Generic JPA Entity History
Want to build a changelog without adding redundant tables? Check out this DIY validation manager that will help you track your history.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeI've always had an issue trying to keep a changelog for my entities on a database. In my early projects, I did this just by adding redundant tables to add this information, basically doubling the number of tables in the original database design.
Since then, I've been looking for a better way.
Today I want to share what I'm brewing as part of Validation Manager, the beginning of a dynamic History system. Below, you'll see the basic design.
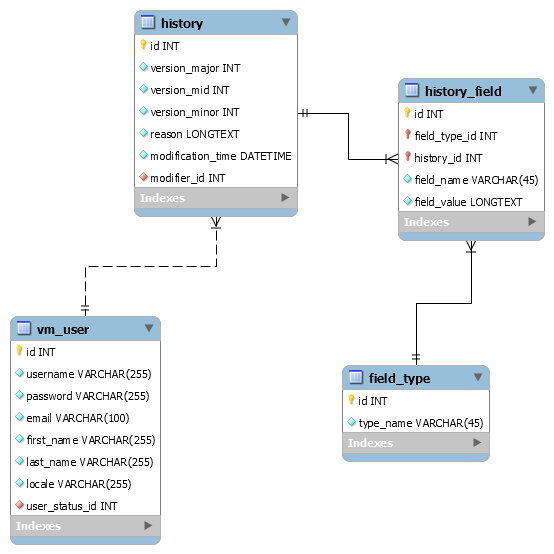
Basically, a History entity storing version (major.mid.minor), modification time, modification reason, and modifier. Each history has a series of fields from certain field types.
In the entities, there is some plumbing to do. Entities need to extend Versionable, a mapped superclass.
package com.validation.manager.core.db.mapped;
import javax.persistence.Basic;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorColumn;
import javax.persistence.Inheritance;
import javax.persistence.InheritanceType;
import javax.persistence.MappedSuperclass;
@MappedSuperclass
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED)
@DiscriminatorColumn(name = "VERSIONABLE_TYPE")
public abstract class Versionable extends AuditedObject {
@Column(name = "dirty")
@Basic(optional = false)
private boolean dirty = false;
public boolean getDirty() {
return this.dirty;
}
/**
* @param dirty the dirty to set
*/
public void setDirty(boolean dirty) {
this.dirty = dirty;
}
@Override
public void update(AuditedObject target, AuditedObject source) {
((Versionable) target).setDirty(((Versionable) source).getDirty());
super.update(target, source);
}
}And the AuditedObject class.
package com.validation.manager.core.db.mapped;
import com.validation.manager.core.db.History;
import com.validation.manager.core.db.VmUser;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
public abstract class AuditedObject
implements Comparable<AuditedObject>, Serializable {
private Integer majorVersion = 0;
private Integer midVersion = 0;
private Integer minorVersion = 1;
private String reason;
private VmUser modifierId;
private Date modificationTime;
public Integer getMajorVersion() {
return this.majorVersion;
}
public void setMajorVersion(Integer majorVersion) {
this.majorVersion = majorVersion;
}
public Integer getMidVersion() {
return this.midVersion;
}
public void setMidVersion(Integer midVersion) {
this.midVersion = midVersion;
}
public Integer getMinorVersion() {
return this.minorVersion;
}
public void setMinorVersion(Integer minorVersion) {
this.minorVersion = minorVersion;
}
public VmUser getModifierId() {
return modifierId;
}
public void setModifierId(VmUser modifierId) {
this.modifierId = modifierId;
}
public String getReason() {
return this.reason;
}
public void setReason(String reason) {
this.reason = reason;
}
public Date getModificationTime() {
return this.modificationTime;
}
public void setModificationTime(Date modificationTime) {
this.modificationTime = modificationTime;
}
/**
* Get history for this entity.
*
* @return history
*/
public abstract List<History> getHistoryList();
/**
* Set history for this entity
*
* @param historyList
*/
public abstract void setHistoryList(List<History> historyList);
/**
* Update the fields.
*
* @param target target object
* @param source source object
*/
public void update(AuditedObject target,
AuditedObject source) {
target.setReason(source.getReason());
target.setModificationTime(source.getModificationTime());
target.setModifierId(source.getModifierId());
target.setMajorVersion(source.getMajorVersion());
target.setMidVersion(source.getMidVersion());
target.setMinorVersion(source.getMinorVersion());
target.setModifierId(source.getModifierId());
target.setReason(source.getReason());
target.setHistoryList(source.getHistoryList());
}
@Override
public int compareTo(AuditedObject o) {
if (!Objects.equals(getMajorVersion(),
o.getMajorVersion())) {
return getMajorVersion() - o.getMajorVersion();
}//Same major version
else if (!Objects.equals(getMidVersion(),
o.getMidVersion())) {
return getMidVersion() - o.getMidVersion();
} //Same mid version
else if (!Objects.equals(getMinorVersion(),
o.getMinorVersion())) {
return getMinorVersion() - o.getMinorVersion();
}
//Everything the same
return 0;
}
/**
* Add history to this entity.
*
* @param history History to add.
*/
public void addHistory(History history) {
if (getHistoryList() == null) {
setHistoryList(new ArrayList<>());
}
getHistoryList().add(history);
}
/**
* Increase major version.
*/
public void increaseMajorVersion() {
setMajorVersion(getMajorVersion() + 1);
setMidVersion(0);
setMinorVersion(0);
}
/**
* Increase major version.
*/
public void increaseMidVersion() {
setMidVersion(getMidVersion() + 1);
setMinorVersion(0);
}
/**
* Increase minor is done by default when updating a record.
*/
}Those just expose interfaces/methods and database fields to the entities. Then we add some mapping between the classes. First, we add the following in the Entity:
@ManyToMany(mappedBy = "nameX")
private List < History > historyList;
...
@XmlTransient
@JsonIgnore
@Override
public List < History > getHistoryList() {
return historyList;
}
@Override
public void setHistoryList(List < History > historyList) {
this.historyList = historyList;
}And update the History entity:
@JoinTable(name = "x_has_history", joinColumns = {
@JoinColumn(name = "history_id", referencedColumnName = "id")
},
inverseJoinColumns = {
@JoinColumn(name = "x_id", referencedColumnName = "id")
})
@ManyToMany
private List < Requirement > nameX;Then we annotate the fields we want to keep track of in the target entity by adding the Auditable annotation to the target field. For example:
@Basic(optional = false)
@NotNull
@Lob
@Size(max = 2147483647)
@Column(name = "description")
@Auditable
private String description;Here's the Annotation class, nothing fancy:
package com.validation.manager.core.api.history;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
*
* @author Javier A. Ortiz Bultron <javier.ortiz.78@gmail.com>
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface Auditable {
}Now that the plumbing is done, we need to inject the version automatically into the system. For that we add an Entity Listener:
package com.validation.manager.core.api.history;
import com.validation.manager.core.DataBaseManager;
import com.validation.manager.core.db.FieldType;
import com.validation.manager.core.db.History;
import com.validation.manager.core.db.HistoryField;
import com.validation.manager.core.db.mapped.Versionable;
import com.validation.manager.core.server.core.FieldTypeServer;
import com.validation.manager.core.server.core.HistoryFieldServer;
import com.validation.manager.core.server.core.HistoryServer;
import com.validation.manager.core.server.core.VMUserServer;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import javax.persistence.PrePersist;
import javax.persistence.PreUpdate;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.reflect.FieldUtils;
import org.eclipse.persistence.jpa.JpaEntityManager;
import org.eclipse.persistence.sessions.CopyGroup;
/**
*
* @author Javier Ortiz Bultron <javier.ortiz.78@gmail.com>
*/
public class VersionListener {
private final static Logger LOG
= Logger.getLogger(VersionListener.class.getSimpleName());
@PrePersist
public synchronized void onCreation(Object entity) {
//Handle audit
if (entity instanceof Versionable
&& DataBaseManager.isVersioningEnabled()) {
try {
Versionable v = (Versionable) entity;
if (v.getReason() == null) {
v.setReason("audit.general.creation");
}
setHistory(v);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
LOG.log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
}
@PreUpdate
public synchronized void onChange(Object entity) {
//Handle audit
if (entity instanceof Versionable
&& DataBaseManager.isVersioningEnabled()) {
try {
Versionable v = (Versionable) entity;
if (v.getReason() == null) {
v.setReason("audit.general.modified");
}
setHistory(v);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
LOG.log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
}
private synchronized void setHistory(Versionable v) throws Exception {
//Only if an auditable field has been modified
if (auditable(v)) {
//Add history of creation
HistoryServer hs = new HistoryServer();
if (v.getModifierId() == null) {
try {
//By default blame system
hs.setModifierId(new VMUserServer(1).getEntity());
}
catch (Exception ex) {
LOG.log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
hs.setReason(v.getReason());
if (v.getHistoryList() != null && !v.getHistoryList().isEmpty()) {
History last = v.getHistoryList().get(v
.getHistoryList().size() - 1);
if ((v.getMajorVersion() == 0 && v.getMidVersion() == 0) // It has default values
|| last.getVersionMajor() == v.getMajorVersion() // Or it has a higher mid/major version assigned.
&& last.getVersionMid() == v.getMidVersion()) {
//Make it one more than latest
hs.setVersionMinor(last.getVersionMinor() + 1);
}
}
hs.setModificationTime(v.getModificationTime() == null
? new Date() : v.getModificationTime());
hs.write2DB();
//Check the fields to be placed in history
updateFields(hs, v);
}
}
public Versionable cloneEntity(Versionable entity) {
CopyGroup group = new CopyGroup();
group.setShouldResetPrimaryKey(true);
Versionable copy = (Versionable) DataBaseManager.getEntityManager()
.unwrap(JpaEntityManager.class).copy(entity, group);
return copy;
}
private synchronized void updateFields(HistoryServer hs, Versionable v)
throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, Exception {
for (Field field : FieldUtils.getFieldsListWithAnnotation(v.getClass(),
Auditable.class)) {
Class type = field.getType();
String name = field.getName();
FieldType ft = FieldTypeServer.findType(type.getSimpleName());
if (ft == null) {
FieldTypeServer fts = new FieldTypeServer();
fts.setTypeName(type.getSimpleName());
fts.write2DB();
ft = fts.getEntity();
}
HistoryFieldServer hf
= new HistoryFieldServer(ft.getId(), hs.getId());
hf.setFieldName(name);
hf.setFieldType(ft);
hf.setHistory(hs.getEntity());
field.setAccessible(true);
Object value = field.get(v);
hf.setFieldValue(value == null ? "null" : value.toString());
hf.write2DB();
hs.getHistoryFieldList().add(hf.getEntity());
}
hs.write2DB();
v.addHistory(hs.getEntity());
DataBaseManager.getEntityManager().persist(v);
}
private synchronized boolean auditable(Versionable v) {
History current;
if (v.getHistoryList() != null && !v.getHistoryList().isEmpty()) {
current = v.getHistoryList().get(v.getHistoryList().size() - 1);
} else {
//Check if the changed fields are auditable or not
return true;
}
for (HistoryField hf : current.getHistoryFieldList()) {
try {
//Compare audit field vs. the record in history.
Object o = FieldUtils.readField(FieldUtils.getField(v.getClass(),
hf.getFieldName(), true), v);
if ((o == null && !hf.getFieldValue().equals("null"))
|| (o != null && !o.equals(hf.getFieldValue()))) {
return true;
}
}
catch (SecurityException | IllegalArgumentException | IllegalAccessException ex) {
LOG.log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
return false;
}
}Each time an Entity that extends Versionable and has Auditable annotated fields is created/modified, a new history entry is added, assuming the change was on the annotated fields. Other changes don't trigger this system.
I see the potential and what else could be done to make this a stand-alone system:
Add an annotation processor to add the fields mentioned above and create/update an orm.xml file.
Have as a separate artifact so it can be reused.
Published at DZone with permission of Javier Ortiz. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments