GitOps: ArgoCD vs FluxCD
Discover the benefits of GitOps, explore a detailed comparison between ArgoCD and FluxCD, and learn how these tools streamline deployments and DevOps workflows.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeGetting Started With GitOps
Most organizations are always looking for ways to streamline their processes and improve efficiency by implementing automation. In recent years, software deployment has been done multiple times in a day rather than weeks or months. Organizations have moved from the waterfall models to hyper-agile methodologies and particularly due to the adoption of microservices architecture, teams are releasing their software much faster. To make this possible, GitOps implements a control-loop pattern more often seen in Kubernetes.
GitOps offers a more consistent and reliable way to handle infrastructure and deployment. In this blog, we'll explore what GitOps is and why it's becoming increasingly popular among DevOps teams. We will also walk through popular GitOps tools like Argo CD and Flux CD.
What Is GitOps?
GitOps comes from the combination of "Git" and "Operations." It is a way of applying continuous deployment to cloud-native applications. It uses Git as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and applications. It means using Git repositories to store and manage all the configuration files that describe how our application should be deployed and run.
GitOps is based on the principle of treating everything from the application code itself to the infrastructure as code that can be version-controlled and managed using Git. So, when we want to make a change to our system, instead of manually executing commands or scripts, we need to make a change to our Git repository. The controller then detects these changes and applies them to our infrastructure. The main benefits of GitOps are speed, traceability, and security.
Benefits of GitOps
Consistency and Reliability
With GitOps, our entire system configuration is stored in version control. This means we always have a clear, auditable record of what should be deployed making it reliable. Everything in the infrastructure and application is kept in sync with the Git repository to maintain consistency.
Faster Recovery and Easier Rollbacks
In case of issues, we can easily roll back to the previous state by reverting to a previous commit in our git history and our automated systems will bring our infrastructure back to that state.
Security
Since Git is used as the central point of control, strict access controls can be implemented. Moreover, all changes go through Git, we can also enforce code reviews and approvals before any changes are applied to our systems.
Improved Developer Experience
With GitOps, developers can use familiar Git workflows to manage infrastructure, bridging the gap between development and operations. This can lead to faster onboarding and improved productivity.
Visibility and Traceability
With all changes recorded in Git, we have a clear record of who changed what and when. This visibility is important for troubleshooting purposes.
Increased Automation
GitOps encourages a high degree of automation. Pushing changes to Git can automatically trigger deployments, reducing manual work and speeding up processes.
Environment Consistency
GitOps makes it easier to maintain consistency between different environments (development, staging, production). Teams can use familiar Git workflows for multiple environments.
Increased Productivity
The time taken for deployment is reduced significantly due to continuous automated deployments. As per DORA’s research, It has been observed that teams can ship 30-100 times more changes per day increasing the overall development output by 2-3 times.
Availability
In GitOps all configuration data is in Git. Therefore, organizations can easily deploy the same Kubernetes platform across different environments. This is easier, faster, and more reliable to scale up and out. It reduces the time needed to restore in case of a problem leading to better availability for organizations.
Argo CD vs Flux CD
When it comes to implementing GitOps for Kubernetes, two of the most popular tools are Argo CD and Flux CD. Both tools are excellent choices for implementing GitOps. Here is a comparison of their features.
| Feature | Argo CD | Flux CD |
|---|---|---|
|
Kubernetes-native |
Yes |
Yes |
|
UI |
Rich web-based UI for managing applications |
Capacitor GUI for Flux provides a dashboard for a quick overview of resources and deployments. |
|
Multi-tenancy |
Built-in |
Limited |
|
Helm support |
Native |
Via Helm Operator |
|
Kustomize support |
Native |
Native |
|
Sync mechanism |
Automatically syncs Git state to Kubernetes cluster |
Syncs Git state to Kubernetes cluster using controllers |
|
Rollback capabilities |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Health status |
Yes |
Relies on Kubernetes status and custom controllers |
|
Image updater |
Argo CD image updater (add-on) |
Built-in image automation controllers. |
|
Advanced deployment strategies |
Integrated with Argo rollouts which provide advanced deployment strategies like blue-green, canary, and experimentation |
Flagger provides support for advanced deployment strategies like A/B testing, canary deployment, and blue-green deployment |
Table: Comparison between ArgoCD and FluxCD
In the next section, we will have a look at a quick demo of Argo CD and Flux CD.
Argo CD
In this quick demo of Argo CD, we will go through the step-by-step process of Argo CD installation on a Kubernetes cluster. We will use Argo CD to deploy a sample guestbook application.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes cluster
- Kubectl installed and configured
- Configuration of the Git repository
Argo CD Installation
To install Argo CD, we need to have a Kubernetes cluster and kubectl installed and configured. You can check out the guide to installing kubectl here.
Create a Namespace for Argo CD
kubectl create namespace argocdInstall Argo CD
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yamlAccess the Argo CD API Server
Port-Forward the Argo CD Server Service
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443Get the Initial Password of the Admin User To Authenticate
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -dUse this password to log into the Argo CD UI using username admin at the forwarded port on the localhost, in this example, it is http://localhost:8080.

Figure 1: Argo CD interface
Deploy a Sample Application: Guestbook
To deploy an app, we need to create an Application object. The spec will have information such as the source of the Kubernetes manifests to deploy the application, destination Kubernetes cluster, namespace, and sync policy. You can also provide more image updater specs via annotations. In this example, we are not using an image updater.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: guestbook
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/argoproj/argocd-example-apps.git
targetRevision: HEAD
path: guestbook
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: guestbook
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=trueCreate the Application
kubectl apply -f application.yamlAfter applying the Argo CD application, the Argo CD controller will automatically monitor and apply the changes in the cluster. You can monitor this from the UI or:
kubectl get apps -n argocd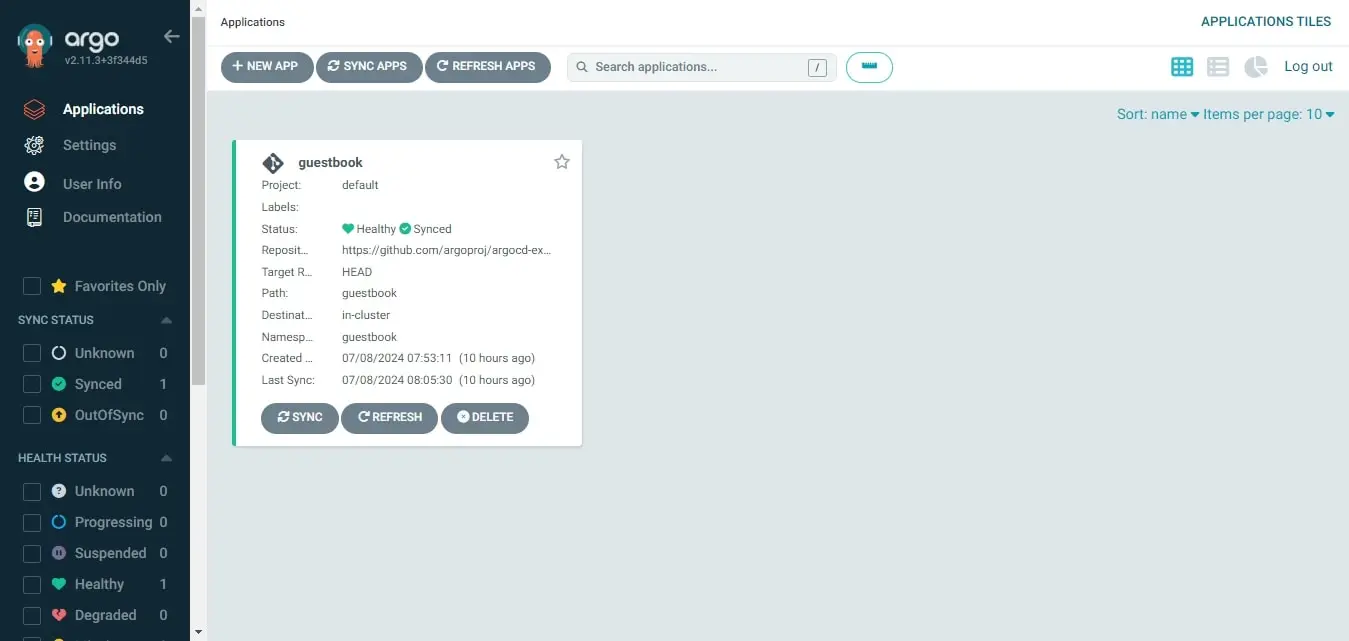
Flux CD
In this demo of Flux CD, we will understand its installation. We will use flux CD to deploy the fleet-infa repository.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes cluster
- GitHub personal access token: If you need help generating a GitHub token, check out this guide.
Objectives
- Bootstrap Flux CD on a Kubernetes Cluster.
- Deploy a sample application using Flux.
- Customize the application configuration through Kustomize patches.
Steps
Install the Flux CLI
The Flux command-line interface (CLI) is used to bootstrap and interact with Flux CD.
curl -s https://fluxcd.io/install.sh | sudo bashExport Your Credentials
Export your GitHub personal access token and username.
export GITHUB_TOKEN=<your-token>
export GITHUB_USER=<your-username>Check Your Kubernetes Cluster
Ensure your cluster is ready for Flux by running:
flux check --preFlux Installation
To bootstrap using a GitHub repository, run:
flux bootstrap github \
--owner=$GITHUB_USER \
--repository=fleet-infra \
--branch=main \
--path=./clusters/my-cluster \
--personalClone the Git Repository
Clone the fleet-infra repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/$GITHUB_USER/fleet-infra
cd fleet-infraAdd podinfo Repository to Flux
Create a GitRepository manifest pointing to the podinfo repository’s master branch:
flux create source git podinfo \
--url=https://github.com/stefanprodan/podinfo \
--branch=master \
--interval=1m \
--export > ./clusters/my-cluster/podinfo-source.yamlCommit and push the podinfo-source.yaml file to the fleet-infra repository:
git add -A && git commit -m "Add podinfo GitRepository"
git pushDeploy podinfo Application
Create a Kustomization manifest to deploy the podinfo application:
flux create kustomization podinfo \
--target-namespace=default \
--source=podinfo \
--path="./kustomize" \
--prune=true \
--wait=true \
--interval=30m \
--retry-interval=2m \
--health-check-timeout=3m \
--export > ./clusters/my-cluster/podinfo-kustomization.yamlCommit and push the podinfo-kustomization.yaml file to the repository:
git add -A && git commit -m "Add podinfo Kustomization"
git pushWatch Flux Sync the Application
Use the flux get command to watch the podinfo app:
flux get kustomizations --watchVerify the Deployment
Check if podinfo has been deployed on your cluster:
kubectl -n default get deployments,servicesGitOps Best Practices
- Git workflows: Separate application repositories from Git workflow repositories. Also, avoid using long-lived branches from different environments.
- Simplify your Kubernetes files: Use tools like Kustomize and Helm to make your Kubernetes files simpler and easier to manage. Use both together to avoid repeating yourself.
- Handle secrets carefully: Do not use your passwords or secrets directly in your Git files even if they are encrypted. Instead, use tools that can fetch secrets when needed.
- Separate build and deployment processes: Separate your build process from your deployment process. Let your CI system build and test your app and then let GitOps handle the build and put it in a server.
Ephemeral Environments Using GitOps
Ephemeral environments, also known as preview environments, are short-lived environments that allow developers to test and preview changes in a production-like environment before merging them into the main branch.
These environments are typically created automatically when a pull request is opened and destroyed when the pull request is closed.
In the context of Kubernetes, tools like Argo CD and Flux CD can automate the creation and management of ephemeral environments, making it easier to implement this practice in a GitOps workflow. For more information on how to implement preview environments on Kubernetes with Argo CD, check out this guide by Piotr Minkowski.
Conclusion
GitOps is a game-changer for managing infrastructure and applications. It boosts consistency, reliability, collaboration, and workflow. Tools like Argo CD and Flux CD exemplify how GitOps streamlines deployment and enhances efficiency. Our comparison shows the strengths and specific use cases of both tools, highlighting how they make GitOps implementation seamless and effective.
Published at DZone with permission of Unnati Mishra. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments