MySQL Setup in Docker for Mac
Docker for Mac allows you to build, debug, and test Dockerized apps on a Mac OS. Check out how to set it up to use MySQL!
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article will provide step-by-step instructions on how to set up MySQL in Docker for Mac and how to access MySQL from the host (Mac) OS. This article assumes that you know what Docker is, understand how to use MySQL, and understand how to use SQL commands to create a user, create a database, and grant privileges.
Before we jump into action, let's learn the basics of Docker for Mac.
Why Docker For Mac?
Docker is an abstraction on top of Linux containers to simplify using and managing containers. Mac OS is Unix and it doesn't have containers directly, as in Linux OS (Ubuntu, Fedora, Core OS, etc.). Hence, a Virtual Machine is set up on top of Mac OS and has an instance (Guest OS) of Linux to run containers. To simplify Docker and Virtual Machine setup in Mac OS, Docker for Mac was created.
According to this documentation, Docker for Mac is:
...an easy-to-install desktop app for building, debugging, and testing Dockerized apps on a Mac. Docker for Mac is a complete development environment deeply integrated with the MacOS Hypervisor framework, networking, and filesystem. Docker for Mac is the fastest and most reliable way to run Docker on a Mac.
Now that we have background info, let's see how to set up MySQL in Docker for Mac.
Follow these instructions to install Docker for Mac. After installing Docker for Mac, please verify the information below.
Note: $ is the prompt. Ignore it and copy the rest of the line.
$docker --version
Docker version 17.09.0-ce, build afdb6d4
Run the MySQL image using the docker run command.
$docker run -p 3306:3306 -d --name mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=password mysql/mysql-serverThis will install the latest version of the MySQL image in Docker Hub. As of this writing, it was 5.7.
If the image was not already available, this command will download the image and run it.
You can verify if MySQL has started using the docker ps command below.
$docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED
a3fb00c34877 mysql/mysql-server "/entrypoint.sh my..." 2 minutes ago
STATUS PORTS NAMES
Up 2 minutes (healthy) 0.0.0.0:3306->3306/tcp, 33060/tcp mysqlLog into MySQL within the docker container using the docker exec command:
$docker exec -it mysql bash
bash-4.2# mysql -uroot -ppassword
mysql>Remember, when we created and ran the MySQL container, we provided MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=password.
Create a database and user, and grant privileges in MySQL (from within the container).
Log into MySQL if you haven't already. After login, the mysql> prompt shows up:
bash-4.2# mysql -uarun -ppassword
mysql>I create a user named arun, grant all privileges, and quit.
Important: This step is required to log into MySQL from outside the container. The root user will not be able to log in from the host OS (Mac OS). Use % instead of localhost in arun@localhost.
mysql> CREATE USER 'arun'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON * . * TO 'arun'@'%';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> quitConnect to MySQL running in Docker from MySQL Workbench. If MySQL Workbench is not installed yet, follow these instructions to install it.
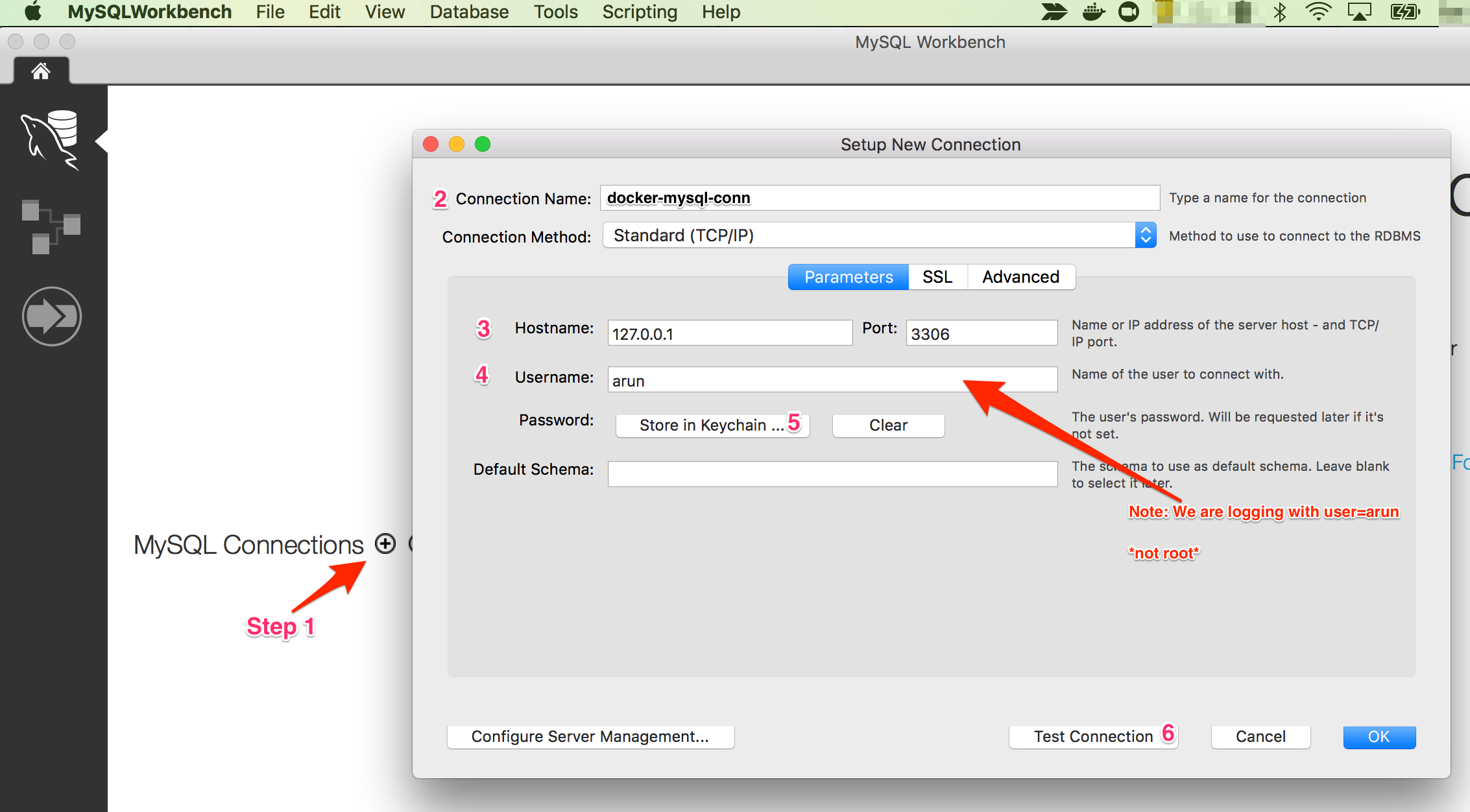
Open MySQL Workbench and click on + to add a new connection. Enter all the information as stated in the screenshot and click on Test Connection.

Enjoy creating and accessing your MySQL database running in a Docker container! For more MySQL docker run options, refer to here.
If there is something that can be improved in this article, please provide your thoughts in the comments.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments