Hibernate Get vs. Load
In this article, the reader will learn about the difference between the get method and the load method in hibernate using get() and load().
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn Hibernate, there is the concept of single-row fetching. In order to get a single row in the respective database table, we will go for either get() or load().
get()
get() always hits the database.
If the serializable id is found, then we will get the respective details.
Example
SwingBowlers swingBowlers = (SwingBowlers) openSession.get(SwingBowlers.class,1);
Serializable id is 1 (jerSeyNo) --> Primary Key
If the serializable id is not found, then we will get the result as null.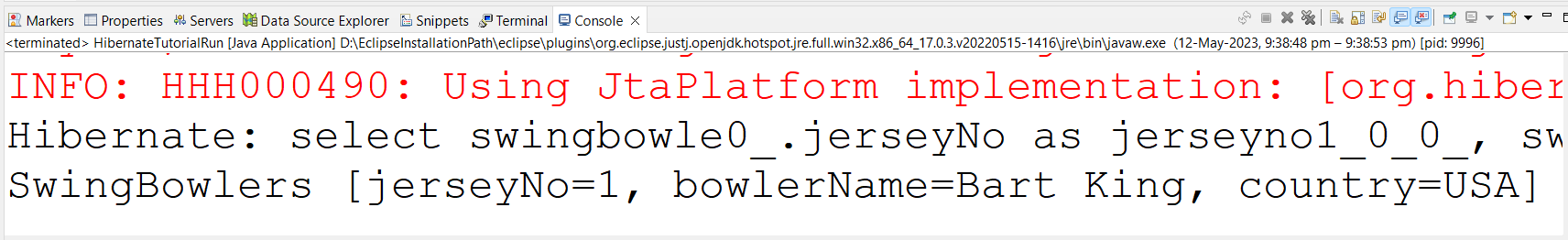 load()
load()
load() always creates a proxy object. If the serializable id is found, then we will get the respective details.
Example
SwingBowlers swingBowlers = (SwingBowlers) openSession.get(SwingBowlers.class,1);
System.out.println(swingBowlers);
Serializable id is 1 (jerSeyNo) --> Primary Key
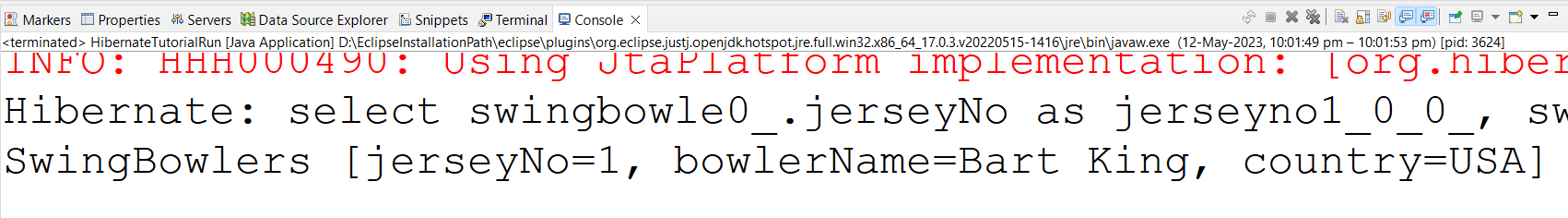
If the serializable id is not found, then we will get a result of org.hibernate.ObjectNotFoundException.
Check whether it still generates a query, even though we are using the load method because we are trying to print object details. [System.out.println(swingBowlers);]. But it's coming from Proxy Object[Dummy Object] only.
Let's look at it practically.
![[System.out.println(swingBowlers);]](https://dz2cdn1.dzone.com/storage/temp/16925608-1684786725563.png)
HibernateTutorialRun.java
package com.blogspot.javacodebypj;
import com.blogspot.javacodebypj.dao.SwingBowlersDaoImpl;
public class HibernateTutorialRun {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingBowlersDaoImpl sbdi = new SwingBowlersDaoImpl();
sbdi.getSwingBowlers();
}
}Explanation: HibernateTutorialRun is a class to run the HibernateTutorial application, and we are using it without a server. Hibernate will run with the server and without the server. We created the main method, and in that, we just created an object for the respective class SwingBowlersDaoImpl. Then we are just using that object reference called the respective method.
SwingBowlersDao.java
package com.blogspot.javacodebypj.dao;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import com.blogspot.javacodebypj.domain.SwingBowlers;
import com.blogspot.javacodebypj.util.HibernateUtil;
public class SwingBowlersDaoImpl implements SwingBowlersDao {
@Override
public void getSwingBowlers() {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
Session openSession = sessionFactory.openSession();
// using load method
SwingBowlers swingBowlers = (SwingBowlers) openSession.load(SwingBowlers.class, 1);
System.out.println(swingBowlers);
}
}Explanation: We just created SwingBowlersDaoImpl class and implemented it with SwingBowlersDao and we are going to override the respective method. We are trying to call HibernateUtil class method, i.e., getSessionFactory method, we will get SessionFactory object, and with the SessionFactory object reference, we are calling openSession method. Then we will get Session object.
Once we get Session object with this session, we can call either use the load method or get method, and we just cast to the respective class because of the load method or get method returns Object. I hope you know the concept of upcasting and downcasting in Java.
SwingBowlers.java
package com.blogspot.javacodebypj.domain;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class SwingBowlers {
@Id
@Column(length = 3)
private int jerseyNo;
@Column(length = 15)
private String bowlerName;
@Column(length = 10)
private String country;
public int getJerseyNo() {
return jerseyNo;
}
public void setJerseyNo(int jerseyNo) {
this.jerseyNo = jerseyNo;
}
public String getBowlerName() {
return bowlerName;
}
public void setBowlerName(String bowlerName) {
this.bowlerName = bowlerName;
}
public String getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SwingBowlers [jerseyNo=" + jerseyNo + ", bowlerName=" + bowlerName + ", country=" + country + "]";
}
}Explanation: Since we are mapping fields to database columns. If it is the same field name as the column in the database table, then there is no need to write the column name value in the annotation level. Similarly, the table name is also the same as the class name SwingBowlersso that's why we are not annotated with @Table. To make it a domain class, we are using @Entity annotation at the top of the respective class.
HibernateUtil.java
package com.blogspot.javacodebypj.util;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class HibernateUtil {
private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
private HibernateUtil() {
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
if (sessionFactory == null) {
Configuration conf = new Configuration().configure();
sessionFactory = conf.buildSessionFactory();
}
return sessionFactory;
}
}Explanation: We are just created SessionFactory as a singleton class.
hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cricketer</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">myRoot4*</property>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<mapping class="com.blogspot.javacodebypj.domain.SwingBowlers" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>Explanation: In this, we have three sections:
- Database-related properties
- Hibernate-related properties
- Mapping class
As you know, we are not using a hibernate mapping xml file, so that's why we just mentioned the mapping class.
dialect: It is used for query generation with respect to the database. In this application, we are using the MySQL database.
show_sql: Once generating queries, we need to see those queries, so we need to mention them as true.
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.blogspot.javacodebypj</groupId>
<artifactId>HibernateTutorial</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>HibernateTutorial</name>
<description>HibernateTutorial by Ponnam Jay</description>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate/hibernate-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.6.14.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>Explanation: We just generated this Maven project structure through Eclipse IDE as a Simple Maven project. We added dependencies like hibernate-core, mysql-connector-java and used Java 1.8 to observe in the pom.xml at the properties section target and source.
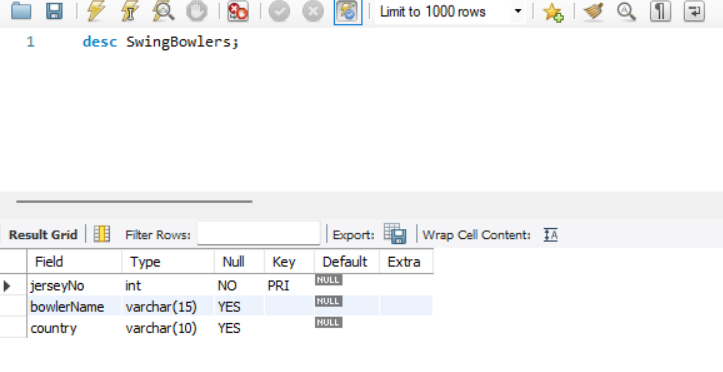
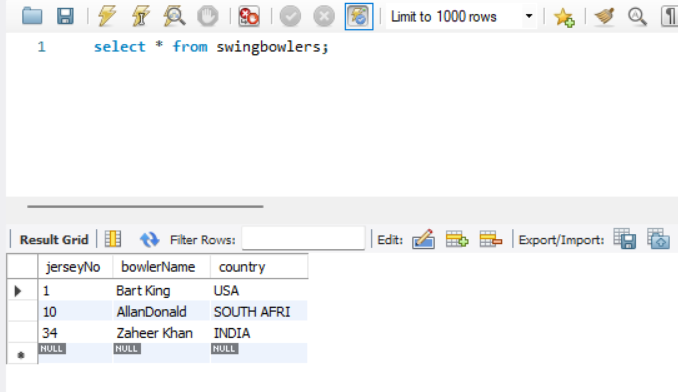
Database Details
Conclusion
If you want to fetch (retrieve) a single row (single record), then you can use either the get method [or] load method.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments