Implementing Multifactor Authentication
In this article, we will go over why we should implement multifactor authentication and the different ways to implement it.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeMultifactor authentication involves providing an extra layer of security by ensuring users provide more than one piece of information for identification. It typically requires a combination of something the user knows (such as pins, passwords, secret questions) and something the user has (such as cards, hardware tokens, phone). Noteworthy is that two-factor authentication is the most used type of multifactor authentication (MFA). More information about Multifactor Authentication (MFA) can be found here.
In this article, we will go over why we should implement multifactor authentication and the different ways to implement it.
Why Should We Implement Multifactor Authentication?
There have been several cases of stolen and hacked passwords. Systems with just simple username and password combinations getting hacked have been on the rise. In this situation, implementing multifactor authentication will prevent hackers from gaining access to your accounts even if your password is stolen. The extra layer of protection that MFA offers ensure that your account is more secure!
What Are the Different Ways to Implement Multifactor?
I'll highlight various ways to implement multifactor below and an in-depth analysis of the process will be provided in the later part of this post. I'll cover multifactor via:
- Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP)
- Short Message Service (SMS)
- Electronic Mail (Email)
- Push Notifications
How Time-based One-Time Passwords Work
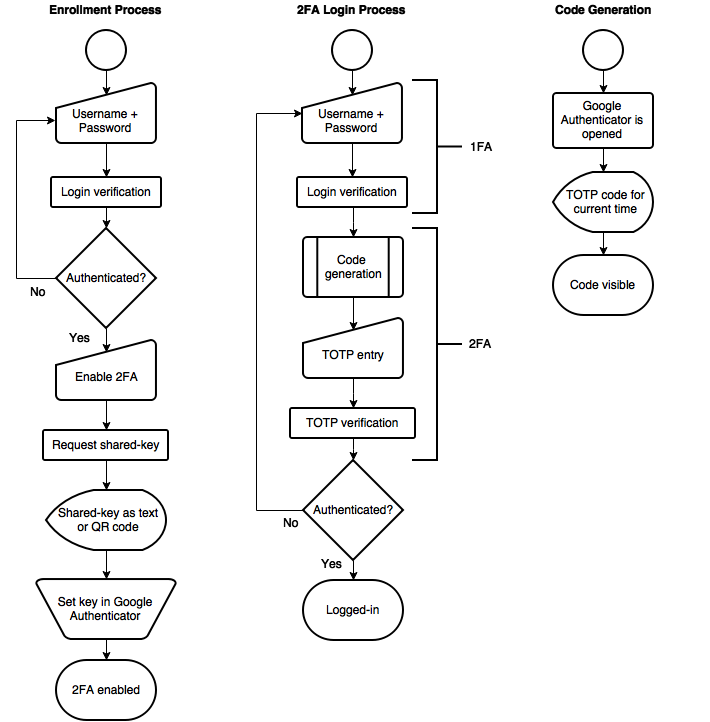
TOTP involves the generation of a one-time password from a shared secret key and the current timestamp using a specific kind of cryptographic function. These cryptographic functions can vary across the board. A simple example of a cryptographic function is SHA-256. TOTP is defined in RFC 6238. The process flow for a typical multifactor application using TOTP involves the enrollment and login processes.
The enrollment process is as follows:
- A user logs into a website/app with a username and password.
- If the credentials are valid, the next stage involves enabling two-factor authentication for the user.
- A shared-key is requested (in form of text or QR code)
- The key is stored by an app that implements TOTP such as Google Authenticator, or Auth0 Guardian
- Two-factor authentication is enabled.
The login process is as follows:
- A user logs into a website/app with a username and password.
- If the credentials are valid, the user is directed to another form where he/she is required to enter a one-time code generated from Google Authenticator or Auth0 Guardian.
- The server verifies that the code is valid and finally authenticates the user.
An alternative implementation is the use of RSA Keys. RSA authentication is basically based on two factors: A password/pin and an authenticator. The authenticator might be a hardware or software token, which is assigned to a user. During login, after entering the password/pin, the user clicks on the token and an authentication code is generated at fixed intervals (usually about 60seconds) using a built-in clock and the device's factory-encoded random key. The key is different for each token and is loaded into the corresponding RSA Authentication Manager.

Note: The generated codes are time-based so the client and the server need to synchronize their clocks for this to work efficiently.
How Short Message Service (SMS) Works
The process for a typical multifactor application using SMS also involves the enrollment and login stages.
The enrollment process is as follows:
- A user logs into a website/application with a username and password.
- A user is asked to enter a valid phone number, probably in the settings page.
- A unique one-time code is generated on the server and then sent to the phone number.
- The user enters the code into the app and multifactor is enabled.
The login process is as follows:
- A user logs into a website/application with a username and password.
- A unique one-time code is generated on the server and then sent to the registered user's phone number.
- The user enters the code into the app.
- If it's valid, the user is authenticated and a session is initiated.

How Electronic Mail (Email)
The process for a typical multifactor application using email is as follows:
- A user logs into a website/application with a username and password.
- A unique one-time code is generated on the server and sent via email to the user.
- The user retrieves the code from the email and enters the code into the app.
- If it's valid, the user is authenticated and a session is initiated.

How Push Notifications Work
The process for a typical multifactor application using push notification is as follows:
- A user logs into a website/application with a username and password.
- Typically, push notifications work with applications such as Auth0 Guardian. A push notification is sent to the Guardian app on your mobile device.
- This notification is a login request.
- It includes information such as the application name, the OS, and browser of the request, the location and the date of the request.
- The user accepts the request and automatically the user is logged in.

Different Ways to Implement Multifactor with Auth0
Implementing multifactor with Auth0 is a breeze. The various ways to implement multifactor with Auth0 are as follows:
- Push Notifications with Auth0 Guardian: Guardian offers a frictionless approach to implementing MFA for your apps, and provides a full MFA experience without requiring integration with third-party utilities. You can find out how to implement push notifications with Auth0 Guardian
- SMS: Auth0 supports sending an SMS with a one-time password code to be used for another step of verification.
- TOTP with Google Authenticator and Duo: Learn how to enable Google Authenticator and Duo Security
- Custom Providers such as Yubikey
- Contextual MFA with custom scripted rules
Conclusion
We have now covered the different ways to implement multifactor authentication in an application and how they work.
Published at DZone with permission of Prosper Otemuyiwa, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments