Fire Up BDD Inside Docker With Cucumber and BDDfire
BDDfire allows you to set up the entire framework with code quality, browser testing, cloud testing, API testing, and Docker integration by running three simple commands.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Freethe key benefits of behavior-driven development (bdd) practices are communication enhancement and customer satisfaction. you can read more on that from dan north and gojko adzic . perhaps the biggest practical challenge that stands in the way of reaping those benefits is the burden of provisioning, installation, maintenance of requisite complex and fussy infrastructure and setting up reliable test infrastructure.
cucumber is one of the most popular bdd frameworks available in the market to achieve the benefits from bdd practices. the problem is that software teams seems to spend a lot of time setting up cucumber and the necessary toolkit around it. the management has to decide the tools and engineers have to research all the available tools to support agile practices like ci, code quality, test reporting, parallel execution, devops integration, etc. the process of getting bdd framework in a mature state becomes lengthy. obviously, such an approach would be time-consuming, inefficient, and costly. in this post, let's see how to get up and running with three simple commands to set up a ruby-cucumber bdd framework with docker support using bddfire .
bddfire
bddfire is an instant ruby-cucumber bdd framework that collectively installs bdd-supporting tools and gets you up and running within a minute. it is a ruby library that creates a skeleton for the ruby-cucumber bdd framework. bddfire will create all the directories and required files to support the latest open-source libraries in the ruby-cucumber framework. you can read about bddfire here .
bddfire features
cucumber is a very popular bdd framework. cucumber becomes more effective when it’s plugged with other open-source libraries. sometimes, we miss most of the useful libraries to be used with ruby-cucumber. bddfire supports lots of modern open-source libraries so that we won’t miss new trends in the world of ruby-cucumber.
bddfire has following features:
- create template directories and files for the cucumber project.
- capybara and webdriver integration for executing acceptance scenarios in real browsers.
- capybara and poltergeist integration to execute scenarios in headless browsers.
- lots of pre-implemented steps so that you don't have to write much code.
- supports api testing using with predefined steps.
- supports test execution inside docker containers with phantomjs.
- supports cuke_sniffer and rubocop libraries which detect smell in the ruby-cucumber framework.
- supports relish for the living documentation.
- rakefile has been automatically created as a part of bddfire.
- supports yard documentation of the cucumber project.
- supports page object pattern .
- load and accessibility testing with gatling and axe engine.
bddfire motivation
bddfire is motivated by few simple facts which could save organisation spending lot time and money on setting up frameworks to enable bdd.
- three commands to get up and running with bdd.
- write your tests, not framework.
- automate with less code.
- set up now, learn later.
three commands toward bdd
with bddfire, we can go from zero to complete bdd framework by running just three simple commands:
$ gem install bddfire $ bddfire fire_cucumber $ cd cucumber && bundle installlet's see how to get up and running with the cucumber-style bdd framework within a few minutes.
requirements
in order to get started with bddfire, we have to make sure that following packages are installed on the machine.
- ruby >2.0.
- docker installed on the machine to run our bdd scenario inside containers.
-
phantomjs
to run scenarios using poltergeist capybara driver. on a mac, you can simply install it using
homebrew
brew install phantomjs. -
gecko driver
to run scenarios inside firefox. on a mac, you can simply install it using homebrew
brew install geckodriver.
bddfire installation
bddfire is a rubygem and it can be installed using:
$ gem install bddfire
if you are using ruby, then you have to run the command using
sudo
. it will take a bit of time to download all the required ruby libraries. once finished without errors, you should be able to use the
bddfire
command. now, run the
bddfire
command from the terminal to see all available options.
$ bddfire usage: bddfire <command-name> [parameters] [options] <command-name> can be one of help prints more detailed help information. fire_cucumber generate a features folder structure. fire_accessibility setup accessibility checks with axe-matchers fire_load setup load and performance tests using gatling version prints the gem version
that's it. we have successfully installed bddfire. now, let's install the ruby-cucumber bdd framework using the
fire_cucumber
command.
$ bddfire fire_cucumber
this will create the
cucumber
directory and set up all of the frameworks within that directory. bddfire will create all the required files for our framework.
let's
cd
into the
cucumber
directory and install the bundler.
$ cd cucumber$ bundle installcongratulations! you have just set up the bdd framework with all the basic toolkits to cover code quality, browser and cloud tests, api tests, and docker integration. let's explore how to use it.
start running scenarios
now that we have installed our ruby-cucumber framework with all files and directories, we can run our first headless scenario using poltergeist .
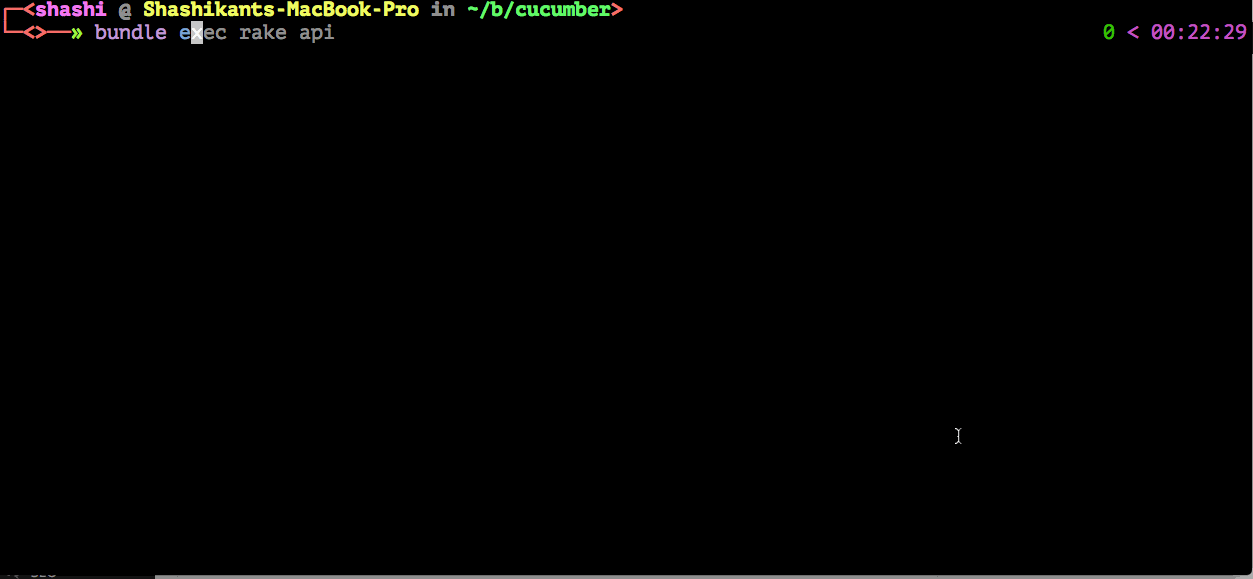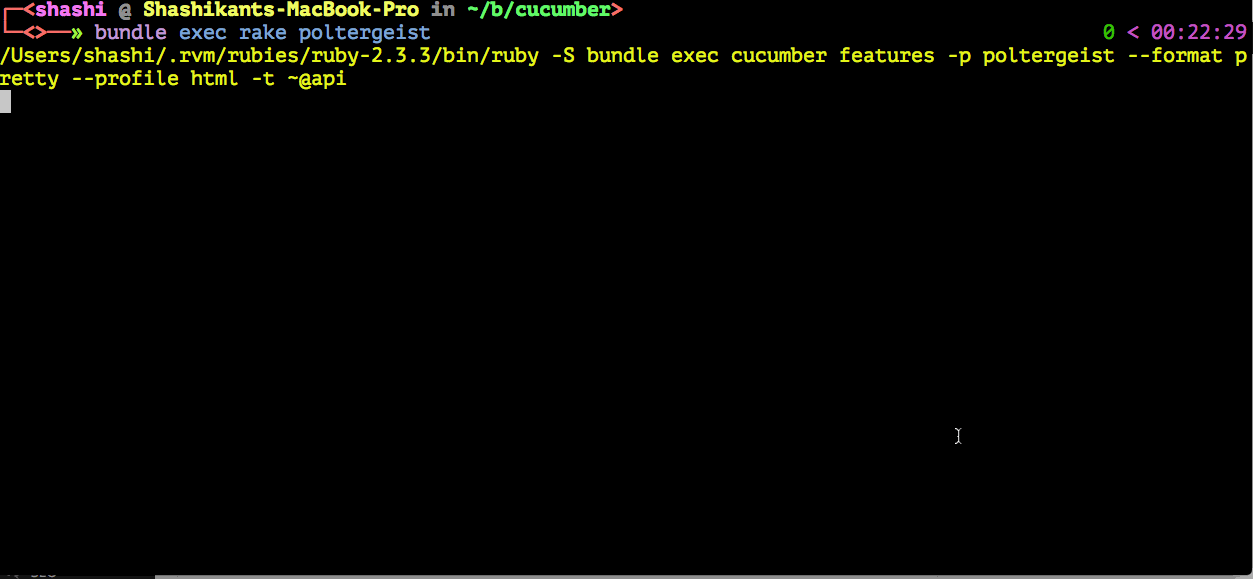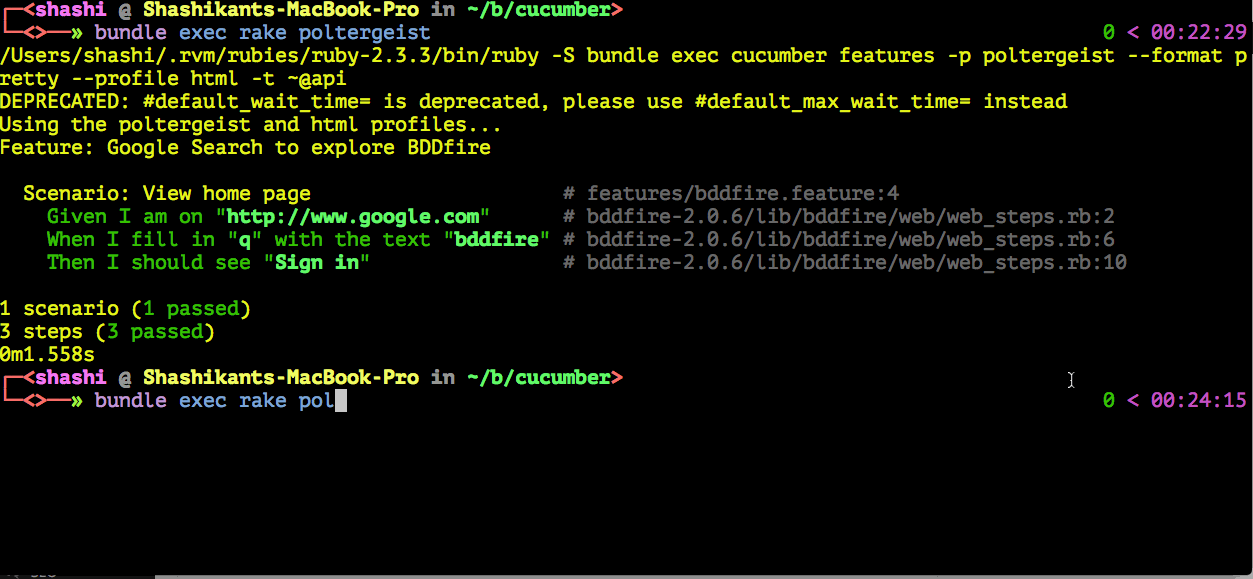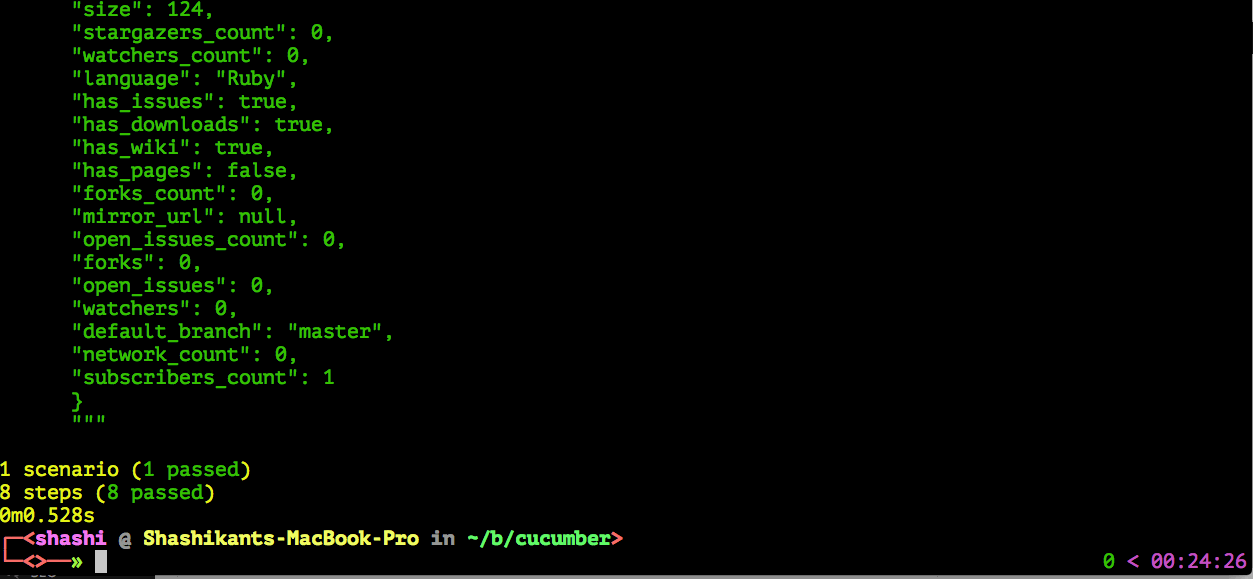
$ bundle exec rake poltergeist
you won't see that the browser as a scenario is executing within headless browser
phantomjs
. however, we can take screenshots and debug information by tweaking
poltergeist
setup in the
features/support/env.rb
file.
real and headless browser support
automated cucumber scenarios can be run with a real browser or with a headless browser. bddfire gives you the option to run them in both. selenium webdriver can be used to run automated cucumber scenarios in real browsers without any additional setup. selenium driver for capybara is setup for you with a default cucumber profile. we can run our scenarios in the firefox or chrome browser like this:
$ bundle exec rake firefox$ bundle exec rake chrome
in a similar way, we can run the scenarios in headless browsers like phantomjs using poltergeist as the capybara driver. the poltergeist driver is already setup for you in the
features/support/env.rb
file. bddfire also created a profile to run scenarios with the headless browser. you can see your scenarios executed but you won’t see any browser launched. this helps run automated cucumber scenarios faster than with real browsers.
there is one more pre-defined scenario for running api test which checks json response from github. we can run that test using:
$ bundle exec rake apicloud testing support
bddfire gives you the option to run tests in third-party cloud testing services like
saucelabs
,
browserstack
, and
testingbot
. in order to use those services, you need to create an account and get an username and assess key. there are various rake tasks to the run tests in the cloud testing services like saucelabs, testing or browserstack. we just need to plug our username and api key in the
feature/support/env.rb
file.
you can then use that access key in the
features/support/env.rb
file to run the automated cucumber scenarios. if you are running tests in browserstack, you will have all the stacks defined in the
browser.json
file. we can use any of them. we need to configure the browserstack username and access key in the driver configuration.
$ bs_stack=osx_firefox bundle exec rake browserstackusing the same setup, you can run automated scenarios in the other third-party testing services like saucelabs and testingbot.
living documentation
bddfire gives you the option to use relish as a living documentation tool. relish publishes feature files online so that the whole team can read and access them. in order to use relish, you need to have a relish account and api token that can be obtained by visiting this link after logging in.
bddfire creates a file
.relish
where you need to paste your token. now, you can publish your feature files online by using:
$ bundle exec relish push {publisher}/{project}code quality
bddfire comes with two code quality checking tools: rubocop to check ruby code quality and cuke_sniffer to detect smells in the cucumber features, step definitions, and hooks. bddfire creates a
.rubocop.yml
file with basic ruby code quality rules. you can change the configuration according to your requirements. with this configuration, you can use rubocop to detect smell in our ruby code
$ bundle exec rake rubocopin a similar way, you can use cuke_sniffer to detect smells in the cucumber project. cuke_sniffer runs through all feature files, step definitions, hooks, and support code. it finds out dead steps and suggests improvement for writing better feature files. you can execute cuke_sniffer like this:
$ bundle exec rake cake_sniffercontinuous integration
bddfire creates a
ci_script
file to run automated cucumber scenarios on a continuous integration server like hudson and jenkins. it clears the workspace by deleting old reports, creates yard documentation for your project, and runs rubocop and cuke_sniffer before executing your scenarios. you can also change this file to suit your project need. you can execute this bash script on any ci by passing one of the rake tasks.
$ ./script/ci_script rake-taskadd a scenario with pre-defined steps
bddfire allows us to use predefined steps so that we don't have to write more code while writing cucumber steps. bddfire has following predefined steps which can be used anytime during your project. this is a major advantage if the test engineer is non-technical. he or she can write automation code using those steps.
browser based pre-defined steps
you can use browser-based steps to run scenarios within browsers like google chome or firefox.
poltergeist based pre-defined steps
you can use headless poltergeist-based steps to run bdd scenarios with phantomjs, which is a headless browser.
api based pre-defined steps
just tag your scenario or feature with
@api
and you can use inbuilt predefined
api-based
steps.
start running scenarios within docker containers
docker has become a powerful tool in the world of continuous delivery and continuous deployment. software teams have to provision all the infrastructure to run as a docker container. it would be awesome if we could able to run cucumber scenarios inside the docker container. fortunately, bddfire has done all that provisioning work for us; however, we can only run phantonjs- and poltergeist-based headless scenarios within docker containers. bddfire will:
- build a docker image with provisioned with ruby and phantomjs.
- map the project directory to docker container and install software.
- run bdd scenarios inside the docker container.
assuming that you have docker installed, you just need to need to execute this docker rake task:
$ bundle exec rake dockerthis will take a while, as docker images will be built from scratch. be patient and watch the bdd scenarios running inside containers at the end.
we can mount the volume of our project repository and docker containers to generate and share test reports. you can modify
dockerfile
and script
docker.sh
according to your needs. in this way, we can run our bdd scenarios inside docker containers.
bddfire will also support non-functional testing like load and performance testing with gatling and accessibility testing using axe engine which we will cover separate article.
conclusion
we have seen that the process of setting up a bdd test framework be very quick using tools like bddfire. we can set up the entire framework with code quality, browser testing, cloud testing, api testing, and docker integration by running three simple commands. now, we can spend more time writing bdd scenarios instead of writing the framework.
Published at DZone with permission of Shashikant Jagtap, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments