How Does Java Handle Aliasing?
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAliasing means there are multiple aliases to a location that can be updated, and these aliases have different types.
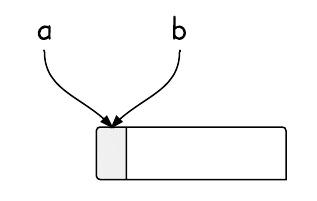
In the following example, a and b are two variable names that have two different types A and B. B extends A.
B[] b = new B[10]; A[] a = b; a[0] = new A(); b[0].methodParent();
In memory, they both refer to the same location.
The pointed memory location are pointed by both a and b. During run-time, the actual object stored determines which method to call.
How does Java handle aliasing problem?
If you copy this code to your eclipse, there will be no compilation errors.
class A {
public void methodParent() {
System.out.println("method in Parent");
}
}
class B extends A {
public void methodParent() {
System.out.println("override method in Child");
}
public void methodChild() {
System.out.println("method in Child");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B[] b = new B[10];
A[] a = b;
a[0] = new A();
b[0].methodParent();
}
}
But if you run the code, the output would be as follows:
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.ArrayStoreException: aliasingtest.A at aliasingtest.Main.main(Main.java:26)
The reason is that Java handles aliasing during run-time. During run-time, it knows that the first element should be a B object, instead of A.
Therefore, it only runs correctly if it is changed to:
B[] b = new B[10]; A[] a = b; a[0] = new B(); b[0].methodParent();
and the output is:
override method in Child
Published at DZone with permission of Ryan Wang. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments