Distributed Tasks Execution and Scheduling in Java, Powered By Redis
A walk through the new features of Redisson node, a way to perform distributed task execution using Redis.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThe ability to immediately execute or schedule a task or job is becoming a typical requirement for a modern distributed Java application. Such requirements have became more essential for those who also use Redis.
Redisson is now providing a new convinient way to perform such distributed task execution and scheduling through the standard JDK ExecutorService and ScheduledExecutorService API, with submitted tasks executed on Redisson nodes, which are connected to the same Redis database.
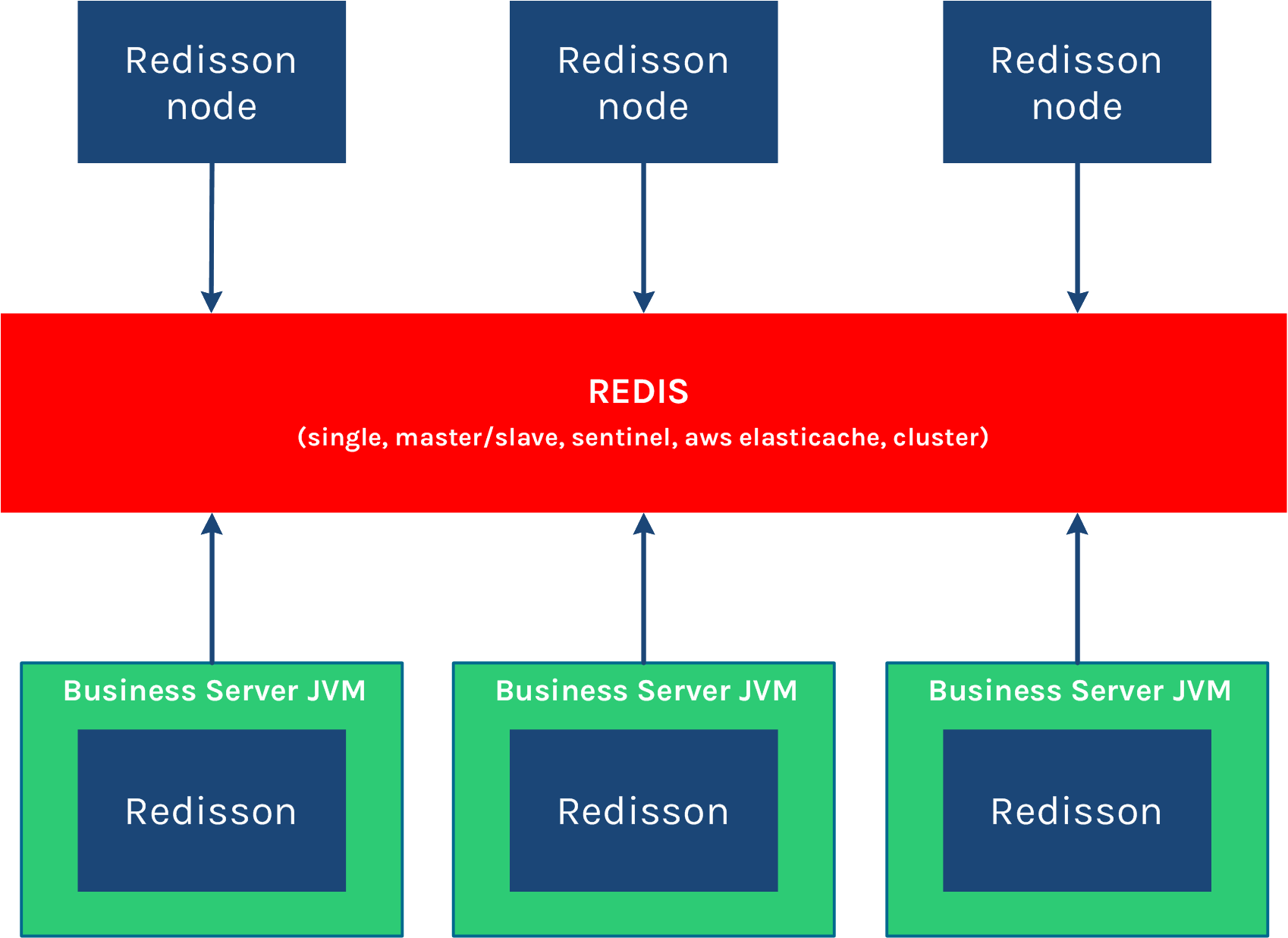
Redisson Node
Redisson Node is a standalone Java application whose sole purpose is to execute tasks that have been submitted to the same Redis instance it's connected to. A Redisson Node can be understood as a remote worker node in a distributed environment.
It can also be spawned as an independant process inside the main application via a Redisson instance.
All task classes are loaded dynamically so you don't need to have them in the classpath of Redisson Node and restart it due to task class changes.
Task Definition
A task should implement either java.util.concurrent.Callable or java.lang.Runnable interface.
Here is an example using Callable interface:
public class CallableTask implements Callable<Long> {
@RInject
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private long anyParam;
public CallableTask() {
}
public CallableTask(long anyParam) {
this.anyParam = anyParam;
}
@Override
public Long call() throws Exception {
// ...
}
}This is an example using Runnable interface:
public class RunnableTask implements Runnable {
@RInject
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private long anyParam;
public RunnableTask() {
}
public RunnableTask(long anyParam) {
this.anyParam = anyParam;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// ...
}
}Task can be parameterized via a constructor. A submitted task can be given access to a Redisson instance via @RInject annotation. This provides the task access to all Redisson features: Redis based Maps, Multimaps, Sets, Lists, Queues, Locks, Semaphores, PublishSubscribe, and many other objects, collections, locks, and services.
Submitting Task for Execution
It's pretty easy to submit a task through our ExecutorService API since RExecutorService already implements java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService.
RExecutorService executorService = redisson.getExecutorService("myExecutor");
executorService.submit(new RunnableTask());
// or with parameter
executorService.submit(new RunnableTask(41));
executorService.submit(new CallableTask());
// or with parameter
executorService.submit(new CallableTask(53));Submitting Task for Scheduled Execution
Scheduled tasks are submitted through using the java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService interface, which is implemented by the RScheduledExecutorService.
RScheduledExecutorService executorService = redisson.getExecutorService("myExecutor");
executorService.schedule(new CallableTask(), 10, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
// or
executorService.schedule(new RunnableTask(), 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
executorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new RunnableTask(), 10, 25, TimeUnit.HOURS);
// or
executorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new RunnableTask(), 5, 10, TimeUnit.HOURS);Scheduling a Task With Cron Expression
As we all understand how high the level of complexity of a moden application can be, the tasks scheduler service allows a user to define more complex scheduling using cron expressions. It is fully compatible with Quartz cron format.
RScheduledExecutorService executorService = redisson.getExecutorService("myExecutor");
executorService.schedule(new RunnableTask(), CronSchedule.of("10 0/5 * * * ?"));
// or
executorService.schedule(new RunnableTask(), CronSchedule.dailyAtHourAndMinute(10, 5));
// or
executorService.schedule(new RunnableTask(), CronSchedule.weeklyOnDayAndHourAndMinute(12, 4, Calendar.MONDAY, Calendar.FRIDAY));Task Cancellation
Any task can be cancelled at any stage:
Future<?> f = executorService.schedule(...);
// or
Future<?> f = executorService.submit(...);
f.cancel(true);No extra work is required to handle cancellation except in some cases when a task is already in the running stage. In this case, cancellation handling is similar to performing a thread interruption in Java.
Let's assume we have a task which aggregates all values in a very big Redis map, which may take a long time:
public class CallableTask implements Callable<Long> {
@RInject
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Override
public Long call() throws Exception {
RMap<String, Integer> map = redissonClient.getMap("myMap");
Long result = 0;
for (Integer value : map.values()) {
// check if task has been canceled
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
// task has been canceled
return null;
}
result += value;
}
return result;
}
}Extended Asynchronous Mode
All standard methods exposed in the java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService and java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService interfaces submit tasks synchronously and receive results in a asynchronous manner through the standard java.util.concurrent.Future object. Redisson also offers a set of RExecutorServiceAsync.*Async companion methods which can also be used to submit tasks fully asynchronously, and allows get task id and binds Listeners to a Future object.
RScheduledExecutorService executorService = redisson.getExecutorService("myExecutor");
RFuture<MyResultObject> future = executorService.submitAsync(new CallableTask());
// or
RScheduledFuture<MyResultObject> future = executorService.scheduleAsync(new RunnableTask(), 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// or
RScheduledFuture<MyResultObject> future = executorService.scheduleAtFixedRateAsync(new RunnableTask(), 10, 25, TimeUnit.HOURS);
future.addListener(new FutureListener<MyResultObject>() {
public void operationComplete(Future<MyResultObject> f) {
// ...
}
});
// cancel task by id
String taskId = future.getId();
// ...
executorService.cancelScheduledTask(taskId);Redisson Node is the latest game-changing feature we have added to the collection of useful toolsets provided by Redisson. We are commited to bring more features into the family in the coming future, please sit tight and be patient.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments