How to Use Caching With Azure Cosmos DB
See how to use caching with Azure Cosmos DB.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeCosmos DB is the new NoSQL database released in Azure Cloud by Microsoft. Unlike relational databases, Cosmos DB is scalable as it is a hosted database service, so it enjoys a lot of popularity among high transaction .NET and .NET Core applications.
However, using Cosmos DB, you need to be wary of performance bottlenecks and cost overhead for accessing the database as Microsoft charges you for each transaction to Cosmos DB. While Cosmos DB is scalable in terms of transaction capacity, it is not as fast because the database service is living in a separate VNet or subscription than the applications. So even if your applications are running in Azure cloud, accessing the database across the VNet is a huge blow to the performance.
Therefore, to tackle these two issues, it is ideal to introduce caching into your Cosmos DB application. You’ll see a dramatic improvement in your application performance and at the same time a significant reduction in operational cost because 80-90% of the time, your application will be fetching data from the cache instead of Cosmos DB.
Using Caching With Cosmos DB
The following code snippet explains how to use caching with Cosmos DB. It is assumed that a Cosmos DB instance contains a collection of Customers.
- Search for the specified customer in the cache, based on the cache key.
- If the item is not the cache, query Cosmos DB to search for the customer.
- If the customer exists in the database collection, retrieve the item.
- Add the specified customer to cache with an expiration value of 5 minutes to ensure data consistency.
var cache = CacheManager.GetCache("demoCache");
// First look for data in cache
var customer = cache.Get("Customer:CustomerID:ALFKI");
// If data not in cache, look in the database
if (customer == null)
{
// Initialize document client to handle read operations with Cosmos DB
var client = new DocumentClient(new Uri("https://20.200.20.103:8081"), "your-auth-token");
var documentUri = UriFactory.CreateDocumentUri("DemoDatabase", "Customers", "ALFKI");
var partitionKey = new PartitionKey("ALFKI");
var requestOptions = new RequestOptions{ PartitionKey = partitionKey };
// Send read request and wait for response
var response = client.ReadDocumentAsync(documentUri, requestOptions).Result;
customer = (Customer)(dynamic)response.Resource;
// Initialize cache item with customer data and expiration metadata
var expiration = new Expiration(ExpirationType.Absolute, TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5));
var cacheItem = new CacheItem(customer) { Expiration = expiration };
// Insert cache item in cache against the required key
cache.Insert("Customer:CustomerID:ALFKI", cacheItem);Using NCache as a Distributed Cache With Cosmos DB
When working with Cosmos DB, it is most likely your application is a high transaction application running in a multi-server environment through a load balancer and is making a lot of database calls. Moreover, a standalone cache will not be possible in this environment, so you need a distributed cache like NCache between the application and the Cosmos DB database.
You need a distributed cache because it allows you to add more cache servers as your transaction load grows, so the cache never becomes a bottleneck. Hence, the number of your application servers doesn’t matter because you can have sufficient cache servers between the application and the database, unlike a relational database which is a major choking point for any scalability.
While Cosmos DB scales much efficiently than a relational database, it is still no match for an in-memory distributed cache like NCache which will sit with your application’s VNet. In fact, a portion of the cache will reside within the application process itself (called a client cache) which gives you in-proc caching speed.
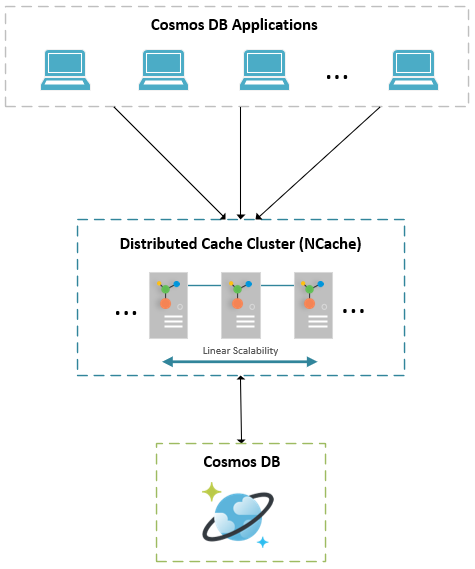
This translates to shorter RTTs as compared to the public cloud deployment of Azure Cosmos DB. Reduced database hits using caching also means fewer charges incurred in terms of Request Units (RUs). Learn more about Cache Operations in NCache.
Caching Collection of Database Items
Using a distributed cache, you enhance your Cosmos DB application performance dramatically by reducing database trips across the network especially for read operations. Thus, while you can retrieve single entities from the database, a far more economical approach in terms of throughput and reduced R/Us is to retrieve the collection of items from the database and apply the operations at the caching tier. Any changes to the state of the collection can later be pushed to the database at the end of the operations.
For this purpose, NCache allows for caching the collection as a single cached item as well as caching the individual elements of the collection, each against its own designated cache key.
Cache Collection as Single Item
You can cache the collection as a single item if you want to load the collection items collectively, for example, all Germany customers. You can query Cosmos DB for all customers in Germany and return the results as a single list which can be added to the cache for further use.
The following code sample shows how to do this for retrieving the list of Germany customers from the database:
var cache = CacheManager.GetCache("demoCache");
// First look for data in cache
var customers = cache.Get<List<Customer>>("CustomersFromGermany");
// If data not in cache, look in the Cosmos DB database
if (customers == null)
{
customers = new List<Customer>();
// Initialize document client to handle read operations with database
var client = new DocumentClient(new Uri("https://20.200.20.103:8081"), "your-auth-code");
var documentCollectionUri = UriFactory.CreateDocumentCollectionUri("DemoDatabase", "Customers");
var feedOptions = new FeedOptions
{
MaxItemCount = -1,
EnableCrossPartitionQuery = true
};
var query = client.CreateDocumentQuery<Customer>(documentCollectionUri, feedOptions)
.Where(c => c.Country == "Germany")
.AsDocumentQuery();
while (query.HasMoreResults)
{
customers.AddRange(query.ExecuteNextAsync<Customer>().Result);
}
// Insert customer collection as single item in cache
if (customers.Count > 0)
{
var expiration = new Expiration(ExpirationType.Absolute, TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5));
CacheItem item = new CacheItem(customers) { Expiration = expiration };
cache.Insert("CustomersFromGermany", customers);
}
}Cache Collection Items Separately
You can associate metadata with cache items in NCache to categorize data through unique identifiers such as tags. This way, multiple items can be retrieved from the cache against a single identifier, for example, customers belonging to Germany.
To achieve this, you can query for Germany customers in Cosmos DB and associate a tag such as Customer:Country:Germany against the resultant items. Caching these items separately will make them available for various query combinations and even faster fetches of a single customer.
Using the previous example, we first search the cache for customers with the tag Customer:Country:Germany. If items do not exist in the cache, query Cosmos DB for items in the Customer collection that have their “Country” attribute specified as “Germany”. However, since we now want to cache the collection items separately, we do the following:
- Once the items are fetched from the database, specify expiration value for the items.
- Specify tag
Customer:Country:Germanyagainst each cache item. - Add items to cache in bulk.
// Use previous example to search cache and Cosmos DB for Germany customers
// Add collection result as items in cache
if (customers.Count > 0)
{
var cacheItemData = new Dictionary<string, CacheItem>();
CacheItem cacheItem = null;
var expiration = new Expiration(ExpirationType.Absolute, TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5));
foreach (var customer in customers)
{
cacheItem = new CacheItem(customer)
{
Tags = new[] { new Tag("Customer:Country:Germany") },
Expiration = expiration
};
cacheItemData.Add($"Customer:CustomerID:{customer.Id}", cacheItem);
}
cache.InsertBulk(cacheItemData);
}NCache Deployment in Azure
NCache is offered in major cloud marketplaces such as Azure and AWS in addition to downloading for on-site use. For all other cloud systems, you can just download and install NCache on a virtual machine in a model of Bring Your Own License (BYOL). NCache is deployed in Azure in the following ways:
- Deploy NCache Cloud in Azure
- Deploy NCache as Virtual Machines
- Using NCache in a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offering in Azure.
For more detail on these options, have a look at Cloud Deployment Options for NCache.
Conclusion
To sum it up, introducing caching in your Cosmos DB application can further push the envelope in terms of speed, reliability, and availability. By using NCache with Cosmos DB, you kill two birds with one stone – one being a boost in application performance because the cache resides within the application process, and second, being the drastic reduction in cost as 80-90% of your data is accessible without making costly database trips to Cosmos DB.
Published at DZone with permission of Iqbal Khan. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments