Error Tracking With Vue.js
In this article, we’ll show you how to add error handling in a Vue.js-based application to capture caught and uncaught errors.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeVue (pronounced /vjuː/, like view) is a progressive framework for building user interfaces on the web. Vue can power sophisticated single-page applications and is often used in combination with modern tooling and supporting libraries. We’ll show you how to add error handling in a Vue application to capture caught and uncaught errors. This gives you an opportunity to recover and update what’s presented to the user, as well as track the error to prioritize fixes. We’ll also show how to monitor errors in production using Rollbar.

How to Handle Errors in Vanilla Vue
You can catch exceptions in vanilla JavaScript using basic try, catch and finally statements. You can use these statements to handle caught exceptions in Vue components. In this example, we are simply logging to the console.
try {
JSON.parse("non-JSON data")
} catch(e) {
console.log('Exception: ', e)
}Vue provides a standard API to add a custom errorHandler. You should configure this on your root Vue instance, typically in a main.js file. However, it only captures errors that occur during component rendering. That means it won’t catch errors that happen later as a result of user behavior, etc.
Vue.config.errorHandler = err => {
console.log('Exception: ', err)
}To handle errors globally across your entire page, you can add a handler to the onerror function on the window.
window.onerror = function(message, source, lineno, colno, error) {
console.log('Exception: ', error)
}While this is great for handling errors during development, when you deploy to production you need a way to track those errors centrally to determine how they are affecting user experience.
Monitor Vue Errors With Rollbar
Errors logged to the console are less useful in a production environment because your developers won’t have access to them. It’s important to monitor errors centrally so you can fix them before more customers are affected. This can help prioritize high impact errors and troubleshoot the causes faster.
Rollbar’s JavaScript SDK lets you track and analyze errors that happen in your Vue applications, including detailed stack traces, request params, telemetry on user behavior, affected users, and more. This helps developers quickly identify and fix errors. Learn more about Rollbar’s JavaScript features.
Below, you can see that we’ve created an example app that triggers an exception when the user clicks on a button. The error message is tracked in Rollbar, including a stack trace where you can see the line of code that caused the error. Rollbar captures errors that occur anywhere in the app.

How to Set up a Vue Project on Rollbar
- Visit https://rollbar.com and sign up for an account if you haven’t done so yet. Next, create your project and select 'Other' from the list of notifiers. Select the client side access token that is generated for you. You’ll need this to configure Rollbar in the steps below.
- To install the vue-rollbar plugin in your project through npm, open the command prompt in the project root directory and run the command below.
npm install vue-rollbar --saveAdding Rollbar in the Error Handler
To add Rollbar to your Vue application, you need to follow some simple steps.
- Add Rollbar in the main.js file. You can find main.js file under the src folder in your root project directory.
var Rollbar = require('vue-rollbar');- Next, you need to use Rollbar with an access token and some optional parameters. Here we've set
captureUncaughtto true, so we don't even need to wire an event handler to theonerrorfunction. Rollbar does this automatically.
Vue.use(Rollbar, {
accessToken: 'ACCESS-TOKEN’',
captureUncaught: true,
captureUnhandledRejections: true,
enabled: true,
source_map_enabled: true,
environment: 'production',
payload: {
client: {
javascript: {
code_version: '1.0'
}
}
}
});- Finally, add the Rollbar error reporting method in the error handler.
Vue.rollbar.error(err);After adding the Rollbar error reporting method, the main.js file looks like this:
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
var Rollbar = require('vue-rollbar');
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
Vue.use(Rollbar, {
accessToken: 'ACCESS-TOKEN',
captureUncaught: true,
captureUnhandledRejections: true,
enabled: true,
source_map_enabled: true,
environment: 'production',
payload: {
client: {
javascript: {
code_version: '1.0'
}
}
}
});
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
render: h => h(App)
})Upload Source Maps to Rollbar
If you use JavasScript, Rollbar can map the error message back to your original source code using source maps. Source maps are essential to debugging production code. They link the browser’s debug output back to the original source code before it was minified or transpiled. To display stack traces with your original code, Rollbar needs access to the source maps for your minified JavaScript.
To upload the source map, you need to add a Rollbar source map API call in your deployment script. Here is an example using curl:
curl https://api.rollbar.com/api/1/sourcemap/ \
-F access_token=’SERVER-ACCESS-TOKEN’\
-F version=’1.0’ \
-F minified_url=https://s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/rollbar-example/app.[hash].js \
-F source_map=dist/static/js/app.[hash].js.map \
-F App.vue=App.vue \
-F HelloWorld.vue=HelloWorld.vueThe parameters in this API call are:
- access_token: The destination project token on Rollbar. This token is generated when a project is created on Rollbar.
- environment: The deployment environment where the service is deployed. We can configure different environments such as development, staging, and production.
- version: The deployed application version. Rollbar will create a link to the repository commit source code if the supplied version is the commit ID.
- minified_url: The full URL of the minified file. It should start with
http:orhttps:, which we’ll strip off. - source_map: The contents of the source map, as a multipart file upload.
Testing the Sample Application
To test that it’s working, create a page that will generate an error message. In the example below, you’ll be able to generate an error by clicking the "Generate an error" button.
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>Rollbar Vue Example</h1>
<ul>
<li>
<button v-on:click="parse">Generate an error</button>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Vue from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
props: {
msg: 'Rollbar Example'
},
data: () => ({
clicks: 0,
json: '{ "not quite: json" }'
}),
methods: {
parse: function () {
JSON.parse(this.json) // SyntaxError: JSON.parse:
}
}
}
</script>Viewing Errors in Rollbar
Open Rollbar to see what these errors look like in your account’s item page. The error we just generated should be called "SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ':'"
Get more details by clicking on the item. You can now see a traceback showing you the exact source code file, method, and line number that generated the error.
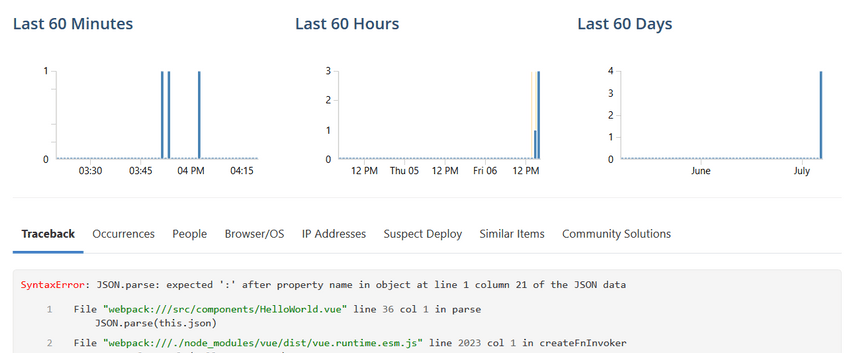
Now that you have Rollbar integrated into your Vue app, any errors that occur will be captured, grouped, and reported to Rollbar. You’ll be able to quickly and easily see which errors are occurring, how often they occur, as well as the full context. This will help you troubleshoot the cause faster and fix the problem so fewer customers are affected. If you haven’t already, sign up for a 14-day free trial of Rollbar.
Published at DZone with permission of Jason Skowronski, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments