An Introduction to Blockchain
Blockchain provides the highest level of hack resistance and security optimization — and its popularity is in no way over just yet.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeInitially, blockchain technology served as a distributed database for carrying out transactions among bitcoin users, but its application is more than that. The lack of a single centralized base for data storage is the main distinguishing feature of the blockchain technology. All the data stored in the centralized base is distributed between interconnected blocks.
These blocks are chained together with the use of complex algorithms. Each piece of information is stored in a block, and new blocks are added for every further piece of information without altering the existing data. This feature provides the highest level of hack resistance and security optimization.
Benefits of Blockchain

Below are some of the advantages of blockchain as shown by experts:
Reasonable security level
Resistant to hacking
Transparent transactions that can be tracked by users in real-time mode
Provides the opportunity to regulate accessibility levels
Can be used to execute swift transactions
Automatically blocks verification after user confirms a transaction
Blockchain Durability and Robustness
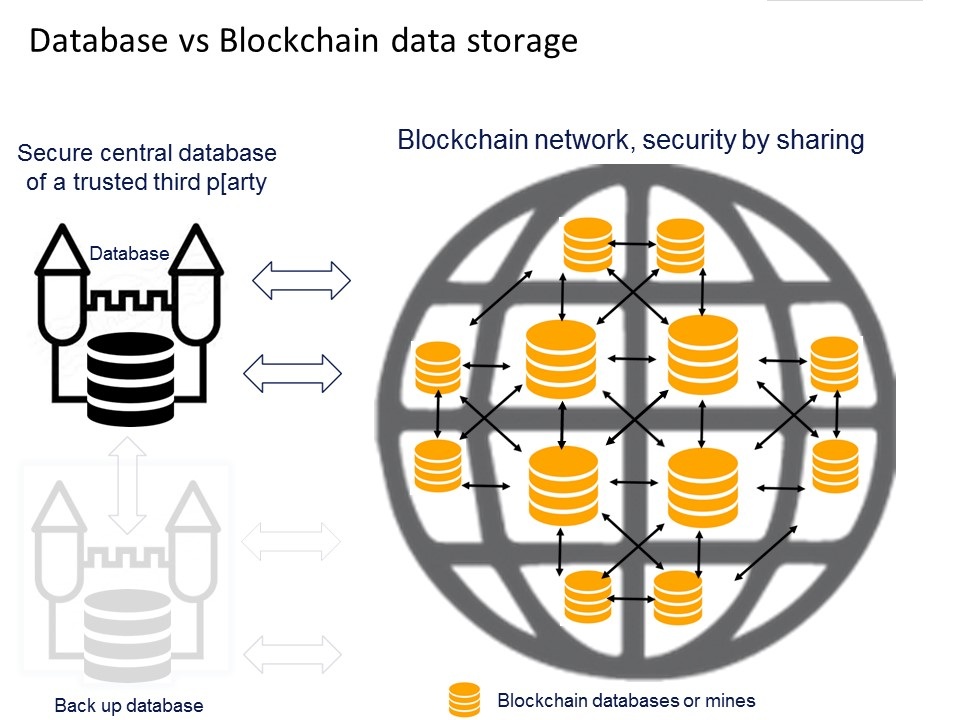
Blockchain technology functions with the internet and has built-in toughness. With its ability to store blocks of information that are equal across its network, the blockchain cannot be controlled by any single unit and has no single point of failure. In 2008, Bitcoin was invented, and since then, the Bitcoin blockchain has been in operation without significant disruption.
Nowadays, mismanagement and hacking have remained the main problems associated with Bitcoin. These issues are not from the underlying concepts but are due to lousy intention and human error. The internet has been durable for the past 30 years and has tracked a record that works well for blockchain as its development continues.
The blockchain is a mechanism that brings every user to the highest degree of accountability. With the blockchain, there are no more human or machine errors. There are also no missed transactions or any exchanges that were not done in line with the agreement of the people involved.
The blockchain has helped guarantee the validity of a transaction by saving it on the central register and on a distributed system of registers that are all connected through a secure authentication mechanism.
Transparent and Incorruptible
The blockchain network operates on a level at which it automatically checks itself every ten minutes. It is a kind of self-auditing system of digital value, which shows that the network reunites every transaction that is done in every ten-minute interval. Each of these groups of transactions is called a "block." The system has a transparent data embedded in it, and it cannot corrupt, even if any of the information on it is altered — two essential properties of the blockchain.
Blockchain has helped solve the problem of manipulation. Often, people advocate trusting Facebook, Google, or their banks. But the whole world cannot trust corporations and organizations entirely — like people in Russia, India, Africa, or Eastern Europe. Blockchain opportunities are highest in those countries.
Blockchain as a Decentralized Technology

Blockchain, by design, is a decentralized technology. Any transaction that is done is a function of the network as a whole — it may not be necessary to create a new way to verify the transaction aspects of a traditional business. For example, trading on the stock market becomes almost simultaneous on the blockchain and decentralization is already a reality. For bitcoin transactions, the database of records is managed by blockchain technology on a global network of computers.
This shows that bitcoin is controlled by its network and not by any central authority. Decentralization shows that blockchain works on a peer-to-peer basis. One of the best examples of a blockchain technology is the BitClave Active Search Ecosystem (BASE). It pays with a user's digital currency, CAT (Consumer Activity Tokens). This currency can be used for online purchases. It is a search engine that allows users to benefit and earn profit from searching and receiving information online.
Who Uses Blockchain?

As it is a web infrastructure, you may not know much about blockchain before it is useful for you. Finance currently offers the most reliable cases for the technology. The World Bank estimated that over $430 billion USD was transferred in 2015, and there is a high request for blockchain developers at the moment. Intermediaries are potential cut-outs of blockchain for these types of transactions. Online transactions are now firmly connected to identity verification, and this may be transformed in the coming years to wallet apps.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments