Identity and Access Management Best Practices
This article examines some of the best practices IT practitioners should follow when working with identity and access management (IAM) systems.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIdentity and access management (IAM) is fundamental to modern cybersecurity and operational efficiency. It allows organizations to secure their data, comply with regulations, improve user productivity, and build a strong foundation for trustworthy and successful business operations. A robust IAM solution also aids in protecting APIs and applications that are built to accelerate the digitalization of services, enabling growth and customer loyalty. This article will examine some of the best practices IT practitioners should follow when working with IAM systems. Even though some of the suggestions are not necessarily new, they still need to be widely adopted to be effective and should be considered as soon as possible.
1. Zero-Trust on Identity
As mentioned in the introduction, APIs are critical in accelerating enterprise digital transformation. However, building and managing multiple APIs comes with various security risks since API calls transfer sensitive data that cyber criminals can easily access if the API endpoints are not strongly secured. A zero-trust approach, where no device or service is trusted, needs a strong focus on identity. By using token-based OAuth solutions, identity credentials can flow through services in a secure and integrity-protected way. This enables all parts of a system to properly authorize requests, trusting only the data coming directly from the IAM system.
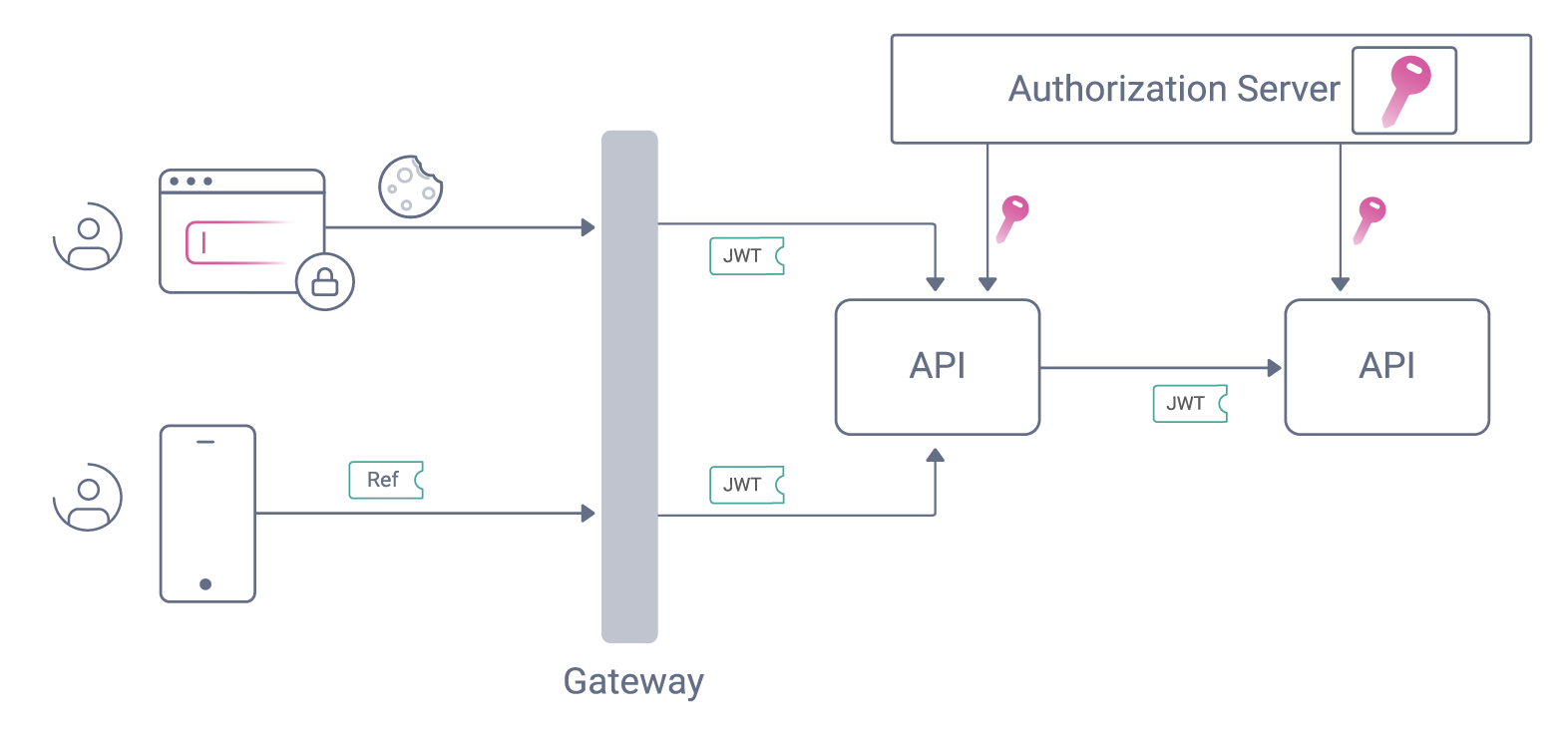
2. Centralized Trust Using Claims
Centralizing trust should be a top priority when operating an Identity and Access Management system. Companies should ensure the IAM system is the only source of truth for claims used to make authorization decisions. Claims contain essential information about the authenticated user, such as the user ID, company ID, or roles. They also provide insight into the token’s context, such as who the issuer is, when the token was issued, and when it expires. Centralized trust also facilitates the validation of identity information in services. The services can easily verify the integrity of the claims and check that nothing has been added or modified in transit.
3. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Another critical IAM best practice is implementing multi-factor authentication. MFA is an authentication method that adds an extra layer of security, helping to authenticate the user's identity. It relies on more than one factor to give access to the user. For example, users might receive a code on their smartphone to authenticate themselves after entering their password to log in to a platform or service. With MFA, there is always a second factor (smartphone, email access, biometric data) as part of the authentication process. This way, unauthorized access is limited.
4. Scalable IAM Solution
When deciding on an IAM solution, it is essential to consider scalability options. The best practice is to choose an IAM system that is flexible and scalable and can be deployed in any environment according to your business needs. A scalable IAM solution should save time and deployment costs and not be restricted by inter-node dependencies. In addition, your IAM solution should accommodate a growing user base without compromising performance or security. Scalability ensures that the IAM system can handle many user identities and access requests efficiently while ensuring that if the organization grows and evolves, it can handle these changes without significant disruptions.
5. Data Privacy
Data privacy best practices are vital to safeguard the information of users, employees, and customers. Data privacy in an IAM system would require an article on its own, but one of the most important steps to take is to implement encryption techniques that protect sensitive data in transit and at rest. Effects of unauthorized access can be minimized by encrypting data stored in databases, configuration files, and communication channels. In addition, regularly perform access reviews to ensure users, employees, and customers have the right level of access to resources. Lastly, ensure the IAM system complies with data privacy regulations and industry-specific requirements.
6. Plan Ahead: Decentralized Identifiers and Verifiable Credentials
Finally, a best practice is to keep an eye on the security capabilities you may need in the near future. Decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and verifiable credentials (VCs) are relatively new concepts in the industry and should be evaluated for future use. They form part of the decentralized identity framework and are being utilized within upcoming standards and technologies that give users more control over their digital identities and which information to share online. Decentralized identifiers are unique identifiers assigned to entities such as users or legal bodies. They are designed to be universally unique. DIDs can be self-generated by the user or the legal entity and aren't managed by central authorities, which means that the entities can have more control over their digital footprint. Verifiable credentials contain identity attributes about users that are cryptographically signed, ensuring authenticity. The user can choose which information to share and not reveal extra personal details. To verify the validity of a VC, entities can use the issuer's public key to validate the signature. DIDs and VCs form the basis of a self-sovereign identity (SSI) model where users can present verifiable credentials without relying on centralized identity providers.
Conclusion
Identity and access management is a vast topic that comprises many security pillars. In this article, we suggested a few best practices to help your organization choose, build, and maintain a robust security infrastructure. Adopting these IAM best practices will enable your organization to scale its security to many APIs, applications, and future use cases.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments