (with different flood zones, using power from different grids to reduces the likelihood of multiple Availability Zone failures at a time) but connected with high-speed Wide Area Network.
It is possible to use multiple Regions to implement web applications with extremely high availability requirements but for most of the uses cases, designing web applications to span across multiple Availability Zones is sufficient.
AWS offers several services that are globally redundant, meaning that a failure of a region doesn't affect their availability. For example, Route 53 (DNS), CloudFront (CDN), IAM (Identity and Access Management) are some of the regionally redundant services.
In addition, there are regional services, which are redundant across multiple Availability Zones such as Amazon S3 (Object Storage), Amazon EFS (Network File System), Amazon DynamoDB (NoSQL), Amazon ALB (Application Load Balancer), and are tolerant for individual Availability Zone failures.
At the Availability Zone level, there are services that are redundant within the data center cluster such as Amazon EBS (Block Storage).
As a rule of thumb, when comparing similar services, the services with higher redundancy will cost more than the ones with less redundancy. For example, if we compare storage, EBS pricing (Availability Zone Level Redundancy) with Amazon EFS (Regional Level Redundancy), EFS is costlier than EBS. However, there are exceptions where some of the redundant services are less costly or free to use, which generates indirect revenue by facilitating the provisioning of other services.
However, there are services that are not redundant by nature. For example, if we take an EC2 instance or a single instance database server, its likely that there will be a downtime due to hardware or software issues. Therefore, it is important to design the web applications for high availability, leveraging redundant services along with multiple instances of nonredundant ones.
Designing for High Availability
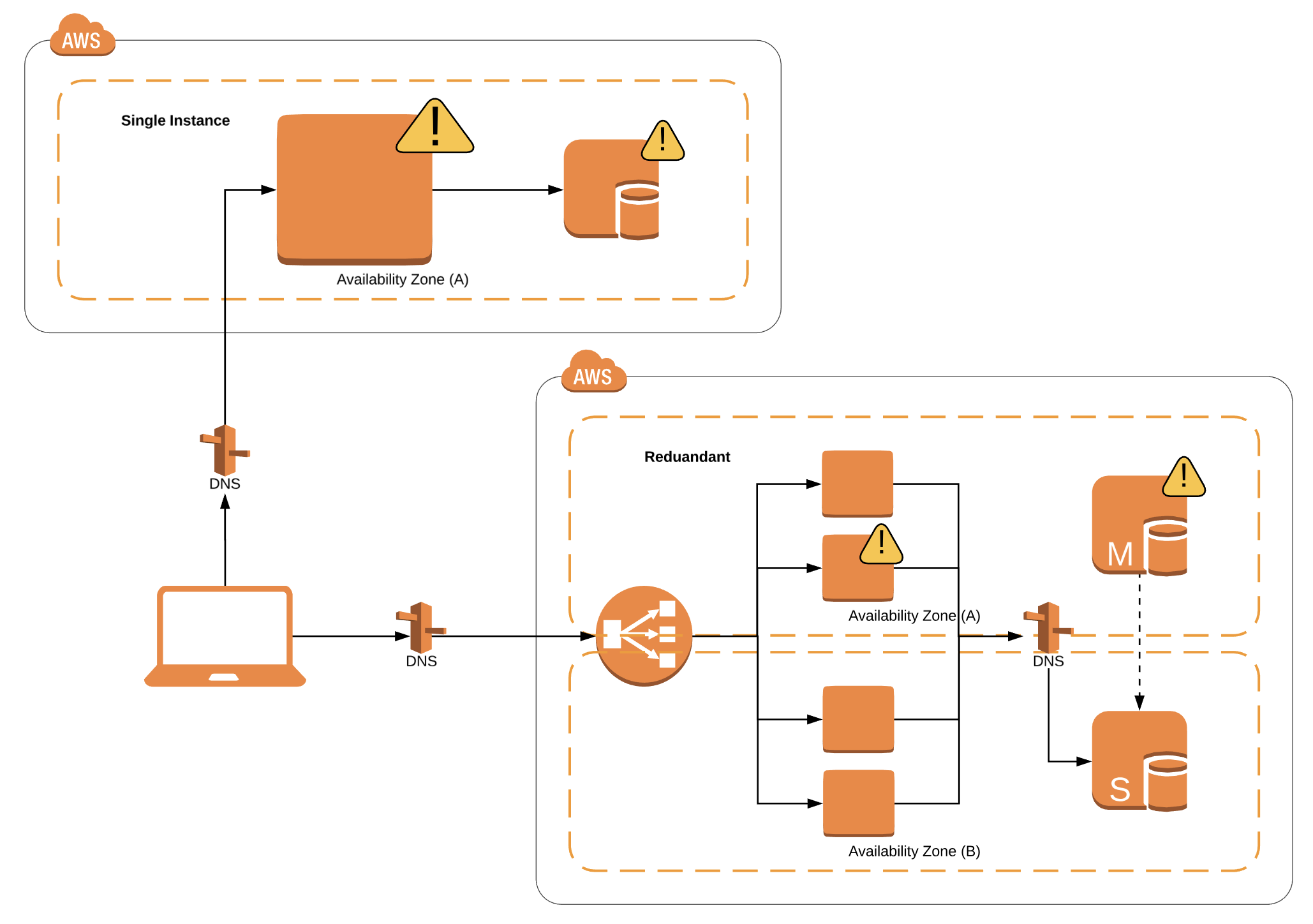
Let us look at how we can convert a traditional 3-tier web application with a web server and a database server to a highly available application.
First of all, it is important to identify single points of failures of the web application. In the particular case, the web server (EC2 instance) or the database server (EC2 instance or single AZ RDS) could potentially go down, affecting the overall availability of the application.
Web Server High Availability
By using an Application Load Balancer (which is highly available with the redundancy across multiple Availability Zones) along with a self-initiating fleet of web servers (EC2 instances), it is possible to make the web server highly available. With the support of Autoscaling Groups and Launch Configurations, it is possible to scale out and in automatically.
However, there are several characteristics that need to be fulfilled by the web server for high availability. One of the most important characteristics is to implement the servers statelessly or externalize the state so that any running server is able to the server any subsequent requests. It is also important to note that it is required to design the VPC with subnets spanning across multiple Availability Zones where we place the fleet of web servers, to achieve the higher level of availability without any additional costs involved. You also need to make sure that there is a health check endpoint at each web server instance so that the load balancer can decide whether to send future traffic or not based on its health. Health checks are also important for autoscaling groups to automatically provision a new instance, shutting down the faulty one.
Database Servers High Availability
If you are using regionally redundant NoSQL data storage such as AWS DynamoDB, AWS internally manages the availability of them. If we are looking at relational databases like MySQL or Postgres, it is recommended to have at least two instances of database servers (Master and Slave with active-passive high availability) which span across Availability Zones. Implementing this with EC2 will be slightly complex since its also required to synchronize the data across these instances as well as to switch to the active version via DNS when a database instance failure happens. If you use Amazon RDS for the relational database, you can enable the multi-AZ feature to implement high availability without any additional complexities.
Multi-Regional Deployment
If you have extremely high availability requirements, you can implement multiple regional deployments of the application with database synchronization across Regions (which can be tricky due to inherited latencies depending on the performance considerations).
In an event of a regional failure, switching between individual deployments in Regions can be done using DNS fail-over routing which can be configured with AWS Route53.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments