Invoke Java Functions in Your DataWeave Transformation and Mule Flow
DataWeave is a language used to query and transform complex data. It is very much so possible to invoke Java/Groovy functions within DataWeave.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeDataWeave makes transformations very easy. DataWeave is a language used to query and transform complex data. It contains a lot of operators, including filters and functions. It supports various formats including XML, JSON, CSV, Java, and EDI out of the box. DataWeave code looks like JSON syntax and is format-neutral. It is very much so possible to invoke Java/Groovy functions within DataWeave.
Invoke MEL Function Within DataWeave Transformation
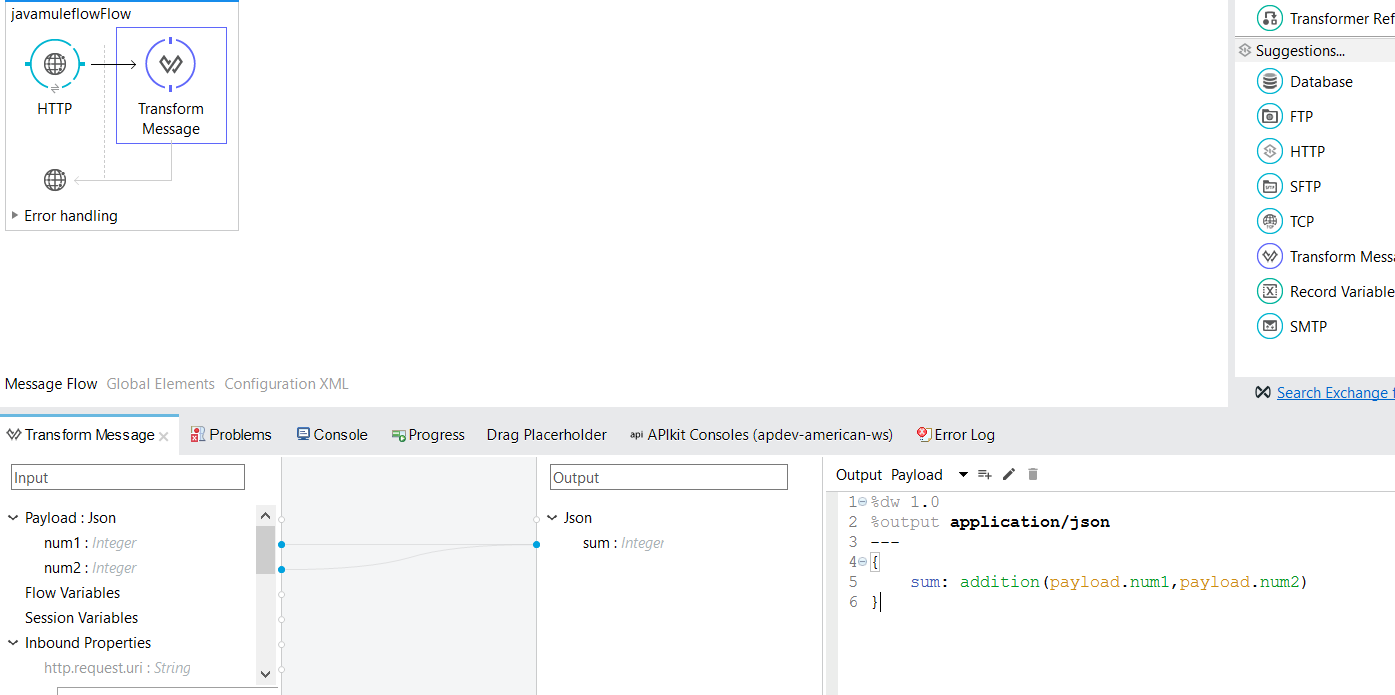
You will receive two numbers as the input message (JSON format) and return an addition of two numbers. Below you can see what will be the input and output:
Input:
{
"num1":1,
"num":2
}Output:
{
"sum":3
}Declare Spring MEL Function
You need declare a Spring MEL function in the global configuration XML as shown below:
<configuration doc:name="Configuration">
<expression-language>
<global-functions>
def toStringLowerCase(name) {
return name.toLowerCase()
}
def addition(a,b) {
return a + b
}
</global-functions>
</expression-language>
</configuration>DataWeave Transform
You need to invoke the function addition expecting two arguments. It invokes the DataWeave transform as shown below:
%dw 1.0
%output application/json
---
{
sum: addition(payload.num1,payload.num2)
}
Invoke Java Function Within DataWeave Transform
Now, you will see how to invoke Java functions with your DataWeave transformation. For example, if you have a class with name TestClass.java that has function addTwoNumbers, accept two arguments and return the sum of two arguments.
package javamuleflow;
public class TestClass {
public int addTwoNumbers(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
}Mule Global Configuration
Now, you need to make the entry of Java function in Mule Global Configuration as shown below:
<configuration doc:name="Configuration">
<expression-language>
<import class="javamuleflow.TestClass" />
<global-functions>
def addition(a,b) {
return javamuleflow.TestClass.addTwoNumbers(a,b);
}
</global-functions>
</expression-language>
</configuration>DataWeave Transform
You need to invoke the function addition expecting two arguments. It invokes the DataWeave transform as shown below:
%dw 1.0
%output application/json
---
{
sum: addition(payload.num1,payload.num2)
}Invoke Java Function Within Mule Flow
Now, you will see how to invoke the Java function with a Mule flow.
Define Spring Beans
You need to define Spring beans in your Mule XML flow as shown below:
<spring:beans>
<spring:bean name="invokeJavaFunc" class="javamuleflow.TestClass"></spring:bean>
</spring:beans>name is just the name of the object in the class and class is the fully qualified name of the Java class.
Invoke Component
Add an invoke component in your flow. This will invoke your Java class in the flow.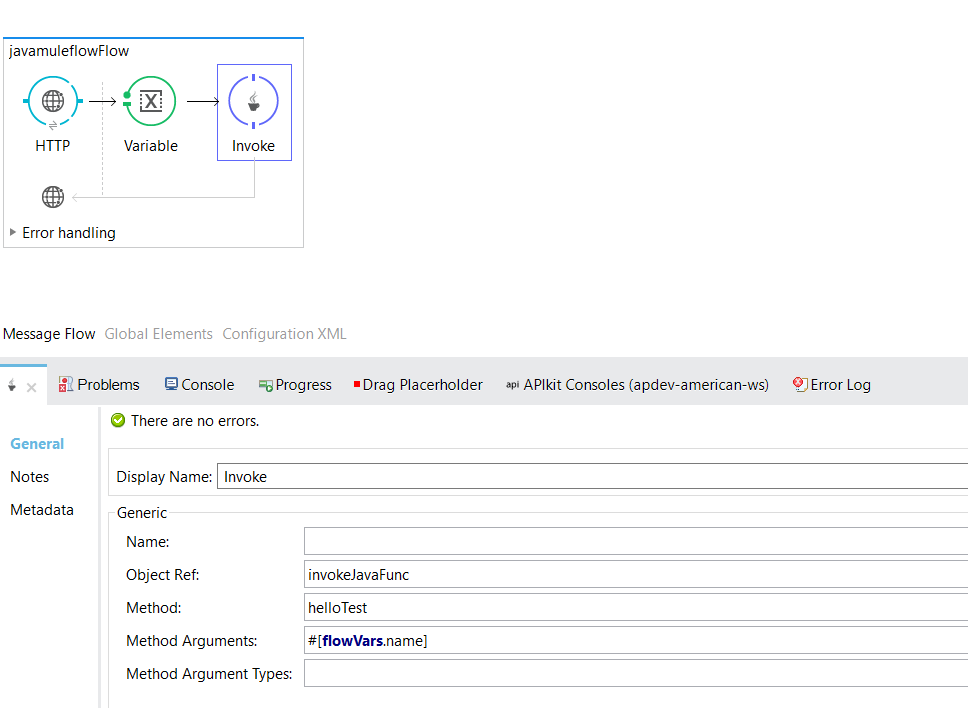 Display Name is a unique name for your component in the application.
Display Name is a unique name for your component in the application.
Name is the name of message processor used for logging purposes.
Object Ref is a bean name. It references an object that contains the method to be invoked.
Method is a function that needs to be invoked.
Method arguments is the parameter that needs to be passed to the function. Multiple arguments can be specified using commas.
Method arguments types is the data type for the argument. Multiple argument types can be specified using commas. Use this property whenever you have multiple methods with the same name in same the class.
Now, you know how to invoke Java functions within your DataWeave transformation and Mule flow!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments